UGC NET Computer Science June 2023 Previous Year Question with Solution
Q1➡ | Theory of Computation  |
| Best Explanation: Answer: C Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
NTA NET CS June 2023
UGC NET Computer Science June 2023 Previous Year Question with Solution
| Q2➡ | Programming Languages What is the output of following code? main () struct s1 { char * z; int i; struct s1 * p; } static struct s 1 a []}={ {“Nagpur”, 1, a+1} {“Raipur’, 2, a+2} {“Kanpur’, 3, a} }; struct s 1* ptr =a; printf (%s %s %s\n”, a[0].z. ptr ->z, a [2]. p ->z;) |
ugc net computer science june 2023 question paper
| i ➥ Nagpur Raipur Kanpur |
| ii ➥ Nagpur Nagpur Nagpur |
| iii ➥ Kanpur Kanpur Kanpur |
| iv ➥ Error |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q3➡ | Linear Programming Problems There are M points on one straight line AB and n points on another straight line AC none of them being A. How many triangles can be formed with these points as vertices? |
| i ➥ mn(m + n – 2) |
| ii ➥ 1/2 * mn(m + n – 2) |
| iii ➥1/2 * mn(m + n – 1) |
| iv ➥mn(m + n – 1) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: The task is to find the number of triangles that can be formed using the given points on two straight lines AB and AC, where there are M points on line AB and n points on line AC (none of them being A). To form a triangle, we need to choose three points—one from each line. Let’s go through the reasoning for the correct answer: Option ii. 1/2 * mn(m + n – 2) : 1/2: This factor accounts for the fact that choosing points A, B, and C is the same as choosing points A, C, and B. It eliminates overcounting. mn: This part represents the number of ways to choose one point from line AB (M choices) and one point from line AC (n choices). (m+n−2): This part represents the number of ways to choose the third point, considering that the chosen points cannot be A. There are M + n points in total, and we subtract 2 (A and one of the chosen points) to ensure that the third point is not A and is distinct from the chosen points on AB and AC. Putting it all together, 1/2*mn(m+n−2) gives the correct count of non-degenerate triangles formed by choosing three points from the given lines. This expression accounts for the necessary combinations and avoids overcounting, making it a suitable formula for calculating the number of triangles. Therefore, option ii is the correct answer: 1/2*mn(m+n−2) |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q4➡ | Discrete Math Consider the following statements. A. The identity is unique in any monoid. B. A monoid is a group if there exists inverse of each element of monoid. C. Semi group has closure, associative and identity properties. D. Quasi group has closure property. Choose the correct answer from the options given below : |
| i ➥ A,B and D only |
| ii ➥ B,C and D only |
| iii ➥ A,B and C only |
| iv ➥ A,C and D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q5➡ | Database Which of the following scenario may lead to an irrecoverable error in a database system? |
| i ➥ A transaction writes a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction |
| ii ➥ A transaction reads a data item after it is read by an uncommitted transaction |
| iii ➥A transaction reads a data item after it is written by a committed transactions |
| iv ➥ A transaction reads a data item after it is written by an uncommitted transaction. |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q6➡ | Artificial Intelligence Consider the following statements A. C-Fuzzy means clustering is a supervised method of learning B. PCA is used for dimension reduction C. Apriori is not a supervised technique D. When a machine learning model becomes so specially tuned to its exact input data that it fails to generalize to other similar data it is called underfitting. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A and B |
| ii ➥ B and C |
| iii ➥ C and D |
| iv ➥ D and A |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q7➡ | Compiler Design Which phase of compiler checks the grammar of programming? |
| i ➥ Code optimization |
| ii ➥ Semantic analysis |
| iii ➥ Code generators |
| iv ➥ Syntax analysis |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q8➡ | Operating System In a multiuser operating system, 20 requests are made to use a particular resource per hour, on an average. The probability that no request is made in 45 minutes is. |
| i ➥ e−15 |
| ii ➥ e−5 |
| iii ➥ 1−e−5 |
| iv ➥ 1−e−10 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: 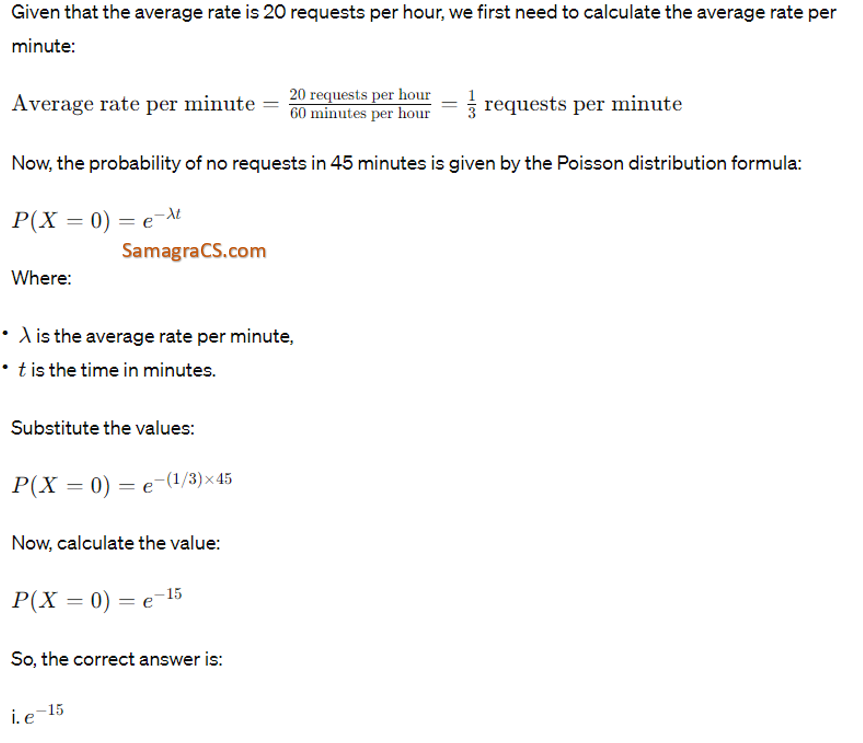 |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q9➡ | Data Structure Consider a hash table of size seven with starting index zero and a hash function (6x+3)mod 4. Assuming the hash table is initially empty. Which of the following is the content of the table when the sequence 1,3,8,10,5, is inserted into the table using closed hashing? Here ” denotes an empty location in the table. |
| i ➥ 1,3,8,10,5,_,_ |
| ii ➥ 3,8,1,_,10,5 |
| iii ➥ _,3,8,1,_,10,5 |
| iv ➥ _1,3,8,10,5,_ |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV (ACCORDING TO UGC *) MAY BE (II) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q10➡ | Computer System Architecture A processor chip is used for application in which 30% of execution time is spent on floating point addition. For the new model of the processor, the design team has come up with redesign the floating point adder to make it twice as fast. What will be possible maximum speed up by this redesign? |
| i ➥ 2.0 |
| ii ➥ 1.06 |
| iii ➥ 1.18 |
| iv ➥ 2.5 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q11➡ | Software Engineering ________ is intended to show that a system both conforms to its specifications and meets the expectations of the system customer. |
| i ➥ Software specification |
| ii ➥ Software design |
| iii ➥ Software evaluation |
| iv ➥ Software validation |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Software Validation : the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and requirements so that it fulfills its intended purpose. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q12➡ | Artificial Intelligence Which is not a basic approach to the problem of conflict resolution in a production system? |
| i ➥ Assigning a preference based on the rule that matched |
| ii ➥ Assigning a preference based the object that matched |
| iii ➥ Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched rule would perform |
| iv ➥ Assigning a preference based on the action that the matched object would perform |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q13➡ | Artificial Intelligence Consider universe positive integer X = {1 <= n <= 8} proposition P = “n is an even integers”, Q= “(3 <= n <= 7) ^(n≠6) “. Then truth set of P ↔ Q is |
| i ➥ {1,4} |
| ii ➥ {2,6} |
| iii ➥ {3,4,5} |
| iv ➥ {1} |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
UGC NET Computer Science June 2023 Previous Year Question with Solution
| Q14➡ | Operating System Consider a disk system with cylinders. The request to access the cylinders occurs in the following sequence: 4,34,10,7,19,73,2,15,6,20 Assuming that the head is currently at cylinder 50, what is the time taken to satisfy all requests if it takes 1 ms to move from one cylinder to adjacent one and shortest seek time first policy is used? |
| i ➥ 119 ms |
| ii ➥ 120 ms |
| iii ➥ 142 ms |
| iv ➥ 146 ms |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q15➡ | Computer Networking In the standard Ethernet with transmission rate of 10Mbps, asssume that the length of the medium is 2500 m and size of a frame is 512 bytes. The propagation speed of a signal in a cable is normally 2 * 10 ^ 8 * m / s The transmission delay and propogation delay are. |
| i ➥ 25.25μs and 51.2μs |
| ii ➥ 51.2μs and 12.5μs |
| iii ➥ 10.24μs and 50.12μs |
| iv ➥ 12.5μs and 51.2μs |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q16➡ | Computer Networking Consider two hosts P and Q that are connected through a router R. The maximum transfer unit (MTU) value of the link between P and R is 1500 bytes and between R and Q is 820 bytes. A TCP segment of size 1400 bytes is transferred from P to Q through R with IP identification value of 0 x 1234. Assume that IP header size is 20 bytes. Further the pcaket is allowed to be fragmented that is Don’t fragment (DF) flag in the IP Header is not set by P. Which of the following statement/s is/are true? A. Two fragments are created at R and IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes B. If the second fragment is lost, then R resends the fragment with IP identification value of 0 × 1234 C. If the second fragment lost, then P requires to resend the entire TCP segment. D. TCP destination port can be determined by analyzing the second fragment only. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B and C only |
| ii ➥ A and C only |
| iii ➥ C and D only |
| iv ➥ B and D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: B Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q17➡ | Computer Networking A TCP server application is programmed to listen on port P on host S. A TCP client is connected to the TCP server over the network, Consider that while TCP connection is active the server is crashed and rebooted. Assume that the client does not use TCP keep alive timer. Which of the following behavior /s is/are possible? Statement I: The TCP application server on S can listen on P after reboot. Statement II: If client sends a packet after the server reboot, it will receive the RST segment. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are true |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
| iii ➥ Statement I is true but Statement II is false |
| iv ➥ Statement I is false but Statement II is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q18➡ | Digital Logic Design Let denote XOR operation. Let 1 and 0 denote the binary constants and F is the Boolean expression over two variables P and Q F(P,Q) = ((1⊕ P) ⊕(P⊕Q)) ⊕ ((P ⊕ Q) ⊕ (Q⊕0)) Which of the following is equivalent expression to F? |
| i ➥ P⊕Q |
| ii ➥ P+Q |
| iii ➥ (P+Q)’ |
| iv ➥ (P⊕Q)’ |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: (Repeated Question Please Remember this on |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q19➡ | Database Let R (A,B, C,D,F) be a relational schema with following functional dependencies: C→F,E→A,EC→D,A→B. Which of the following is a key for R ? |
| i ➥ CD |
| ii ➥ EC |
| iii ➥ AE |
| iv ➥ AC |
| Best Explanation: Answer: B Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q20➡ | Computer System Architecture 256Mb DRAM is organized as a 32M×8 memory externally and as a 16 K×16 K square array internally. Each row must be refreshed at least once every 50 mili second to forestall loss of data; refreshing one row takes 100 nanoseconds. What fraction of the total memory bandwidth is lost to refresh cycles? |
| i ➥ 6.6% |
| ii ➥ 3.3% |
| iii ➥ 9.9% |
| iv ➥ 4.3% |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q21➡ | Artificial Intelligence Consider the following statements about heap sort algorithm: A. The MAX-HEAPIFY procedure which runs in O lg(n) time, is the key to maintaining the max heap property B. The BUILD-MAX-HEAP procedure, which runs in O lg(n) time, produces max-heap from an unordered input array C. The MAX-HEAP-INSERT, which runs in O (lg n) time, implements the insertion operation D. The HEAP-INCREASE-KEY procedure runs in O (n lg n) time, to set the key of new node of its correct value Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B only |
| ii ➥ A, C only |
| iii ➥ B, D only |
| iv ➥ A, B, C, D |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q22➡ | Operating System Consider the following table of arrival time and burst time for three processes P0,P1 P2:  The pre-emptive shortest job first scheduling algorithm is used. Scheduling is carried out only at arrival or completion of a process. What is the average waiting time for the three processes? |
| i ➥ 3 ms |
| ii ➥ 3.67 ms |
| iii ➥ 4.47 ms |
| iv ➥ 4 ms |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q23➡ | Artificial Intelligence Which of the following is not a mutation operator in a genetic algorithm? A. Random resetting B. Scramble C. Inversion D. Difference Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A and B only |
| ii ➥ B and D only |
| iii ➥ C and D only |
| iv ➥ D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: The mutation operators mentioned are commonly used in genetic algorithms: A. Random resetting: This is a mutation operator where a randomly selected gene is reset to a new random value. B. Scramble: This is a mutation operator that involves randomly selecting a subset of genes and changing their positions in the chromosome. C. Inversion: This mutation operator involves selecting a subset of genes and reversing their order. D. Difference: The term “Difference” is not a standard mutation operator in genetic algorithms. So, the correct answer is: D. Difference |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q24➡ | Artificial Intelligence Given below are two statements: Statement I: Fuzzifier is a part of a fuzzy system Statement II: Inference engine is a part of fuzzy system In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q25➡ | Computer Graphics Match List I with List II 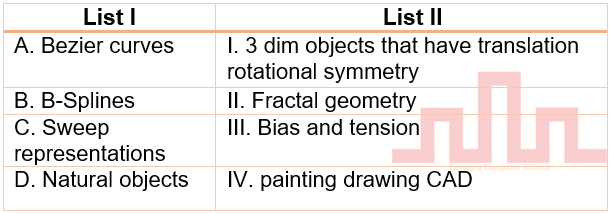 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-IV B-I C-III D-II |
| ii ➥ A-II B-111 C-I V D-I |
| iii ➥ A-IV B-III C-I D-II |
| iv ➥ A-II B-IV C-I D-III |
| Best Explanation: Answer: Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q26➡ | Data Structure A three dimensional array in C ++ is declared as int A[a][b] [c]. Consider that array elements are stored in row major order and indexing begin from 0. Here the address of an item at the location A[r][s][t] computed in terms of word length w of an integer is |
| i ➥ |
ii ➥ 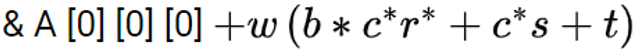 |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | Compiler Design Which of the following parser is most powerful parser? |
| i ➥ Operator precedence |
| ii ➥ SLR |
| iii ➥ Canonical LR |
| iv ➥ LALR |
| Best Explanation: Answer: C Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q28➡ | Operating System Consider the following statements: S1: LRU page replacement algorithm suffers from the belady’s anomaly S2: Shortest remaining time first scheduling may cause starvations S3: Stack is shared by all threads in a process |
| i ➥ S1 S2 and S3 are true |
| ii ➥ S1, S3 false and S2 is true |
| iii ➥ S1, S2 are false and S3 is true |
| iv ➥ S1, S2 and S3 are false |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q29➡ | Artificial Intelligence Which of the following is not a solution representation in a genetic algorithm? |
| i ➥ Binary valued |
| ii ➥ Real valued |
| iii ➥ Permutation |
| iv ➥ Combinations |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: In a genetic algorithm, various representations can be used to encode potential solutions to the problem being optimized. The choice of representation depends on the nature of the problem and the encoding that best suits it. Some common solution representations in genetic algorithms include: 1. Binary Representation: Solutions are represented as strings of binary digits (0s and 1s). 2. Real-Valued Representation: Solutions are represented as arrays of real numbers. 3. Permutation Representation: Solutions are represented as permutations of a set of elements. 4. Integer Representation: Solutions are represented as arrays of integers. 5. Tree Representation: Solutions are represented as tree structures, often used for problems with hierarchical or tree-like structures. 6. Path Representation: Solutions are represented as paths or sequences, often used for problems like the Traveling Salesman Problem. The representation chosen should match the problem’s characteristics and make it possible to perform genetic operations such as crossover and mutation effectively. The choice of representation depends on the specific problem being solved. Answer is (IV) |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q30➡ | Programming Languages How will you free the memory allocated by the following program? include stdio.h include stdlib.h define MAXROW 3 define MAXCOL 4 int main() { int **p, i, j; p = (int **) malloc(MAXROW * sizeof(int*)); return 0; } |
| i ➥ memfree (int p); |
| ii ➥ dealloc (p); |
| iii ➥ malloc (p,0); |
| iv ➥ free (p); |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
UGC NET Computer Science June 2023 Previous Year Question with Solution
Q31➡ | Discrete Math |
| i ➥ Not a homomorphism |
| ii ➥ A one-one homomorphism, which is not onto |
| iii ➥ An onto homomorphism, which is not one to one |
| iv ➥ An homomorphism |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q32➡ | Computer Graphics Consider the rectangle with vertices (0,0),(0,2),(3,0),(3,2). There is scaling of 2 towards x-axis and 3 towards y-axis. The new coordinates of the rectangle are. |
| i ➥ (0,0),(6,0),(0,4),(6,4) |
| ii ➥ (0,0),(6,0),(0,4),(3,2) |
| iii ➥ (0,0),(6,0),(0,6),(6,6) |
| iv ➥ (0,0),(4,0),(0,6),(4,6) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q33➡ | Linear Programming Problems Match List I with List II 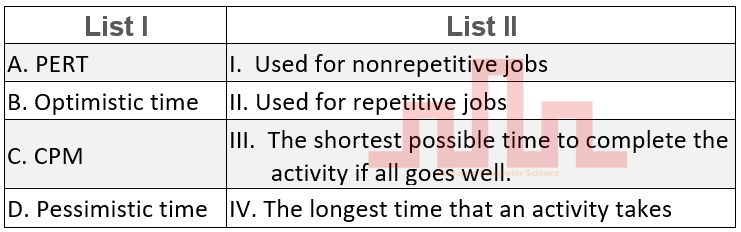 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-III B-IV C-II D-I |
| ii ➥ A-IV B-I C-I D-III |
| iii ➥ A-I B-III C-II D-III |
| iv ➥ A-I B-III C-II D-IV |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q34➡ | Programming Languages What is x in the following program? # include < stdioh > int main ( ) { typedef (*( *arrfptr[3])())[10]; arrfptr x ; return 0 ; } |
| i ➥ x is a pointer |
| ii ➥ x is a array of three pointer |
| iii ➥ x is an array of three function pointer |
| iv ➥ Error in x declaration |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q35➡ | Data Structure Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R. Assertion A: It is possible to create doubly linked list using only one pointer with every node. Reason R: By storing the XOR of the addresses of the previous and next nodes. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q36➡ | Artificial Intelligence Which of the following is not a property of a good system for representation of knowledge in a particular domain? |
| i ➥ Presentation adequacy |
| ii ➥ infrential adequacy |
| iii ➥ Infential efficiency |
| iv ➥ acquisitional efficiency |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q37➡ | Software Engineering Match List I with List II 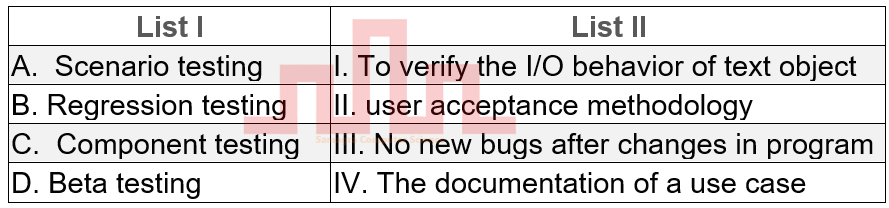 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-IV B-III C-II D-I |
| ii ➥ A-II B-I C-III D-IV |
| iii ➥ A-IV B-III C-I D-II |
| iv ➥ A-III B-I C-IV D-II |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: A. Scenario testing → IV. The documentation of a use case B. Regression testing → III. No new bugs after changes in program C. Component testing → I. To verify the I/O behavior of text object D. Beta testing → II. user acceptance methodology |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q38➡ | Artificial Intelligence Which is not the component of the natural language understanding process? |
| i ➥ Morphological analysis |
| ii ➥ Semantic analysis |
| iii ➥ Pragmatic analysis |
| iv ➥ Meaning analysis |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Meaning analysis, is not a component of the natural language understanding process. Meaning analysis is a broader term that encompasses the entire process of understanding natural language. The other three options are all specific components of the process. * Morphological analysis is the process of breaking down words into their constituent morphemes. * Semantic analysis is the process of understanding the meaning of words and phrases. * Pragmatic analysis is the process of understanding the meaning of utterances in context. Therefore, the answer is iv, meaning analysis. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q39➡ | Data Structure The total cost of retrieving records in sorted order using an unclustered B+ tree is (P-Average number of records per data page N- Data pages F- Ratio of the size of a data entry to the size of a data record) |
| i ➥ (F*N)+P |
| ii ➥ (F+N)*P |
| iii ➥ F*N*P |
| iv ➥ F+P/N |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation:  |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q40➡ | Theory of Computation Given below are two statements: Statement I: If f and g are two functions and f = O(g) but g≠o(f), we say that the growth rate of g is smaller than that of f. Statement II: The class of all decision problems decided by a TM in exponential time, that is O(2k), k being a constant. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q41➡ | How many integral solutions are there to x + y + z + w = 29 ,where x >= 1, y >= 2, z >= 3 and w >= 0 ? |
| i ➥ 2400 |
| ii ➥ 2600 |
| iii ➥ 2800 |
| iv ➥ 3000 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q42➡ | Linear Programming Problems Given below are two statements: Which of the following statement/s is/are correct with respect to virtual memory Statement I: Address translation is performed for every logical address used during the execution of a program Statement II: A program can execute only when all of its components are loaded in the memory In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q43➡ | Algorithms |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q44➡ | Database Which one of the following is NOT a part of ACID properties of a database transaction? |
| i ➥ Atomicity |
| ii ➥ Consistency |
| iii ➥ Isolation |
| iv ➥ Deadlock-freedom |
| Best Explanation: Answer: D Explanation: • A – Atomicity • C – Consistency • I – Isolation • D – Durability |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q45➡ | Digital Logic Design What is the (4+4) fit binary fixed point equivalent of -(3.72)10 ? |
| i ➥ 0011.1100 |
| ii ➥ 0011.1010 |
| iii ➥ 1100.0100 |
| iv ➥ 0011.1011 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Integer part: • The integer part of -3 is 33 in binary, which is 00110011 in 4 bits. Fractional part: • Convert the fractional part 0.720.72 to binary: • 0.72×2=1.440.72×2=1.44 (First bit: 1) • 0.44×2=0.880.44×2=0.88 (Next bit: 0) • 0.88×2=1.760.88×2=1.76 (Next bit: 1) Continuing this process: • 0.76×2=1.520.76×2=1.52 (Next bit: 1) • 0.52×2=1.040.52×2=1.04 (Next bit: 1) • 0.04×2=0.080.04×2=0.08 (Next bit: 0) • 0.08×2=0.160.08×2=0.16 (Next bit: 0) • The binary representation of 0.720.72 is 1011010010110100. Combine the binary representations: • Combine the integer and fractional parts with the binary point: • 0011.101101000011.10110100 Adjust to (4+4) fit binary fixed-point: • The total number of bits is 8 (4 bits for the integer part and 4 bits for the fractional part). • So, we need to truncate or round to fit into the (4+4) format. In this case, we truncate the extra bits. • The result is 1100.01001100.0100. Therefore, the correct answer is: iii ➥ 1100.0100 |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q46➡ | Database Consider a popular sports news site. At a given moment, 20,000 concurrent users submit a request (a transaction, T) once every 2 minutes on average. Each transaction requires the webapp to download a new article that on average has 3k bytes in length. What is the throughput? |
| i ➥ 8 megabits per second |
| ii ➥ 4 megabits per second |
| iii ➥ 6 megabits per second |
| iv ➥ 2 megabits per second |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q47➡ | Algorithms A. If some NP-complete problem P is in IP that IP = N B. TSP is in NIP C. SAT is in NP D. Hamilton circuit problem is not NP-complete Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B and C only |
| ii ➥ B, C and D only |
| iii ➥ C, D and A only |
| iv ➥ D, A and B only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q48➡ | Database Consider the following statements: A. A database design is in BCNF if each member of the set of relation schemas that constitutes the design is in BCNF B. A BCNF schema can have transitive dependency C. It is always possible to obatin a 3NF design without sacrificing a lossless join There are multivalued dependencies in 4NF |
| i ➥ A, B and C only |
| ii ➥ B, C and D only |
| iii ➥ A, B and D only |
| iv ➥ A. C and D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q49➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the following language: 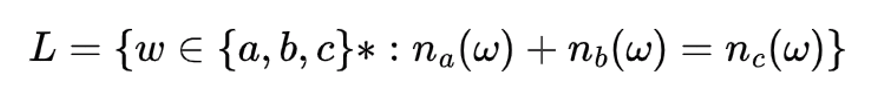 L is… |
| i ➥ Context free but not linear |
| ii ➥ Not context free |
| iii ➥ Context free and linear |
| iv ➥ Linear |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q50➡ | Computer Graphics The clipping process in computer graphics is used for |
| i ➥ Adding graphics |
| ii ➥ Copying |
| iii ➥ Zooming |
| iv ➥ Removing objects and lines |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Removing objects and lines: The clipping process in computer graphics is primarily used for removing or discarding portions of objects or lines that are outside a specified region, known as a clipping window or viewport. This is done to ensure that only the visible parts of objects or lines are rendered, optimizing performance and improving the efficiency of the rendering process. Other’s Options : i. Adding graphics Explanation: Clipping is not typically used for adding graphics. Instead, it focuses on deciding which portions of existing graphics are visible within a specified region (clipping window) and should be rendered. ii. Copying Explanation: Clipping is not directly associated with copying. Clipping is more about deciding what parts of an object or scene should be displayed, removing portions that are outside the viewing area. iii. Zooming Explanation: Clipping is not directly related to zooming. Zooming usually involves scaling objects, and while the clipping process may be involved in the rendering of the zoomed view, it is not the primary purpose. Important Point : In computer graphics, the clipping process is used for controlling the display of objects or parts of objects that are within a specified region, called a clipping window or viewport. Clipping is crucial in computer graphics for several reasons: Viewing Window: Culling Objects: Clipping helps to eliminate or “clip away” parts of objects that are outside the viewing window. This ensures that only the visible portions of objects are rendered, optimizing performance. Visible Region: Improving Efficiency: Clipping helps in discarding portions of objects that are not visible or are outside the current viewing region. This improves rendering efficiency. Efficient Rendering: Hidden Surface Removal: Clipping can be used as a part of hidden surface removal algorithms to eliminate surfaces or portions of surfaces that are not visible in the final image. Realism: Enhancing Realism: Clipping allows for a more realistic rendering of scenes by showing only the parts of objects that are within the user’s view, simulating the way the human eye perceives the environment. Performance Optimization: Reducing Processing Load: By eliminating unnecessary portions of objects early in the rendering pipeline, the computational load is reduced, leading to better overall performance. User Interaction: User-Defined Views: Clipping can be used to define user-specific views or perspectives within a larger scene, allowing users to focus on specific areas of interest. Windowing Operations: Creating Viewports: Clipping is an essential part of creating viewports or windows within a graphical interface. This is important in applications like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and graphical user interfaces. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q51➡ | Computer Graphics Given below are two statements: Statement I: subsystem models show logical grouping of objects into coherent subsystem Statement II: State machine models show how objects change their states in response to events. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q52➡ | Operating System Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R. Assertion A: A process involves a library function to create a thread. Reason R: The threads make system calls to convey their resource and I/O requirement to the Kernel. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q53➡ | Operating System Match List I with List II 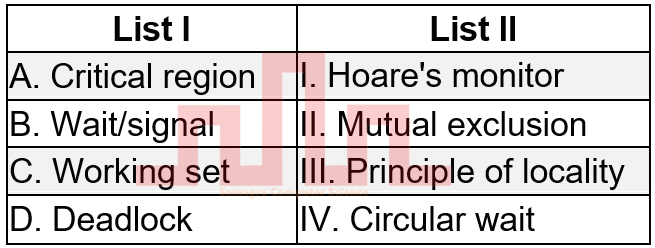 |
| i ➥ A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II |
| ii ➥ A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV |
| iii ➥ A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV |
| iv ➥ A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q54➡ | Operating System Consider the following statements about the software product line system: Statement I: At the interaction level, components provide an operator display interface and an interface with the communication system used. Statement II: At the I/O management level, components handle operator authentication, report generator and query manager. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q55➡ | Operating System Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.A virtual memory system uses first-in first-out page replacement policy and allocates a fixed number of frames to a process Assertion A: Increasing number of page frames allocated to a process sometimes increases the page fault rate. Reason R: Some programs do not exhibit locality of reference. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q56➡ | Computer Networking Match List I with List II 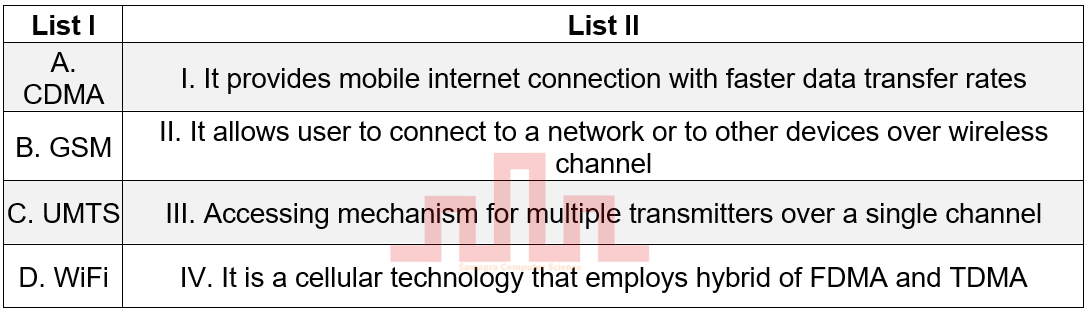 |
| i ➥ A-III B-IV C-II D-I |
| ii ➥ A-III B-IV C-I D-II |
| iii ➥ A-II B-III C-IV D-I |
| iv ➥ A-II B-I C-IV D-III |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q57➡ | Algorithms Match List I with List II 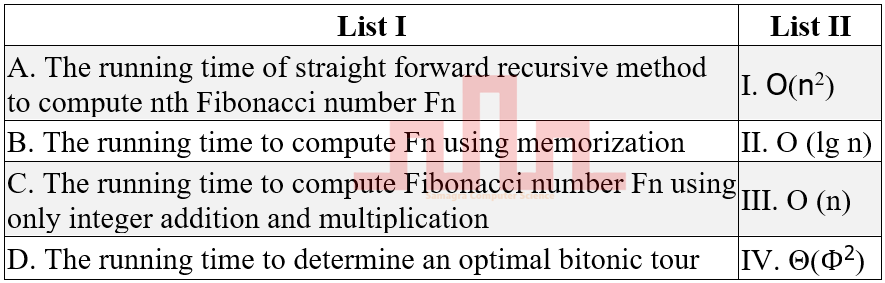 |
| i ➥ A-I B-III C-IV D-II |
| ii ➥ A-IV B-III C-II D-I |
| iii ➥ A-I B-II C-IV D-III |
| iv ➥ A-IV B-II C-III D-I |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q58➡ | Data Structure Suppose a circular queue of capacity ( n−1) elements is implemented with an array of n elements. Assume that the insertion and deletion operations are carried out using REAR and FRONT as array index variable respectively. Initially, REAR=FRONT=0. The conditions to detect queue empty and queue full are |
| i ➥ EMPTY: REAR ==FRONT FULL : ( REAR+1) mod n== FRONT |
| ii ➥ EMPTY: ( FRONT +1)mod n== REAR FULL: REAR+1 mod n==FRONT |
| iii ➥ EMPTY REAR+1) mod n==FRONT FULL: REAR == FRONT |
| iv ➥ EMPTY: REAR== FRONT FULL: ( FRONT+1) mod n== REAR |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q59➡ | Database Given below are two statements: Which of the following concurrency control protocol ensures both conflict serializability and freedom from deadlock? Statement I: Two phase locking Statement II: Timestamp ordering In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q60➡ | Database A B-tree used as an index for a large database table has four levels including the root node. If a new key is inserted in this index, then maximum number of nodes that could be newly created in the process is |
| i ➥ 5 |
| ii ➥ 4 |
| iii ➥ 3 |
| iv ➥ 2 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q61➡ | The following table shows the time between failures for a software : 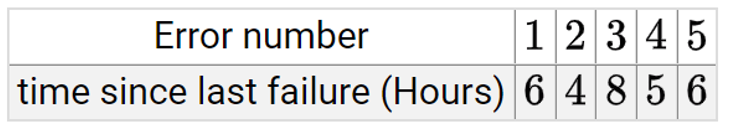 The reliability of the system for one hour operation assuming an exponential model is- |
| i ➥ e ^ (- 9/29) |
| ii ➥ e ^ (- 7/29) |
| iii ➥ e ^ (- 5/29) |
| iv ➥ e ^ (- 3/29) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q62➡ | Discrete Math If A={4n +2|n is a natural number } and B = {3n | n is a natural number }. Which of the following is correct for A ∩ B ? |
| i ➥ { 12n ^ 2 +6n|n is a natural number } |
| ii ➥ {24n 12 n is a natural number } |
| iii ➥ { 60n +30|n is a natural number } |
| iv ➥ { 12n -6|n is a natural number } |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q63➡ | Database Match List I with List II 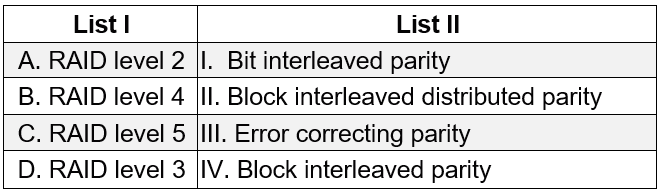 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A. A-IV B-III C-I D-II |
| ii ➥ B. A-III B-IV C-II D-I |
| iii ➥ C. A-III B-I C-II D-IV |
| iv ➥ D. A-I B-III C-IV D-I |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: RAID 0 Striping: Data is distributed among all the disks as blocks, sectors, or some other unit. RAID 1 Mirroring: Duplicate all data in another set of disks RAID 2 Hamming Code: Strips are very small (single byte or word). Error-correcting code is calculated for bits on data disk and stored in the corresponding bit positions on parity disks RAID 3 Bit-interleaved parity: A simple parity bit (not error correcting) is computed for all the bits in the same position on the data disks and stored in same bit position of parity disk RAID 4 Block-interleaved parity Stripes are relatively large. A parity strip is computed for all the strips in the same position on the data disks and stored in parity disk RAID 5 Block-interleaved distributed parity Distributes the parity strips across all disks. Most versatile RAID level RAID 6 Block-interleaved dual distributed parity Two different parity calculations are carried out and stored in separate blocks on different disks. P: EXOR and Q: Data check algorithm |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q64➡ | Software Engineering Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R. Assertion A: Validity checks real need of system users Reason R: Completeness checks system user defined requirements. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q65➡ | Database Let R ( A,B,C, D) be a relational schema with following function dependencies: A→B,B→C C→D and D→B The decomposition of R into (A,B) (B,C) (B,D) |
| i ➥ gives a lossless join, and is dependency preserving |
| ii ➥ gives lossless join, but is not dependency preserving |
| iii ➥ does not give a lossless join, but is dependency preserving |
| iv ➥ does not give a lossless join and is not dependency preserving |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q66➡ | Computer Graphics Which of the following transforms in 2 dimension is used to resize a 2-dimensional object? |
| i ➥ Translation |
| ii ➥ Rotation |
| iii ➥ Scaling |
| iv ➥ Shearing |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q67➡ | Algorithms List I A. Parallel FFT B. Iterative FFT C. Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method D. Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form List II I. θ (n2) II. θ (n) III. θ (log n) IV. θ (n log n) Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-III B-I C-II D-III |
| ii ➥ A-II B-I C-III D-IV |
| iii ➥ A-III B-IV C-I D-II |
| iv ➥ A-II B-III C-IV D-I |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (III) Explanation: Let’s go into more detail for each algorithm and its time complexity: List I: A. Parallel FFT – Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is an algorithm used for efficiently computing the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse. The parallel version of FFT has a time complexity of θ(n log n). This complexity arises from the divide-and-conquer strategy used in FFT algorithms. B. Iterative FFT – Iterative FFT refers to an FFT algorithm that is implemented in an iterative manner. The time complexity for iterative FFT is θ(log n). This complexity is achieved by breaking down the problem into smaller subproblems in a logarithmic fashion. C. Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method – Horner’s method is an algorithm for evaluating a polynomial by factoring it in a specific way. The time complexity of evaluating a polynomial at n points using Horner’s method is θ(n). This is because each evaluation involves n multiplications and n additions. D. Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form – Multiplying two polynomials in point value form involves multiplying their corresponding coefficients. The time complexity for this operation is θ(n^2) since it requires pairwise multiplication of each coefficient. List II: I. θ(n^2) – Represents the time complexity that grows quadratically with the input size n. II. θ(n) – Represents the time complexity that grows linearly with the input size n. III. θ(log n) – Represents the time complexity that grows logarithmically with the input size n. IV. θ(n log n) – Represents the time complexity that grows linearithmically with the input size n. Now, let’s match the algorithms with their time complexities: A. Parallel FFT – IV. θ(n log n) B. Iterative FFT – III. θ(log n) C. Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method – II. θ(n) D. Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form – I. θ(n^2) |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q68➡ | Operating System At a particular time of computation, the value of a counting semaphore is 7. Then 20p operations and ‘ x ‘ V operations were completed on this semaphore. If the final value of semaphore is 5. x will be |
| i ➥ 15 |
| ii ➥ 22 |
| iii ➥ 18 |
| iv ➥ 13 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation:  |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q69➡ | Discrete Math Let (Z,+) denote the group of all integers under addition. Then the number of all automorphisms of (Z,+) is |
| i ➥ 1 |
| ii ➥ 2 |
| iii ➥ 3 |
| iv ➥ 4 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: In the case of the group of all integers under addition, (Z, +), the number of automorphisms is 2. 1.The identity function: The identity function is an automorphism that maps each integer to itself. It preserves the group’s operation and structure. 2. The negation function: The negation function is also an automorphism. It maps each integer to its additive inverse, effectively reversing the sign. This function also preserves the group’s operation and structure. These two automorphisms are the only possible automorphisms for the group (Z, +). So, the number of automorphisms of (Z, +) is 2. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q70➡ | Software Engineering Which of the following is used to determine the cost performance index? |
| i ➥ Budgeted cost of work performed-budget at completion |
| ii ➥ Budgeted cost of work performed ÷ budget at completion |
| iii ➥ Budgeted cost of work performed ÷ Actual cost of work performed |
| iv ➥ Budgeted cost of work performed-Actual cost of work performed |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: he Cost Performance Index (CPI) is used to determine how efficiently the project is using its resources. It measures the cost efficiency by comparing the budgeted cost of work performed (BCWP) to the actual cost of work performed (ACWP). The formula for CPI is: CPI = BCWP / ACWP So, the correct option is: C. Budgeted cost of work performed ÷ Actual cost of work performed |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q71➡ | Database Given the basic E R diagram and relational model, which of the the following is incorrect? |
| i ➥ An attribute of an entity can have more than one value |
| ii ➥ An attribute of an entity can be composite |
| iii ➥ In a row of relational table, an attribute can have more than one value |
| iv ➥ In a row of a relational table, an attribute can have exactly one value or a NULL value |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: ER Model can have multi valued attributes and composite attributes. Multi valued Attributes → Phone no., email-id Composite Attributes → Address (Street, City, Pin Code)In Relational Model attributes are atomic can have exactly one value or a NULL value. Ans : C is incorrect. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q72➡ | Discrete Math Let N denote the set of all natural numbers and R be the relation on N*N defined by (a,b)R(c,d), if ad(b+c)=bc(a+d). Then R is |
| i ➥ Symmetric only |
| ii ➥ Reflexive only |
| iii ➥ Transitive only |
| iv ➥ An equivalence relation |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q73➡ | Computer Networking Match List I with List II 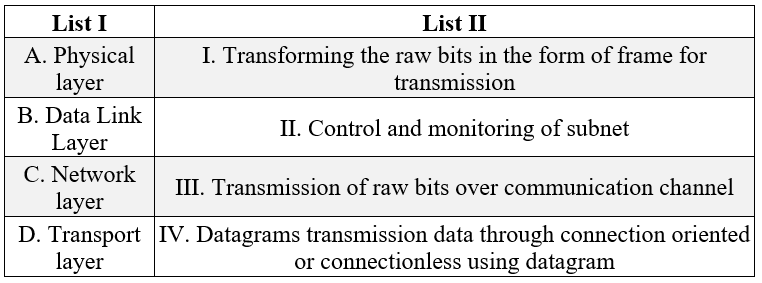 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-III B-II C-I D-IV |
| ii ➥ A-II B-III C-I D-IV |
| iii ➥ A-III B-I C-II D-IV |
| iv ➥ A-II B-IV C-I D-III |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: A. Physical layer → III Transmission of raw bits over communication channel B. Data Link Layer → I. Transforming the raw bits in the form of frame for transmission C. Network layer → II. Control and monitoring of subnet D. Transport layer → IV. Datagrams transmission data through connection oriented or connectionless using datagram |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q74➡ | Theory of Computation A. The set of turning machine codes for TM’s that accept all inputs that are palindromes (possible along with some other inputs) is decidable B. The language of codes for TM’s M that when started with blank tape, eventually write a 1 somewhere on the tape is undecidable C. The language accepted by a TM M is L (M) is always recursive D. Post’s correspondence problem is undecidable Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B and C only |
| ii ➥ B, C and D only |
| iii ➥ A and C only |
| iv ➥ B and D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q75➡ | Programming Languages What will be the output of the following code? What will be the output of the following code?  |
| i ➥ 20 |
| ii ➥ 24 |
| iii ➥ Garbage |
| iv ➥ Error |
| Best Explanation: Answer: ii Explanation: a = 0x10 → 10 in hexadecimal = 16 in Decimal b = 010 → 10 in octal = 8 in decimal c = a+b = 16+8 = 24 |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q76➡ | Artificial Intelligence Match List I with List II List I A. Expert system B. Fuzzy system C. Operator in genetic algorithm D. Supervised technique List II I. Decision tree II. Scramble III. Inference engine IV. Mycin Choose the correct answer from the options given below: Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-IV B-I C-III D-II |
| ii ➥ A-III B-IV C-II D-I |
| iii ➥ A-IV B-III C-II D-I |
| iv ➥ A-I B-II C-III D-IV |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q77➡ | Operating System Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R . Assertion A : I/O protection is ensured by a hardware trap Reason R : I/O interrupt caused by the condition like I/O completion and device malfunction occuring within the I/O devices In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q78➡ | Discrete Math Match List I with List II List I A. A Δ B B. A−(B∪C) C. A−(B∩C) D. A∩(B−C) List II I. (A−B)∪(A−C) II. (A−B)∩(A−C) III. (A−B)∪(B−A) IV. (A∩B)−(A∩C) Choose the correct answer from the options given below: Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-III B-II C-I D-IV |
| ii ➥ A-II B-III C-IV D-I |
| iii ➥ A-IV B-III C-I D-II |
| iv ➥ A-IV B-I C-III D-II |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q79➡ | Computer Graphics Southerland Hodgeman method is used on Southerland Hodgeman method is used on |
| i ➥ Smooth curves |
| ii ➥ Line segment |
| iii ➥ Convex polygons |
| iv ➥ Concave polygons |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is a polygon clipping algorithm used to clip a polygon against a convex polygon (often referred to as a clipping window). Here’s a detailed explanation: Objective: The primary goal of the Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is to clip a polygon against a convex clipping window, retaining only the parts of the polygon that are inside the window. Algorithm Steps: Input: The algorithm takes as input the vertices of the polygon to be clipped. The vertices are assumed to be in order, either clockwise or counterclockwise. Clipping Against Each Edge: The algorithm clips the polygon against each edge of the convex window one at a time. For each edge of the window, it iterates through each pair of consecutive vertices of the polygon. Clipping Process: For each pair of consecutive vertices, the algorithm checks whether they are inside or outside the clipping edge. It classifies the vertices as either inside or outside the edge and produces a new list of vertices representing the clipped polygon. Output: After processing all edges, the algorithm produces a new list of vertices that form the clipped polygon. Explanation: The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm works by iteratively clipping the polygon against each edge of the convex window. At each step, it checks the relative positions of the vertices with respect to the current clipping edge. If both vertices are inside the edge, the second vertex is added to the output list. If the first vertex is inside and the second is outside, the point of intersection of the polygon edge with the clipping edge is added to the output list. If both vertices are outside, no new vertices are added. The process is repeated for each edge of the convex window, resulting in a new set of vertices that represent the clipped polygon. Use Case: The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is commonly used in computer graphics for rendering and displaying only the visible parts of a polygon within a specified viewing window or viewport. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q80➡ | Theory of Computation Consider following statements: A. A context free language is generated by LR(0) grammar if and only if it is accepted by a deterministic pushdown automata and has prefix property B. If M1 is the single tape TM simulating multilape TM M, then time taken by M1 to simulate n moves is (n3 ) C. Push down automata behaves like a Turning machine when it has one auxiliary memory. D. L={anbncn:n≥1} is not context free but context sensitive. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B and C only |
| ii ➥ A, B only |
| iii ➥ C, D only |
| iv ➥ B, C only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q81➡ | Artificial Intelligence An observational technique that can be used to understand operational process and help to derive requirement for software to support operational process is known as. |
| i ➥ Requirement specification |
| ii ➥ Structural specification |
| iii ➥ Ethnography |
| iv ➥ Natural language specification |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q82➡ | Artificial Intelligence Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R. Assertion A: Dendral is an expert system Reason R: The rationality of an agent is not related to its reaction to the environment. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: DENDRAL, an early expert system, was initiated in 1965 by AI researcher Edward Feigenbaum and geneticist Joshua Lederberg, both from Stanford University in California. Initially known as Heuristic DENDRAL, it specialized in chemical analysis. The system could analyze complex compounds, such as those composed of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen, using spectrographic data. DENDRAL’s capability to hypothesize molecular structures from this data demonstrated performance comparable to expert chemists. The program found applications in both industry and academia. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| i ➥ Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are correct and R is NOT the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III A is true but R is false(* according ugc) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q84➡ | Discrete Math Let R = {x | x ∈ N, x is multiple of 3 and x ≤ 100} and S = {x, x ∈ N, x is a multiple of 5 and x < 100}. What is the number of elements in (R∩S) × (S∩R)? |
| i ➥ 36 |
| ii ➥ 33 |
| iii ➥ 20 |
| iv ➥ 6 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Set R contains elements: (3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24,….93, 96, 99) Set S contains elements: (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30,…85, 90, 95) R cap S = {15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90} S cap R = {15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90} Since the cardinality (number of elements in the sets) of both sets are 6. So (R∩S) x (S∩R) = 6*6 = 36 Option (A) is correct. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q85➡ | Software Engineering Consider the following statements: A. Dynamic metrics are collected by measurements made of a program in execution B. Static metrics are collected by measurements made of representations of the system C. The assessment of software quality is an objective process D. An important part of quality assurance in the selection of standards that should apply to the software development process. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B C only |
| ii ➥ B, C and D only |
| iii ➥ A, C and D only |
| iv ➥ A, B and D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q86➡ | Programming Languages What is the output of following code? ![What is the output of following code?
1. main ()
2. {
3. static float a[]={13.24,1.5,4.5,5.4,3.5}
4. float * j, * k;
5. j= a};
6. k= a + 4
7. j=j * 2;
8. k = k / 2;
9. printf ("% f % f",* j,*k);
10. }](https://samagracs.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/What-is-the-output-of-following-code.png) |
| i ➥ 13.25,4.5 |
| ii ➥ 1.5,3.5 |
| iii ➥ 13.24,1.5,4.5,5.4,3.5 |
| iv ➥ Illegal use of pointer in main function |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
UGC NET Computer Science June 2023 Previous Year Question with Solution
| Q87➡ | Digital Logic Design Find the sum of all four digit numbers formed using the digits 1,2,4 and 6. |
| i ➥ 86,658 |
| ii ➥ 88,8858 |
| iii ➥ 91,958 |
| iv ➥ 93,358 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q88➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the following finite automata F1 that accepts a language L 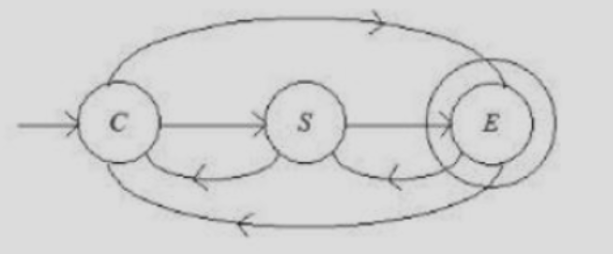 Let F2 be a finite automata which is obtained by reversal of F1. Then which of the following is correct? |
| i ➥ L(F1) ≠ L(F2) |
| ii ➥ L (F1)=L(F2) |
| iii ➥ L (F1)≤ L(F2) |
| iv ➥ L (F1)≥ L(F2) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q89➡ | Compiler Design The maximum yield length of the following CNF CFG is S→AB A→CD B→e C→a D→b |
| i ➥ 8 |
| ii ➥ 7 |
| iii ➥ 4 |
| iv ➥ 5 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: iii Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q90➡ | Compiler Design The compiler for high level language that runs on one machine and produces code for other machine is called- |
| i ➥ Cross compiler |
| ii ➥ Multipass compiler |
| iii ➥ Optimizing Compiler |
| iv ➥ One pass Compiler |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I (*) Explanation: It is a defination of Cross compiler A Two pass/multi-pass Compiler is a type of compiler that processes the source code or abstract syntax tree of a program multiple times. In multipass Compiler, we divide phases into two passes as: First Pass: is refers as (a). Front end (b). Analytic part (c). Platform independent Second Pass: is refers as (a). Back end (b). Synthesis Part (c). Platform Dependent |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q91➡ | Operating System Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index): for j = [0….1023]{ temp = 0 for i = [0…16] temp = temp +T[i][j] print (temp/ 17.0); T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is page and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is “least recently used “, If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format. What is fault ratio of row major to column major arrangements? |
| i ➥ 1024 : 1 |
| ii ➥ 1301: 1 |
| iii ➥ 1240: 1 |
| iv ➥ 9107: 8 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q92➡ | Operating System Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index): for j = [0….1023]{ temp = 0 for i = [0…16] temp = temp +T[i][j] print (temp/ 17.0); T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is page and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is “least recently used “, If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format. Consider again that T is stored in column-major format, what is the main memory hit ratio? |
| i ➥ 80% |
| ii ➥ 95.6% |
| iii ➥ 97.8% |
| iv ➥ 99.9% |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q93➡ | Operating System Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index): for j = [0….1023]{ temp = 0 for i = [0…16] temp = temp +T[i][j] print (temp/ 17.0); T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is page and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is “least recently used “, If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format. How many page faults will be encountered? |
| i ➥ 16, 402 |
| ii ➥ 17, 408 |
| iii ➥ 18, 208 |
| iv ➥ 18, 608 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q94➡ | Operating System Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index): for j = [0….1023]{ temp = 0 for i = [0…16] temp = temp +T[i][j] print (temp/ 17.0); T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is page and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is “least recently used “, If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format. Consider that T is stored in column major format, how many page faults will be encountered? |
| i ➥ 14 |
| ii ➥ 15 |
| iii ➥ 16 |
| iv ➥ 17 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q95➡ | Operating System Consider the following program fragment that deals with a table T with 17 rows and 1024 columns, computing an average for each column and printing it to screen (i is row index and j is column index): for j = [0….1023]{ temp = 0 for i = [0…16] temp = temp +T[i][j] print (temp/ 17.0); T [i] [j] and temp are 32 bit floating point values and memory is word addressable. The temporary variable temp is kept in a processor register so access to temp does not involve a memory reference. The main memory is page and holds 16 pages of size 1024 words, the page replacement policy is “least recently used “, If T is stored in the virtual address space in row major format. What is the main memory hit ratio? |
| i ➥ 0 |
| ii ➥ 1 |
| iii ➥ 2 |
| iv ➥ 3 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q96➡ | Computer Networking IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal) 45000054000300002006…. What is the size of datagram? |
| i ➥ 64 bytes |
| ii ➥ 74 bytes |
| iii ➥ 84 bytes |
| iv ➥ 104 bytes |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q97➡ | Computer Networking IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal) 45000054000300002006… What is the efficiency of this datagram? |
| i ➥ 76.19% |
| ii ➥ 80.50% |
| iii ➥ 82.24% |
| iv ➥ 85.45% |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q98➡ | Computer Networking IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal) 45000054000300002006…. What is the protocol of the payload being carried by the packet? |
| i ➥ ICMP |
| ii ➥ SCTP |
| iii ➥ TCP protocol |
| iv ➥ IGMP |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q99➡ | Computer Networking IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal) 45000054000300002006…. How many more routers can the packet travel to? |
| i ➥ 22 |
| ii ➥ 26 |
| iii ➥ 30 |
| iv ➥ 32 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q100➡ | Computer Networking IP datagram has arrived with following partial information in the header (in hexadecimal) 45000054000300002006….. What is the header size? |
| i ➥ 10 bytes |
| ii ➥ 20 bytes |
| iii ➥ 30 bytes |
| iv ➥ 40 bytes |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |

