Q.1➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023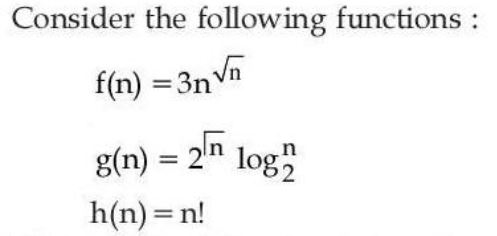 Which of the following is true? |
| i ➥ h(n) is 0(f(n)) |
| ii ➥ h(n) is 0 (g(n)) |
| iii ➥ g(n) is not 0 (f(n)) |
| iv ➥ f(n) is 0(g(n)) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (IV) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.2➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023 Which of the following(s) are main memory ? (A) Virtual memory (B) Cache memory (C) RAM (D) SSD Choose the correct answer from the options given below : |
| i ➥ (A) and (C) Only |
| ii ➥ (B) and (C) Only |
| iii ➥ (C) and (D) Only |
| iv ➥ (A), (B) and (C) Only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (II) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.3➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023 Which of the following is TRUE? |
| i ➥ The cost of searching an AVL tree is ϴ (log n) but that of binary search is 0(n) |
| ii ➥ The cost of searching an AVL tree in ϴ (log n) but that of complete binary tree is ϴ(n log n) |
| iii ➥ The cost of searching a binary tree is 0(log n) but that of AVL tree is ϴ (n) |
| iv ➥ The cost of searching an AVL tree is ϴ (n log n) but that of binary search tree is 0(n) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (I) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.4➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 List I A. Parallel FFT B. Iterative FFT C. Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method D. Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form List II I. θ (n2) II. θ (n) III. θ (log n) IV. θ (n log n) Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-III B-I C-II D-III |
| ii ➥ A-II B-I C-III D-IV |
| iii ➥ A-III B-IV C-I D-II |
| iv ➥ A-II B-III C-IV D-I |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (III) Explanation: Let’s go into more detail for each algorithm and its time complexity: List I: A. Parallel FFT – Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is an algorithm used for efficiently computing the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse. The parallel version of FFT has a time complexity of θ(n log n). This complexity arises from the divide-and-conquer strategy used in FFT algorithms. B. Iterative FFT – Iterative FFT refers to an FFT algorithm that is implemented in an iterative manner. The time complexity for iterative FFT is θ(log n). This complexity is achieved by breaking down the problem into smaller subproblems in a logarithmic fashion. C. Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method – Horner’s method is an algorithm for evaluating a polynomial by factoring it in a specific way. The time complexity of evaluating a polynomial at n points using Horner’s method is θ(n). This is because each evaluation involves n multiplications and n additions. D. Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form – Multiplying two polynomials in point value form involves multiplying their corresponding coefficients. The time complexity for this operation is θ(n^2) since it requires pairwise multiplication of each coefficient. List II: I. θ(n^2) – Represents the time complexity that grows quadratically with the input size n. II. θ(n) – Represents the time complexity that grows linearly with the input size n. III. θ(log n) – Represents the time complexity that grows logarithmically with the input size n. IV. θ(n log n) – Represents the time complexity that grows linearithmically with the input size n. Now, let’s match the algorithms with their time complexities: A. Parallel FFT – IV. θ(n log n) B. Iterative FFT – III. θ(log n) C. Evaluation of polynomial at n points by Horner method – II. θ(n) D. Product of two polynomials that are represented in point value form – I. θ(n^2) |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.5➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 Match List I with List II 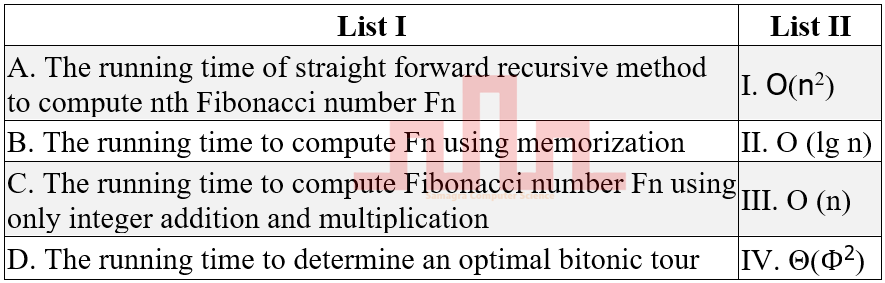 |
| i ➥ A-I B-III C-IV D-II |
| ii ➥ A-IV B-III C-II D-I |
| iii ➥ A-I B-II C-IV D-III |
| iv ➥ A-IV B-II C-III D-I |
| Best Explanation: Answer: II Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.6➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 A. If some NP-complete problem P is in IP that IP = N B. TSP is in NIP C. SAT is in NP D. Hamilton circuit problem is not NP-complete Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B and C only |
| ii ➥ B, C and D only |
| iii ➥ C, D and A only |
| iv ➥ D, A and B only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.7➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.8➡ | NET December 2022 Given the FFT we can have ……………….. time procedure for multiplying two polynomials A(X) and B (X) of degree bound n where input and output representations are in coefficient form, assuming n is a power of 2. |
| i ➥ O(n2) |
| ii ➥ O(n.nlog2n) |
| iii ➥ O(2n) |
| iv ➥ O(log2n) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (ii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.9➡ | NET December 2022 Consider the graph below : 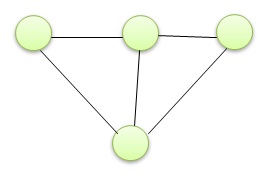 How many spanning trees can be found? |
| i ➥ 10 |
| ii ➥ 5 |
| iii ➥ 9 |
| iv ➥ 8 |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iv) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.10➡ | NET December 2022 Circuit satisfiability problem: Given a Boolean combinatorial circuit composed of AND, OR and NOT gates, is it satisfiable ? One output Boolean combinatorial circuit is satisfiable means for the given inputs the output will be 1. (A) The circuit satisfiability problem belongs to class NP (B) The circuit satisfiability problem is at least as hard as any language in NP (C) The circuit satisfiability is NP- Complete (D) The size of the circuit is Θ( K2+1) (E) If P≠NP this situation would contradict the NP – completeness of the problem. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, C , D only |
| ii ➥ B, D, E only |
| iii ➥ A, B, C only |
| iv ➥ B, C, D only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.11➡ | NET December 2022 Match List (I) with List (II) : 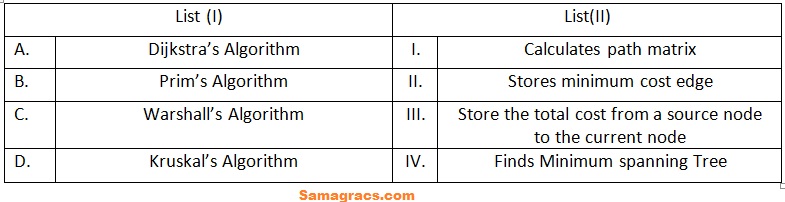 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-(I), B-(II), C-(III), D-(IV) |
| ii ➥ A-(III), B-(II), C-(I), D-(IV) |
| iii ➥ A-(II), B-(I), C-(IV), D-(III) |
| iv ➥ A-(III), B-(IV), C-(II), D-(I) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (ii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.12➡ | NET December 2022 Given the graph below which one of the following edges cannot be added in that order to find a minimum spanning tree using algorithm. 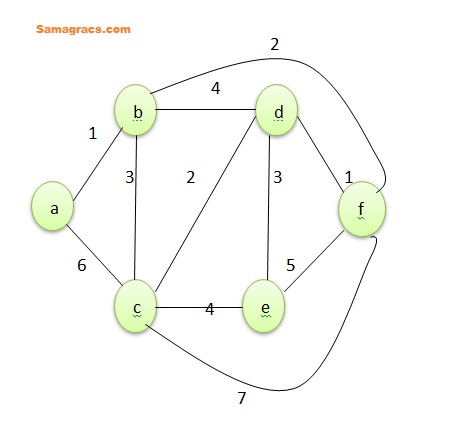 (A) a-b (B) d-f (C) b-f (D) d-c (E) d-e Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A, B, C, D, E |
| ii ➥ A, B, D, C, E |
| iii ➥ B, A, C, E, D |
| iv ➥ B, A, D, C, E |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.13➡ | NET June 2022 The solution of the recurrence relation T(n)=3T(n/4)+nlgn is |
| i ➥ θ(n2logn) |
| ii ➥ θ(nlogn) |
| iii ➥ θ(nlogn)2 |
| iv ➥ θ(nloglogn) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (ii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.14➡ | NET June 2022 Which of the following algorithm design approach is used in Quick sort algorithm? |
| i ➥ Dynamic programming |
| ii ➥ Back tracking |
| iii ➥ Divide and conquer |
| iv ➥ Greedy approach |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.15➡ | NET June 2022 |
| i ➥ (A)-(III),(B)-(II),(C)-(I),(D)-(IV), (E)-(V) |
| ii ➥ (A)-(II),(B)-(III),(C)-(I),(D)-(IV),(E)-(V) |
| iii ➥ (A)-(II),(B)-(III),(C)-(I),(D)-(V),(E)-(IV) |
| iv ➥ (A)-(III),(B)-(I),(C)-(II),(D)-(IV), (E)-(V) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.16➡ | NET June 2022 Assume that f(n) and g(n) are asymptotically positive. Which of the following is correct? |
| i ➥ f(n) = O(g(n)) and g(n) = O(h(n))⇒f(n) = ω(h(n)) |
| ii ➥ f(n) =Ω(g(n)) and g(n) = Ω(h(n)) ⇒ f(n) = O(h(n)) |
| iii ➥ f(n) = o(g(n)) and g(n) = o(h(n))⇒f(n) = O(h(n)) |
| iv ➥ f(n) = ω(g(n)) and g(n) =ω(h(n))⇒f(n) = Ω(h(n)) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.17 | NET June 2022 Consider the following statements of approximation algorithm : Statement (I) : Vertex-cover is a polynomial time 2-approximation algorithm Statement (II) : TSP-tour is a polynomial time 3 –approximation algorithm for travelling salesman problem with the triangle inequality. Which of the following is correct? |
| i ➥ Statement (I) true and Statement (II) false |
| ii ➥ Statement (I) and Statement (II) true |
| iii ➥ Statement (I) and Statement (II) true |
| iv ➥ Statement (I) and Statement (II) true |
| Best Explanation: Answer:(i) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.18➡ | NET June 2021 In the following table, the left column contains the names of standard graph algorithms and the right column contains the time complexities of the algorithms. Here, n and m are number of vertices and edges, respectively. Match each algorithm with its time complexity. 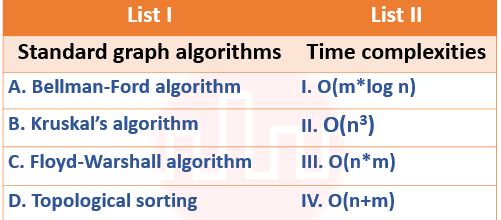 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: Options:- |
| i ➥ A – II, B – I, C – III, D – IV |
| ii ➥ A – II, B – IV, C – III, D – I |
| iii ➥ A – III, B – I, C – II, D – IV |
| iv ➥ A – III, B – IV, C – I, D – II |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.19➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2020 Consider the undirected graph below: 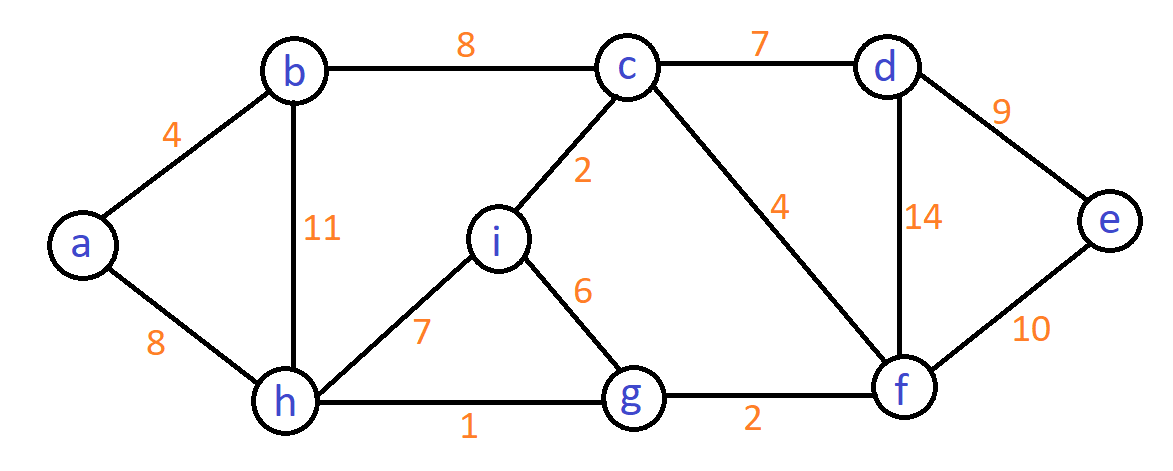 Using Prim’s algorithm to construct a minimum spanning tree starting with node a, which one of the following sequences of edges represents a possible order in which the edges would be added to construct the minimum spanning tree? |
| i ➥ (a,b), (a,h), (g,h), (f,g), (c,f), (c,i), (c,d), (d,e) |
| ii ➥ (a,b), (b,h), (g,h), (g,i), (c,i), (c,f), (c,d), (d,e) |
| iii ➥ (a,b), (b,c), (c,i), (c,f), (f,g), (g,h), (c,d), (d,e) |
| iv ➥ (a,b), (g,h), (g,f), (c,f), (c,i), (f,e), (b,c), (d,e) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.20➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2020 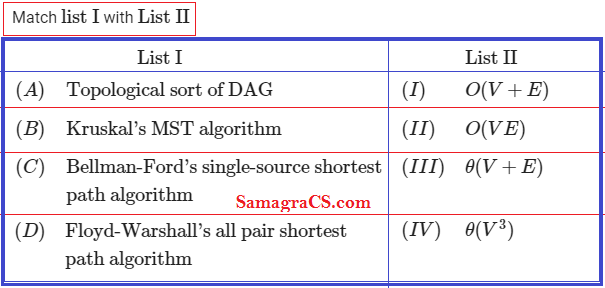 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II |
| ii ➥ A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II |
| iii ➥ A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV |
| iv ➥ A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.21➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2020 If algorithm A and another algorithm B take log2(n) and √n microseconds, respectively, to solve a problem, then the largest size n of a problem these algorithms can solve, respectively, in one second are________ and ________. |
| i ➥ 2106 and 106 |
| ii ➥ 2106 and 1012 |
| iii ➥ 2106 and 6 X 106 |
| iv ➥ 2106 and 6 X 1012 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.22➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2020 The running time of an algorithm is O(g(n)) if and only if |
| i ➥ its worst-case running time is O(g(n)) and its best-case running time is (g(n))(O=big O) |
| ii ➥ its worst-case running time is Ω(g(n)) and its best-case running time is O(g(n))(O=big O) |
| iii ➥ O(g(n))=Ω(g(n))(O=big O) |
| iv ➥ o(g(n)) ∩ ω(g(n))is non-empty set, (o=small o) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.23➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2020 Consider the following statements: (a) The running time of dynamic programming algorithm is always θ(ρ) where ρ is number of sub-problems. (b) When a recurrence relation has cyclic dependency, it is impossible to use that recurrence relation (unmodified) in a correct dynamic program. (c) For a dynamic programming algorithm, computing all values in a bottom-up fashion is asymptotically faster than using recursion and memorization. (d) If a problem X can be reduced to a known NP-hard problem, then X must be NP-hard. Which of the statement(s) is (are) true? |
| i ➥ Only (b) and (a) |
| ii ➥ Only (b) |
| iii ➥ Only (b) and (c) |
| iv ➥ Only (b) and (d) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.24➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2019 The time complexity to multiply two polynomials of degree n using Fast Fourier transform method is: |
| i ➥ θ(n lg n) |
| ii ➥ θ(n2) |
| iii ➥ θ(n) |
| iv ➥ θ(lg lg n ) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.25➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2019 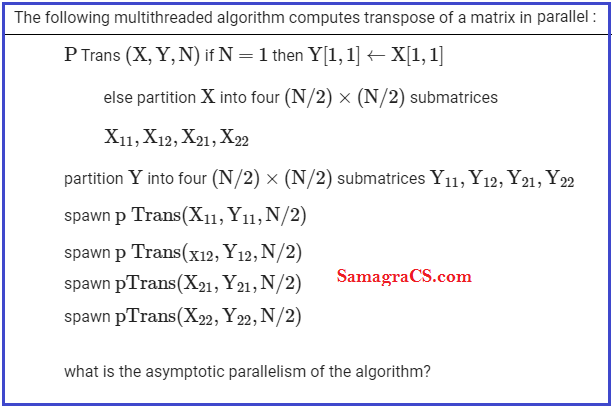 |
i ➥ 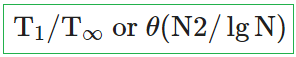 |
ii ➥ 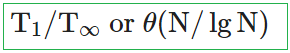 |
iii ➥ 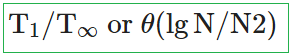 |
iv ➥ 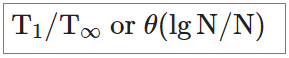 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.26➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2019 Give asymptotic upper and lower bound for T(n) given below. Assume T(n) is constant for n≤2. T(n)= 4T(√n)+lg^2 n |
| i ➥ T(n)= θ(lg*(lg^2 n)lg n) |
| ii ➥ T(n)= θ(lg^2n lg n) |
| iii ➥ T(n)= θ(lg^2 n (lg lg n)) |
| iv ➥ T(n)= θ(lg (lg n)lg n) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.27➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2019 When using Dijkstra’s algorithm to find shortest path in a graph, which of the following statement is not true? |
| i ➥ It can find shortest path within the same graph data structure |
| ii ➥ Every time a new node is visited, we choose the node with smallest known distance/cost (weight) to visit first |
| iii ➥ Shortest path always passes through least number of vertices |
| iv ➥ The graph needs to have a non-negative weight on every edge |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.28➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2019 The weight of minimum spanning tree in graph G, calculated using Kruskal’s algorithm is : 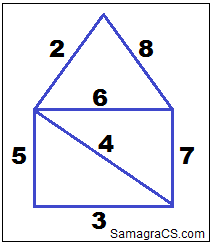 Graph-G |
| i ➥ 14 |
| ii ➥ 15 |
| iii ➥ 17 |
| iv ➥ 18 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.29➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2019 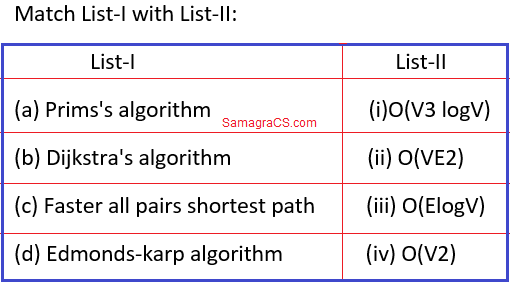 |
| i ➥ (a)-(ii); (b)-(iv); (c)-(i); (d)-(iii) |
| ii ➥ (a)-(iii); (b)-(iv); (c)-(i); (d)-(ii) |
| iii ➥ (a)-(ii); (b)-(i); (c)-(iv); (d)-(iii) |
| iv ➥ (a)-(iii); (b)-(i) (c)-(iv); (d)-(ii) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.30➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2019 Consider the following steps: S1 : Characterize the structure of an optimal solution S2 : Computer the value of an optimal solution in bottom-up fashion Which of the step(s) is/are common to both dynamic programming and greedy algorithms? |
| i ➥ Only S1 |
| ii ➥ Only S2 |
| iii ➥ both S1 and S2 |
| iv ➥ neither S1 nor S2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.31➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2019 Which of the following is best running time to sort n integers in the range 0 to n2-1 |
| i ➥ O(log n) |
| ii ➥ O(n) |
| iii ➥ O(n log n) |
| iv ➥ O(n2) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.32➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2019 Which of the following is an application of depth-first search? |
| i ➥ Only topological sort |
| ii ➥ Only strongly connected components |
| iii ➥ Both topological sort and strongly connected components |
| iv ➥ Neither topological sort not strongly connected components |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.33➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2019 There are many sorting algorithms based on comparison. The running time of heap sort algorithm is O(nlogn). Let P, but unlike Q, heapsort sorts in place where (P,Q) is equal to |
| i ➥ Merge sort, Quick sort |
| ii ➥ Quick sort, Insertion sort |
| iii ➥ Insertion sort, Quick sort |
| iv ➥ insertion sort, Merge sort |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.34➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2019 Consider the complexity class CO-NP as the set of languages L such that L’ ε NP, and the following two statements: S1 : P ⊆ CO-NP S2 : If NP ≠ CO-NP, then P ≠ NP Which of the following is/are correct? |
| i ➥ Only S1 |
| ii ➥ Only S2 |
| iii ➥ Both S1 and S2 |
| iv ➥ Neither S1 nor S2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.35➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2018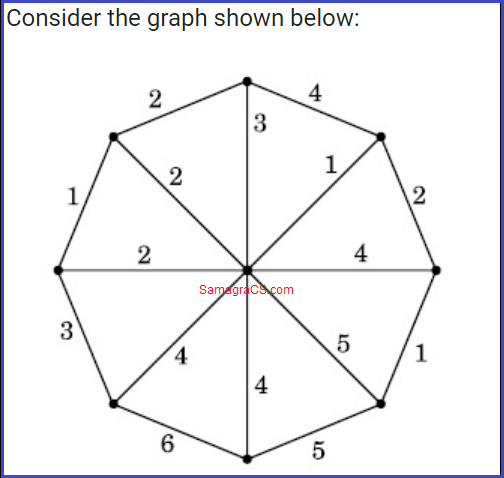 Use Kruskal’s algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree of the graph. The weight of this minimum spanning tree is: |
| i ➥ 13 |
| ii ➥ 16 |
| iii ➥ 17 |
| iv ➥ 14 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.36➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2018 let r= a(a + b)*, s=aa*b and t=a*b be three regular expressions. Consider the following: (i) L(s) ⊆ L(r) and L(s) ⊆ L(t) (ii). L(r) ⊆ L(s) and L(s) ⊆ L(t) |
| i ➥ Only (i) is correct |
| ii ➥ Both (i) and (ii) are correct |
| iii ➥ Only (ii) is correct |
| iv ➥ Neither (i) nor (ii) is correct |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.37➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2018 The second smallest of n elements can be found with _ comparisons in worst case. |
| i ➥ n + ceil(lg n) -2 |
| ii ➥ n-1 |
| iii ➥ lg n |
| iv ➥ 3n/1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.38➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2018 Consider two sequences X and Y : X = <0,1,2,1,3,0,1 > Y = <1,3,2,0,1,0 > The length of longest common sub-Sequence between X and Y is |
| i ➥ 4 |
| ii ➥ 2 |
| iii ➥ 3 |
| iv ➥ 5 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.39➡ | NTA UGC NET December 2018 The solution of recurrence relation : T(n)=2T(sqrt(n))+lg(n) is |
| i ➥ O(lg (n) lg(n)) |
| ii ➥ O(lg (n)) |
| iii ➥ O(n lg (n)) |
| iv ➥ O(lg (n) lg(lg(n))) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.40➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2018 The solution of the recurrence relation T(m)=T(3m/4)+1 is : |
| i ➥ θ(lg m) |
| ii ➥ θ(m) |
| iii ➥ θ(mlg m) |
| iv ➥ θ(lglg m) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.41➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2018 Which of the following algorithms solves the single-source shortest paths ? |
| i ➥ Prim’s algorithm |
| ii ➥ Floyd – Warshall algorithm |
| iii ➥ Johnson’s algorithm |
| iv ➥ Dijkstra’s algorithm |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.42➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2018 A text is made up of the characters A, B, C, D, E each occurring with the probability 0.08, 0.40, 0.25, 0.15 and 0.12 respectively. The optimal coding technique will have the average length of : |
| i ➥ 2.4 |
| ii ➥ 1.87 |
| iii ➥ 3.0 |
| iv ➥ 2.15 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.43➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2018 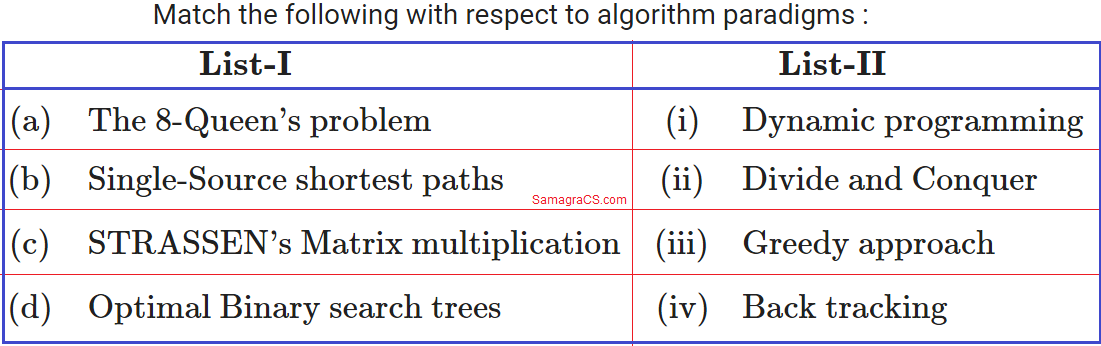 Code: |
| i ➥ (a)-(iv),(b)-(i), (c)-(iii), (d)-(ii) |
| ii ➥ (a)-(iv),(b)-(iii), (c)-(i), (d)-(ii) |
| iii ➥ (a)-(iii),(b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i) |
| iv ➥ (a)-(iv),(b)-(iii), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.44➡ | NTA UGC NET JUNE 2018 The maximum number of comparisons needed to sort 9 items using radix sort is (assume each item is 5 digit octal number) : |
| i ➥ 45 |
| ii ➥ 72 |
| iii ➥ 360 |
| iv ➥ 450 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.45➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 Consider an array representation of an n element binary heap where the elements are stored from index 1 to index n of the array. For the element stored at index i of the array (i<=n), the index of the parent is: |
| i ➥ floor ((i+1)/2) |
| ii ➥ ceiling ((i+1)/2) |
| iii ➥ floor (i/2) |
| iv ➥ ceiling (i/2) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.46➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 The following numbers are inserted into an empty binary search tree in the given order: 10, 1, 3, 5, 15, 12, 16 What is the height of the binary search tree ? |
| i ➥ 3 |
| ii ➥ 4 |
| iii ➥ 5 |
| iv ➥ 6 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.47➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 Let G be an un-directed connected graph with distinct edge weight. Let E max be the edge with maximum weight and E min the edge with minimum weight. Which of the following statements is false? |
| i ➥ Every minimum spanning tree of G must contain E min |
| ii ➥ If E max is in minimum spanning tree, then its removal must disconnect G. |
| iii ➥ No minimum spanning tree contains E max |
| iv ➥ G has a unique minimum spanning tree |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.48➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 A list of n strings, each of length n, is sorted into lexicographic order using merge – sort algorithm. The worst case running time of this computation is : |
| i ➥ O(n log n) |
| ii ➥ O(n2 log n) |
| iii ➥ O(n2 + log n) |
| iv ➥ O(n3 ) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.49➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 You are given a sequence of n elements to sort. The input sequence consists of n/k sub-sequences,each containing k elements. The elements in a given sub-sequence are all smaller than the elements in the succeeding sub-sequence and larger than the elements in the preceding sub-sequence. Thus, all that is needed to sort the whole sequence of length n is to sort the k elements in each of the n/k sub-sequences. The lower bound on the number of comparisons needed to solve this variant of the sorting problem is |
| i ➥ Ω(n) |
| ii ➥ Ω(n/k) |
| iii ➥ Ω(nlogk ) |
| iv ➥ Ω(n/klogn/k) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.50➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 T(n)= 8T (n/2)+Cn, if n>1 = b, if n=1 Consider the recurrence relation: Where b and c are constants. The order of the algorithm corresponding to above recurrence relation is: |
| i ➥ N |
| ii ➥ n2 |
| iii ➥ n log n |
| iv ➥ n3 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.51➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 Consider the following two sequences : X = < B, C, D, C, A, B, C > and Y = < C, A, D, B, C, B > The length of longest common subsequence of X and Y is : |
| i ➥ 5 |
| ii ➥ 3 |
| iii ➥ 4 |
| iv ➥ 2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.52➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 A text is made up of the characters a, b, c, d, e each occurring with the probability 0.11, 0.40, 0.16, 0.09 and 0.24 respectively. The optimal Huffman coding technique will have the average length of: |
| i ➥ 2.40 |
| ii ➥ 2.16 |
| iii ➥ 2.26 |
| iv ➥ 2.15 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.53➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 An undirected graph G (V, E) contains n (n > 2) nodes named v1 , v2 ,…,vn. Two nodes vi and vj are connected if and only if 0 <│i−j│≤2. Each edge (vi , vj ) is assigned a weight i+j. The cost of the minimum spanning tree of such a graph with 10 nodes is: |
| i ➥ 88 |
| ii ➥ 91 |
| iii ➥ 49 |
| iv ➥ 21 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.54➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2017 If b is the branching factor and m is the maximum depth of the search tree, what is the space complexity of greedy search? |
| i ➥ O(b+m) |
| ii ➥ O(bm) |
| iii ➥ O(bm) |
| iv ➥ O(mm) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.55➡ | NTA UGC NET January 2017 The asymptotic upper bound solution of the recurrence T(n)= 2T(n/2)+(n/lg) is relation given by |
| i ➥ O(n2) |
| ii ➥ O(n lg n) |
| iii ➥ O(n lg lg n) |
| iv ➥ O(lg lg n) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.56➡ | UGC NET January 2017 Any decision tree that sorts n elements has height_______. |
| i ➥ Ω(lg n) |
| ii ➥ Ω(n) |
| iii ➥ Ω(n lg n) |
| iv ➥ Ω(n2) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.57➡ | UGC NET January 2017 Red-black trees are one of many search tree schemes that are “balanced” in order to guarantee that basic dynamic-set operations take________time in the worst case. |
| i ➥ O(1) |
| ii ➥ O(lg n) |
| iii ➥ O(n) |
| iv ➥ O(n lg n) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.58➡ | UGC NET January 2017 The minimum number of scalar multiplication required, for parenthesization of a matrix-chain product whose sequence of dimensions for four matrices is <5, 10, 3, 12, 5> is. |
| i ➥ 630 |
| ii ➥ 580 |
| iii ➥ 480 |
| iv ➥ 405 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.59➡ | UGC NET January 2017 Dijkstra’s algorithm is based on |
| i ➥ Divide and conquer paradigm |
| ii ➥ Dynamic programming |
| iii ➥ Greedy Approach |
| iv ➥ Backtracking paradigm |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.60➡ | UGC NET January 2017 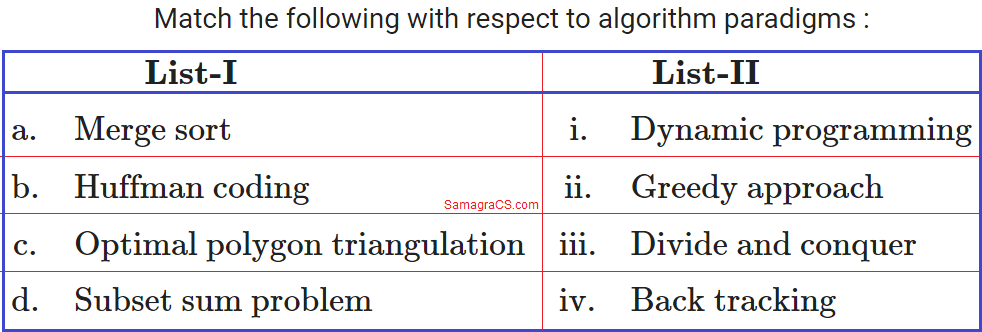 |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii |
| iii ➥ a-ii, b-i, c-iii, d-iv |
| iv ➥ b-iii, b-ii, c-i, d-iv |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.61➡ | UGC NET August 2016 Consider the problem of a chain < A1, A2, A3, A4 > of four matrices. Suppose that the dimensions of the matrices A1, A2, A3 and A4 are 30 × 35, 35 × 15, 15 × 5 and 5 × 10 respectively. The minimum number of scalar multiplications needed to compute the product A1 A2A3A4 is___ |
| i ➥ 14875 |
| ii ➥ 21000 |
| iii ➥ 9375 |
| iv ➥ 11875 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.62➡ | UGC NET August 2016 Consider a weighted complete graph G on the vertex set {ν1, ν2, …. νn} such that the weight of the edge (νi, νj) is 4 | i – j|. The weight of minimum cost spanning tree of G is : |
| i ➥ 4n2 |
| ii ➥ N |
| iii ➥ 4n-4 |
| iv ➥ 2n-2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.63➡ | UGC NET August 2016 If there are n integers to sort, each integer has d digits, and each digit is in the set {1, 2, …,k}, radix sort can sort the numbers in: |
| i ➥ O (k (n + d)) |
| ii ➥ O(d (n + k)) |
| iii ➥ O((n + k) lg d) |
| iv ➥ O((n + d) lg k) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.64➡ | UGC NET August 2016 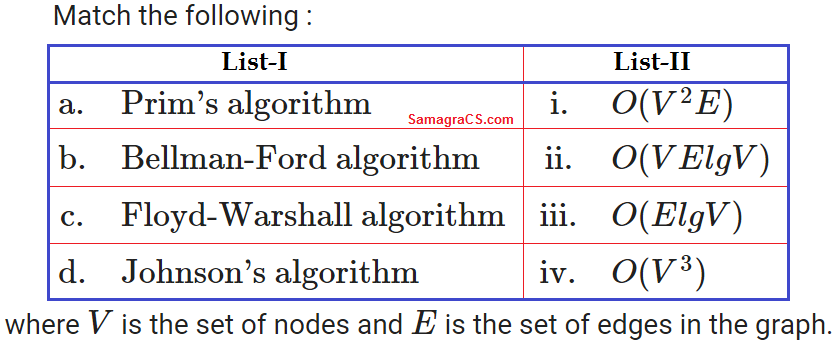 |
| i ➥ a-i, b-iii, c-iv, d-ii |
| ii ➥ a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv |
| iii ➥ a-iii, b-i, c-iv, d-ii |
| iv ➥ a-iii, b-i, c-ii, d-iv |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.65➡ | UGC NET July 2016 The runtime for traversing all the nodes of a binary search tree with n nodes and printing them in an order is: |
| i ➥ O(lg n) |
| ii ➥ O(n lg n) |
| iii ➥ O(n) |
| iv ➥ O(n 2 ) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.66➡ | UGC NET July 2016 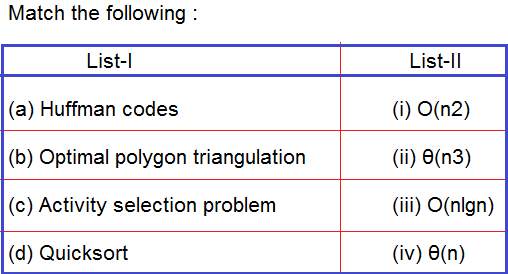 |
| i ➥ (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii) |
| ii ➥ (a)-(i), (b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iii) |
| iii ➥ (a)-(iii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i) |
| iv ➥ (a)-(iii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.67➡ | UGC NET December 2015 In general, in a recursive and non-recursive implementation of a problem (program): |
| i ➥ Both time and space complexities are better in recursive than in non-recursive program. |
| ii ➥ Both time and space complexities are better in non-recursive than in recursive program |
| iii ➥ Time complexity is better in recursive version but space complexity is better in non-recursive version of the program. |
| iv ➥ Space complexity is better in recursive version but time complexity is better in non-recursive version of the program. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
