Computer Graphics NTA UGC NET Question Analysis
| Q.1➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023 The Hue of a colour is related to its : |
| i ➥ Luminance |
| ii ➥ Saturation |
| iii ➥ Incandescence |
| iv ➥ Wavelength |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (IV) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.2➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023 Consider the three points P1(1, 2, 0), P2(3, 6, 20) and P3(2, 4, 6) and a view point C(0, 0, 10). Choose the correct options. (A) P1 obscure P2, if viewed from C. (B) P2 obscure P1, if viewed from C. (C) P3 does not obscure P1, if viewed from C. (D) P2 does not obscure P3, if viewed from C. Choose the correct answer from the options given below : |
| i ➥ (A), (B) and (C) Only |
| ii ➥ (A), (C) and (D) Only |
| iii ➥ (B), (C) and (D) Only |
| iv ➥ (A), (B) and (D) Only |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (II) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.3➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023 Match List – I with List – II. List – I (A) Bresenham (B) Cohen-Sutherland (C) Sutherland-Hodgeman (D) Z-Buffer List – II (1) Hidden surface removal (II) Line drawing algorithm (III) Line clipping algorithm (IV) Polygon clipping algorithm Choose the correct answer from the options given below : |
| i ➥ (A)-(III), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) |
| ii ➥ (A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(I), (D)-(IV) |
| iii ➥ (A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I) |
| iv ➥ (A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(III), (D)-(1) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (III) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.4➡ | UGC NET DEC 2023 Consider a triangle PQR with coordinates as P(0,0) Q(2, 2) and R(10, 4) If this triangle is to be magnified to four times its size while keeping R(10, 4) fixed, then the coordinates of the magnified triangle are: |
| i ➥ (-20,12), Q(- 20, – 4) and R(10, 4) |
| ii ➥ (-30,12), Q(- 22, – 4) and R(10, 4) |
| iii ➥ (25,10), Q(22, – 4) and R(10, 4) |
| iv ➥ (30,12), Q(- 22, 4) and R(10, 4) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (II) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.5➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 Match List I with List II 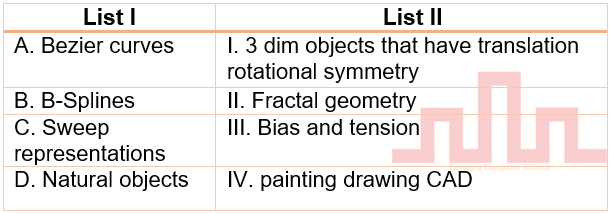 Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A-IV B-I C-III D-II |
| ii ➥ A-II B-111 C-I V D-I |
| iii ➥ A-IV B-III C-I D-II |
| iv ➥ A-II B-IV C-I D-III |
| Best Explanation: Answer: Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.6➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 Southerland Hodgeman method is used on Southerland Hodgeman method is used on |
| i ➥ Smooth curves |
| ii ➥ Line segment |
| iii ➥ Convex polygons |
| iv ➥ Concave polygons |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is a polygon clipping algorithm used to clip a polygon against a convex polygon (often referred to as a clipping window). Here’s a detailed explanation: Objective: The primary goal of the Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is to clip a polygon against a convex clipping window, retaining only the parts of the polygon that are inside the window. Algorithm Steps: Input: The algorithm takes as input the vertices of the polygon to be clipped. The vertices are assumed to be in order, either clockwise or counterclockwise. Clipping Against Each Edge: The algorithm clips the polygon against each edge of the convex window one at a time. For each edge of the window, it iterates through each pair of consecutive vertices of the polygon. Clipping Process: For each pair of consecutive vertices, the algorithm checks whether they are inside or outside the clipping edge. It classifies the vertices as either inside or outside the edge and produces a new list of vertices representing the clipped polygon. Output: After processing all edges, the algorithm produces a new list of vertices that form the clipped polygon. Explanation: The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm works by iteratively clipping the polygon against each edge of the convex window. At each step, it checks the relative positions of the vertices with respect to the current clipping edge. If both vertices are inside the edge, the second vertex is added to the output list. If the first vertex is inside and the second is outside, the point of intersection of the polygon edge with the clipping edge is added to the output list. If both vertices are outside, no new vertices are added. The process is repeated for each edge of the convex window, resulting in a new set of vertices that represent the clipped polygon. Use Case: The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is commonly used in computer graphics for rendering and displaying only the visible parts of a polygon within a specified viewing window or viewport. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.7➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 Which of the following transforms in 2 dimension is used to resize a 2-dimensional object? |
| i ➥ Translation |
| ii ➥ Rotation |
| iii ➥ Scaling |
| iv ➥ Shearing |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.8➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 Given below are two statements: Statement I: subsystem models show logical grouping of objects into coherent subsystem Statement II: State machine models show how objects change their states in response to events. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below. |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are correct |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct |
| Best Explanation: Answer: I Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.9➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 The clipping process in computer graphics is used for |
| i ➥ Adding graphics |
| ii ➥ Copying |
| iii ➥ Zooming |
| iv ➥ Removing objects and lines |
| Best Explanation: Answer: IV Explanation: Removing objects and lines: The clipping process in computer graphics is primarily used for removing or discarding portions of objects or lines that are outside a specified region, known as a clipping window or viewport. This is done to ensure that only the visible parts of objects or lines are rendered, optimizing performance and improving the efficiency of the rendering process. Other’s Options : i. Adding graphics Explanation: Clipping is not typically used for adding graphics. Instead, it focuses on deciding which portions of existing graphics are visible within a specified region (clipping window) and should be rendered. ii. Copying Explanation: Clipping is not directly associated with copying. Clipping is more about deciding what parts of an object or scene should be displayed, removing portions that are outside the viewing area. iii. Zooming Explanation: Clipping is not directly related to zooming. Zooming usually involves scaling objects, and while the clipping process may be involved in the rendering of the zoomed view, it is not the primary purpose. Important Point : In computer graphics, the clipping process is used for controlling the display of objects or parts of objects that are within a specified region, called a clipping window or viewport. Clipping is crucial in computer graphics for several reasons: Viewing Window: Culling Objects: Clipping helps to eliminate or “clip away” parts of objects that are outside the viewing window. This ensures that only the visible portions of objects are rendered, optimizing performance. Visible Region: Improving Efficiency: Clipping helps in discarding portions of objects that are not visible or are outside the current viewing region. This improves rendering efficiency. Efficient Rendering: Hidden Surface Removal: Clipping can be used as a part of hidden surface removal algorithms to eliminate surfaces or portions of surfaces that are not visible in the final image. Realism: Enhancing Realism: Clipping allows for a more realistic rendering of scenes by showing only the parts of objects that are within the user’s view, simulating the way the human eye perceives the environment. Performance Optimization: Reducing Processing Load: By eliminating unnecessary portions of objects early in the rendering pipeline, the computational load is reduced, leading to better overall performance. User Interaction: User-Defined Views: Clipping can be used to define user-specific views or perspectives within a larger scene, allowing users to focus on specific areas of interest. Windowing Operations: Creating Viewports: Clipping is an essential part of creating viewports or windows within a graphical interface. This is important in applications like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and graphical user interfaces. |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.10➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2023 Consider the rectangle with vertices (0,0),(0,2),(3,0),(3,2). There is scaling of 2 towards x-axis and 3 towards y-axis. The new coordinates of the rectangle are. |
| i ➥ (0,0),(6,0),(0,4),(6,4) |
| ii ➥ (0,0),(6,0),(0,4),(3,2) |
| iii ➥ (0,0),(6,0),(0,6),(6,6) |
| iv ➥ (0,0),(4,0),(0,6),(4,6) |
| Best Explanation: Answer: III Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.11➡ | NET December 2022 Assertion A: A Raster scan device is a CRT graphic device and can use a television monitor for display. Reason R: In Raster scan display the picture is composed of a series of dots. These dots are traced out as a series of horizontal lines. Television works in a similar fashion. In the light of the above statements: choose the correct answer from the options given below |
| i ➥ Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A |
| ii ➥ Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A |
| iii ➥ A is true but R is false |
| iv ➥ A is false but R is true |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (i) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
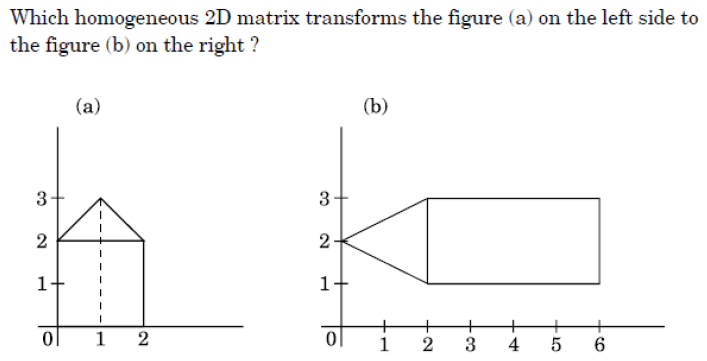
| Q.12➡ | NET June 2022 This transformation is called: 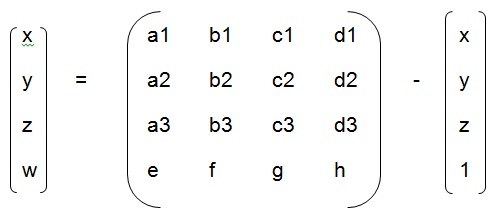 |
| i ➥ Scaling |
| ii ➥ Shear |
| iii ➥ Homography |
| iv ➥ Steganography |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (iii) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.13➡ | NET June 2022 Hidden surface removal problem with minimal 3 D pipeline can be solved with |
| i ➥ Painter’s algorithm |
| ii ➥ Window clipping algorithm |
| iii ➥ Brute force rasterization algorithm |
| iv ➥ Flood fill algorithm |
| Best Explanation: Answer: (i) Explanation: Upload Soon |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.14➡ | NET June 2021 What is the transformation matrix M that transforms a square in the xy-plane defined by (1, 1)T, (-1,1)T,(-1,-1)T and (1,-1)T to a parallelogram whose corresponding vertices are (2, 1)T, (0,-1)T,(-2,-1)T and (0,-1)T? |
i ➥ 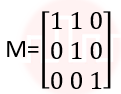 |
ii ➥ 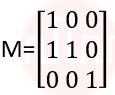 |
iii ➥ 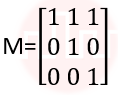 |
iv ➥ 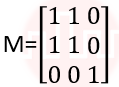 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.15➡ | NET June 2021 Given below are two statements Statement I: The maximum number of sides that a triangle might have when clipped to a rectangular viewport is 6. Statement II: In 3D graphics, the perspective transformation is nonlinear in z. In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below Options:- |
| i ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are true. |
| iii ➥ Statement I is false but Statement II is true. |
| iv ➥ Statement I is true but Statement II is false. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.16➡ | NET June 2021 Suppose you have eight ‘black and white’ images taken with a 1-megapixel camera and one ‘8-color’ image taken by an 8-megapixel camera. How much hard disk space in total do you need to store these images on your computer? |
| i ➥ 1 GB |
| ii ➥ 3 GB |
| iii ➥ 3 MB |
| iv ➥ 4 MB |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.17➡ | NET June 2021 Suppose a Bezier curve P(t) is defined by the Following four control points in the xy-plane: P0=(-2, 0); P1=(-2,4);P2=(2,4); and P3=(2,0). Then which of the following statement are correct ? A. Bezier curve P(t) has degree 3. B. B. bezier curve P(t) may extend outside the convex full of its control points. Choose the correct answer from the options below: |
| i ➥ A and B only |
| ii ➥ A and C only |
| iii ➥ A, B, and C |
| iv ➥ B and C only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.18➡ | NET June 2021 Which of the statements given below are correct? The midpoint (or Bresenham) algorithm for rasterizing lines is optimized relative to DDA algorithm in that A. it avoids round-off operations. B. it is incremental. C. it uses only integer arithmetic. D. all straight lines can be displayed as straight (exact). Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A and B only |
| ii ➥ A and C only |
| iii ➥ A, B, and C only |
| iv ➥ A, B, C, and D |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.19➡ | NET November 2020 Given below are different properties of 3D projections from A.D. Identify the correct order on the basis of property true of (i) a perspective projection only (ii) an orthographic projection only (iii) both orthographic and projective transformations and (iv) neither orthographic nor projective transformation, respectively. (A) Straight lines are mapped to straight lines. (B) Distance and angles are (in general) preserved. (C) Far away objects appear the same size as closer ones. (D) Requires homogeneous coordinates in order for it to be encoded into linear transformation. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i➥ D, C, B, A |
| ii➥ B, C, D, A |
| iii➥ D, C, A, B |
| iv➥ C, D, B, A |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
Q.20➡ | NET November 2020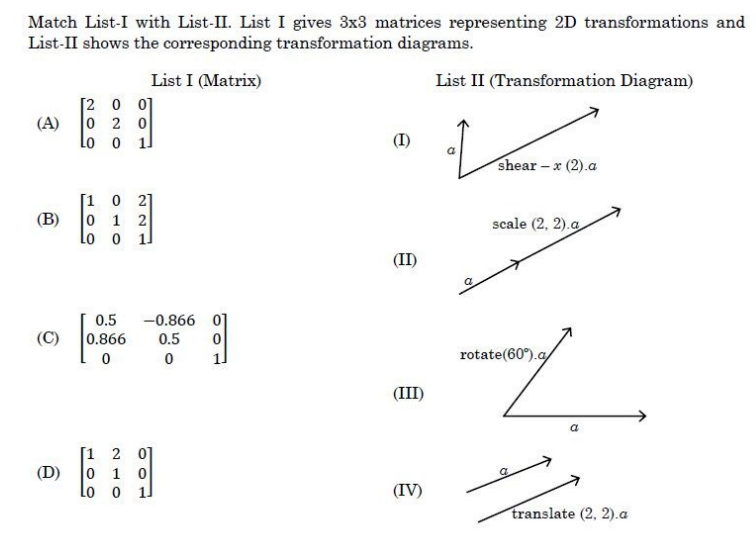 |
| i ➥ A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I |
| ii ➥ A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I |
| iii ➥ A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I |
| iv ➥ A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.21➡ | NET November 2020 Given below are two statements: Statement I: Bezier curves are curves that interpolate all of their control points Statement II: A cubic bezier curve has four control points. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below |
| i ➥ Both statement I and Statement II are true |
| ii ➥ Both Statement I and Statement II are false |
| iii ➥ Statement I is correct but Statement II is false |
| iv ➥ Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Topic | Help-Line |
| Q.22➡ | NET November 2020 Concerning phong shading and gouraud shading in a 3D scene, which of the following statements are true? (A) Gouraud shading requires more computation than phong shading (B) Gouraud shading linearly interpolates the color of an interior pixel from the color at the vertices. (C) Phong shading interpolates over the normal vectors specified at the vertices. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ (A) and (B) only |
| ii ➥ (A) and (C) only |
| iii ➥ (B) and (C) only |
| iv ➥ (A), (B) and (C) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.23➡ | NET November 2020 The context of 3D Computer graphics, which of the following statements is/are correct? A) Under perspective projection, each set of parallel lines in the object do not stay parallel in the image (except those that are parallel to the view plane to start with). B) Applying a perspective transformation in the graphics pipeline to a vertex involves dividing by its ‘z’ coordinate. C) Perspective transformation is a linear transformation. Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ (A) and (B) only |
| ii ➥ (A) and (C) only |
| iii ➥ (B) and (C) only |
| iv ➥ (A), (B) and (C) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Network Security | Help-Line |
| Q.24➡ | NET December 2019 If we want to resize a 1024 × 768 pixels image to one that is 640 pixels wide with the same aspect ratio, what would be the height of the resized image? |
| i ➥ 420 Pixels |
| ii ➥ 460 Pixels |
| iii ➥ 480 Pixels |
| iv ➥ 540 Pixels |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.25➡ | NET December 2019 Consider the following statement with respect to approaches to fill area on raster systems: (P) To determine the overlap intervals for scan lines that cross the area. (Q) To start from a given interior position and paint outward from this point until we encounter the specified boundary conditions. Select the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ P only |
| ii ➥ Q only |
| iii ➥ Both P and Q |
| iv ➥ Neither P nor Q |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.26➡ | NET December 2019 A rectangle is bounded by the lines x = 0; y=0, x = 5 and y = 3. The line segment joining (–1, 0) and (4, 5), if clipped against this window will connect the points _____. |
| i ➥ (0, 1) and (3, 3) |
| ii ➥ (0, 1) and (2, 3) |
| iii ➥ (0, 1) and (4, 5) |
| iv ➥ (0, 1) and (3, 5) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.27➡ | NET December 2019 Which of the following algorithms is not used for line clipping? |
| i ➥ Cohen-Sutherland algorithm |
| ii ➥ Southerland-Hodgeman algorithm |
| iii ➥ Liang-barsky algorithm |
| iv ➥ Nicholl-Lee-Nicholl algorithm |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.28➡ | NET June 2019 Using the phong reflectance model, the strength of the specular highlight is determined by the angle between |
| i ➥ The view vector and the normal vector |
| ii ➥ The light vector and the normal vector |
| iii ➥ The light vector and the reflected vector |
| iv ➥ the reflected vector and the view vector |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
Q.29➡ | NET June 2019 |
| i ➥ Both S1 and S2 are true |
| ii ➥ Only S1 is true |
| iii ➥ Only S2 is true |
| iv ➥ Both S1 and S2 are false |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.30➡ | NET June 2019 Consider a raster system with resolution 640 by 480. What size is frame buffer (in bytes) for this system to store 12 bits per pixel? |
| i ➥ 450 kilobytes |
| ii ➥ 500 Kilobytes |
| iii ➥ 350 kilobytes |
| iv ➥ 400 kilobytes |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.31➡ | NET December 2018 In 3D Graphics, which of the following statements about perspective and parallel projection is/are true? P: In a perspective projection, the farthest an object is from the center of projection, the smaller it appears. Q: Parallel projection is equivalent to a perspective projection where the viewer is standing infinitely far away R: Perspective projections do not preserve straight lines. |
| i ➥ P and R only |
| ii ➥ P,Q and R |
| iii ➥ Q and R only |
| iv ➥ P and Q only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
i ➥ 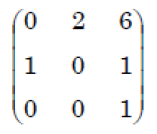 |
ii ➥ 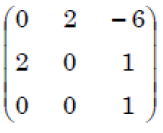 |
iii ➥ 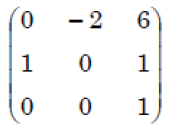 |
iv ➥ 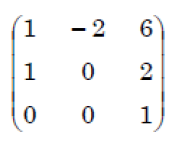 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.33➡ | NET December 2018 In 3D Graphics, which of the following statement/s is/are true ? P: Back-face culling is an example of an image-precision visible-surface determination. Q: Z-Buffer is a 16-bit, 32-bit, or 64-bit field associated with each pixel in a frame buffer that can be used to determine the visible surface at each pixel. |
| i ➥ P only |
| ii ➥ Neither P nor Q |
| iii ➥ P and Q |
| iv ➥ Q only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.34➡ | NET June 2018 A graphic display system has a frame buffer that is 640 pixels wide, 480 pixels high and 1 bit of color depth. If the access time for each pixel on the average is 200 nanoseconds, then the refresh rate of this frame buffer is approximately : |
| i ➥ 16 frames per second |
| ii ➥ 19 frames per second |
| iii ➥ 21 frames per second |
| iv ➥ 23 frames per second |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| i ➥ S1 only |
| ii ➥ S2 only |
| iii ➥ Both S1 and S2 |
| iv ➥ Neither S1 Nor S2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.36➡ | NET June 2018 Consider the matrix 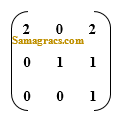 representing a set of planar (2D) geometric transformations in homogeneous coordinates. Which of the following statements about the matrix M is True ? |
| i ➥ M represents first, a scaling of vector (2, 1) followed by translation of vector (1, 1) |
| ii ➥ M represents first, a translation of vector (1, 1) followed by scaling of vector (2, 1) |
| iii ➥ M represents first, a scaling of vector (3, 1) followed by shearing of parameters (−1, 1) |
| iv ➥ M represents first, a shearing of parameters (−1, 1) followed by scaling of vector (3, 1) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.37➡ Net November 2017 Paper III Which of the following is not a component of Memory tube display ? |
| i ➥ Flooding gun |
| ii ➥ Collector |
| iii ➥ Ground |
| iv ➥ Liquid Crystal |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.38➡ Net November 2017 Paper III Which of the following is not true in case of Oblique Projections? |
| i ➥ Parallel projection rays are not perpendicular to the viewing plane. |
| ii ➥ Parallel lines in space appear parallel on the final projected image. |
| iii ➥ Used exclusively for pictorial purposes rather than formal working drawings. |
| iv ➥ Projectors are always perpendicular to the plane of projection. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.39➡ Net November 2017 Paper III With respect to CRT, the horizontal retrace is defined as: |
| i ➥ The path an electron beam takes when returning to the left side of the CRT. |
| ii ➥ The path an electron beam takes when returning to the right side of the CRT. |
| iii ➥ The technique of turning the electron beam off while retracing. |
| iv ➥ The technique of turning the electron beam on/off while retracing. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.40➡ Net November 2017 Paper III Find the equation of the circle x2+y2=1 in terms of x’y’ coordinates, assuming that the xy coordinate system results from a scaling of 3 units in the x’ direction and 4 units in the y’ direction. |
| i ➥ 3(x’)2 + 4(y’)2 = 1 |
| ii ➥ (x’/3)2 + (y’/4)2 = 1 |
| iii ➥ (3x’)2 + 4(y’)2 = 1 |
| iv ➥ 1/3(x’)2 + 1/4(y’)2 = 1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.41➡ Net November 2017 Paper III Find the normalization transformation that maps a window whose lower left corner is at (1, 1) and upper right corner is at (3, 5) onto a viewport that is the entire normalized device screen. |
i ➥ 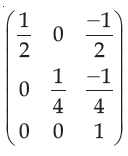 |
ii ➥ 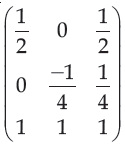 |
iii ➥ 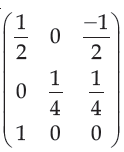 |
iv ➥ 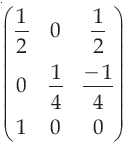 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.42➡ | Net November 2017 Paper III The three aspects of Quantization, programmers generally concerned with are: |
| i ➥ Coding error, Sampling rate and Amplification |
| ii ➥ Sampling rate, Coding error and Conditioning |
| iii ➥ Sampling rate, Aperture time and Coding error |
| iv ➥ Aperture time, Coding error and Strobing |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.43➡ | Net January 2017 Paper III Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ? |
| i ➥ Persistence is the term used to describe the duration of phosphorescence. |
| ii ➥ The control electrode is used to turn the electron beam on and off. |
| iii ➥ The electron gun creates a source of electrons which are focused into a narrow beam directed at the face of CRT. |
| iv ➥ All of the above |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.44➡ | Net January 2017 Paper III A segment is any object described by GKS commands and data that start with CREATE SEGMENT and Terminates with CLOSE SEGMENT command. What functions can be performed on these segments ? |
| i ➥ Translation and Rotation |
| ii ➥ Panning and Zooming |
| iii ➥ Scaling and Shearing |
| iv ➥ Translation, Rotation, Panning and Zooming |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
Q.45➡ | Net January 2017 Paper III  Code: |
| i ➥ a-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv |
| ii ➥ a-i, b-iii, c-ii, d-iv |
| iii ➥ a-iv, b-iii, c-ii, d-i |
| iv ➥ a-iv, b-ii, c-i, d-iii |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.46➡ | Net January 2017 Paper III Below are the few steps given for scan-converting a circle using Bresenham’s Algorithm. Which of the given steps is not correct ? |
| i ➥ Compute d = 3 – 2r (where r is radius) |
| ii ➥ Stop if x > y |
| iii ➥ If d < 0, then d = 4x + 6 and x = x + 1 |
| iv ➥ If d ≥, then d = 4 * (x – y) + 10, x = x + 1 and y = y + 1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.47➡ | Net January 2017 Paper III Which of the following is/are side effects of scan conversion ? 1. Aliasing 2. Unequal intensity of diagonal lines 3. Overstriking in photographic applications 4. Local or Global aliasing |
| i ➥ 1 and 2 |
| ii ➥ 1,2 and 3 |
| iii ➥ 1, 3 and iv |
| iv ➥ i , ii, iii, and iv |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.48➡ | Net January 2017 Paper III Consider a line AB with A=(0,0) and B=(8,4). Apply a simple DDA algorithm and compute the first four plots on this line. |
| i ➥ [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 2)] |
| ii ➥ [(0, 0), (1, 1.5), (2, 2), (3, 3)] |
| iii ➥ [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2. 2.5), (3, 3)] |
| iv ➥ [(0, 0), (1, 2), (2, 2), (3, 2)] |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q.49➡ | Net Auguest 2016 Paper III Consider a raster grid having XY-axes in positive X-direction and positive upward Y-direction with Xmax = 10, Xmin = –5, Ymax = 11, and Ymin = 6. What is the address of memory pixel with location (5, 4) in raster grid assuming base address 1 (one) ? |
| i ➥ 150 |
| ii ➥ 151 |
| iii ➥ 160 |
| iv ➥ 161 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.50➡ | Net Auguest 2016 Paper III Consider a N-bit plane frame buffer with W-bit wide lookup table with W > N. How many intensity levels are available at a time ? |
| i ➥ 2N |
| ii ➥ 2W |
| iii ➥ 2N+W |
| iv ➥ 2N-1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.51➡ | Net Auguest 2016 Paper III Consider the Bresenham’s line generation algorithm for a line with gradient greater than one, current point (xi, yi) and decision parameter, di. The next point to be plotted (xi+1, yi+1) and updated decision parameter, di+1, for di < 0 are given as _. |
| i ➥ xi+1 = xi +1 yi+1 = yi di+1 = di+ 2 dy |
| ii ➥ xi+1 = xi yi+1 = yi +1 di+1 = di+ 2 dx |
| iii ➥ xi+1 = xi yi+1 = yi +1 di+1 = di+ 2(dx -dy) |
| iv ➥ xi+1 = xi +1 yi+1 = yi +1 di+1 = di+ 2(dy -dx) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.52➡ | Net Auguest 2016 Paper III A point P(2, 5) is rotated about a pivot point (1, 2) by 60°. What is the new transformed point P’ ? |
| i ➥ (1, 4) |
| ii ➥ (–1, 4) |
| iii ➥ (1, – 4) |
| iv ➥ (– 4, 1) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.53➡ | Net Auguest 2016 Paper III In perspective projection (from 3D to 2D), objects behind the centre of projection are projected upside down and backward onto the view-plane. This is known as _. |
| i ➥ Topological distortion |
| ii ➥ Vanishing point |
| iii ➥ View confusion |
| iv ➥ Perspective foreshortening |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q.54➡ | Net Auguest 2016 Paper III The Liang-Barsky line clipping algorithm uses the parametric equation of a line from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2) along with its infinite extension which is given as : x = x1 + ∆x.u y = y1 + ∆y.u Where ∆x = x2– x1, ∆y = y2– y1, and u is the parameter with 0 ≤ u ≤ 1. A line AB with endpoints A(–1, 7) and B(11, 1) is to be clipped against a rectangular window with xmin = 1, xmax = 9, ymin = 2, and ymax = 8. The lower and upper bound values of the parameter u for the clipped line using Liang-Barsky algorithm is given as : |
| i ➥ (0, 2/3) |
| ii ➥ (1/6 , 5/6) |
| iii ➥ (0, 1/3) |
| iv ➥ (0, 1) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |