GATE 2006 CSE previous year questions
| Q1➡ | Engineering mathematics Consider the polynomial p(x) = a0 + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3, where ai ≠ 0, ∀i. The minimum number of multiplications needed to evaluate p on an input x is: |
| i ➥ 3 |
| ii ➥ 4 |
| iii ➥ 6 |
| iv ➥ 9 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Numerical methods | Help-Line |
| Q2➡ | Engineering mathematics Let X, Y, Z be sets of sizes x, y and z respectively. Let W = X×Y and E be the set of all subsets of W. The number of functions from Z to E is: |
| i ➥ Z2xy |
| ii ➥ Z×2xy |
| iii ➥ Z2x+y |
| iv ➥ 2xyz |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sets and functions | Help-Line |
| Q3➡ | Engineering mathematics The set {1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9} under multiplication modulo 10 is not a group. Given below are four plausible reasons. Which one of them is false? |
| i ➥ It is not closed |
| ii ➥ 2 does not have an inverse |
| iii ➥ 3 does not have an inverse |
| iv ➥ 8 does not have an inverse |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sets and relations | Help-Line |
| Q4➡ | Engineering mathematics A relation R is defined on ordered pairs of integers as follows: (x,y) R(u,v) if x < u and y > v. Then R is: |
| i ➥ Neither a Partial Order nor an Equivalence Relation |
| ii ➥ A Partial Order but not a Total Order |
| iii ➥ A Total Order |
| iv ➥ An Equivalence Relation |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sets and relations | Help-Line |
| Q5➡ | Computer networks For which one of the following reasons does Internet Protocol (IP) use the time-to- live (TTL) field in the IP datagram header? |
| i ➥ Ensure packets reach destination within that time |
| ii ➥ Discard packets that reach later than that time |
| iii ➥ Prevent packets from looping indefinitely |
| iv ➥ Limit the time for which a packet gets queued in intermediate routers |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | IP header | Help-Line |
| Q6➡ | Operating systems Consider three CPU-intensive processes, which require 10, 20 and 30 time units and arrive at times 0, 2 and 6, respectively. How many context switches are needed if the operating system implements a shortest remaining time first scheduling algorithm? Do not count the context switches at time zero and at the end. |
| i ➥ 1 |
| ii ➥ 2 |
| iii ➥ 3 |
| iv ➥ 4 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process scheduling | Help-Line |
| Q7➡ | Compiler design Consider the following grammar. S -> S * E S -> E E -> F + E E -> F F -> id Consider the following LR(0) items corresponding to the grammar above. (i) S -> S * .E (ii) E -> F. + E (iii) E -> F + .E Given the items above, which two of them will appear in the same set in the canonical sets-of-items for the grammar? |
| i ➥ (i) and (ii) |
| ii ➥ (ii) and (iii) |
| iii ➥ (i) and (iii) |
| iv ➥ None of the above |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Parsers | Help-Line |
| Q8➡ | Digital logic design You are given a free running clock with a duty cycle of 50% and a digital waveform f which changes only at the negative edge of the clock. Which one of the following circuits (using clocked D flip-flops) will delay the phase of f by 180°? |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sequential circuits | Help-Line |
| Q9➡ | Computer organization A CPU has 24-bit instructions. A program starts at address 300 (in decimal). Which one of the following is a legal program counter (all values in decimal)? |
| i ➥ 400 |
| ii ➥ 500 |
| iii ➥ 600 |
| iv ➥ 700 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Machine instructions | Help-Line |
| Q10➡ | Data structures In a binary max heap containing n numbers, the smallest element can be found in time |
| i ➥ O(n) |
| ii ➥ O(log n) |
| iii ➥ O(log log n) |
| iv ➥ O(1) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Heap tree | Help-Line |
| Q11➡ | Algorithms Consider a weighted complete graph G on the vertex set {v1, v2, … vn} such that the weight of the edge (vi, vj) is 2|i – j|. The weight of a minimum spanning tree of G is: |
| i ➥ n-1 |
| ii ➥ 2n-2 |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ n2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Minimum spanning tree | Help-Line |
| Q12➡ | Algorithms To implement Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm on unweighted graphs so that it runs in linear time, the data structure to be used is: |
| i ➥ Queue |
| ii ➥ Stack |
| iii ➥ Heap |
| iv ➥ B-tree |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | AC path | Help-Line |
| Q13➡ | Data structures A scheme for storing binary trees in an array X is as follows. Indexing of X starts at 1 instead of 0. The root is stored at X[1]. For a node stored at X[i], the left child, if any, is stored in X[2i] and the right child, if any, in X[2i+1]. To be able to store any binary tree on n vertices the minimum size of X should be. |
| i ➥ log2n |
| ii ➥ n |
| iii ➥ 2n+1 |
| iv ➥ 2n-1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Binary trees | Help-Line |
| Q14➡ | Algorithms Which one of the following in place sorting algorithms needs the minimum number of swaps? |
| i ➥ Quick sort |
| ii ➥ Insertion sort |
| iii ➥ Selection sort |
| iv ➥ Heap sort |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sorting | Help-Line |
| Q15➡ | Algorithms Consider the following C-program fragment in which i, j and n are integer variables. for (i = n, j = 0; i >0; i /= 2, j += i); Let val(j) denote the value stored in the variable j after termination of the for loop. Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ val(j) = θ(logn) |
| ii ➥ val(j) = θ(√n) |
| iii ➥ val(j) = θ(n) |
| iv ➥ val(j) = θ(n logn) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Time complexity | Help-Line |
| Q16➡ | Algorithms Let S be an NP-complete problem and Q and R be two other problems not known to be in NP. Q is polynomial time reducible to S and S is polynomial-time reducible to R. Which one of the following statements is true? |
| i ➥ R is NP-complete |
| ii ➥ R is NP-hard |
| iii ➥ Q is NP-complete |
| iv ➥ Q is NP-hard |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | P-NP | Help-Line |
| Q17➡ | Algorithms An element in an array X is called a leader if it is greater than all elements to the right of it in X. The best algorithm to find all leaders in an array |
| i ➥ Solves it in linear time using a left to right pass of the array |
| ii ➥ Solves it in linear time using a right to left pass of the array |
| iii ➥ Solves it using divide and conquer in time θ(nlogn) |
| iv ➥ Solves it in time θ(n2) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Time complexity | Help-Line |
| Q18➡ | Engineering mathematics We are given a set X = {x1, …. xn} where xi = 2i. A sample S ⊆ X is drawn by selecting each xi independently with probability pi = 1/2. The expected value of the smallest number in sample S is: |
| i ➥ 1/n |
| ii ➥ 2 |
| iii ➥ √n |
| iv ➥ n |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Probability | Help-Line |
| Q19➡ | Theory of computation Let L1 = {0n+m1n0m|n,m >= 0}, L2 = {0n+m1n+m0m|n,m >= 0}, and L3 = {0n+m1n+m0n+m|n,m >= 0}. Which of these languages are NOT context free? |
| i ➥ L1 only |
| ii ➥ L3 only |
| iii ➥ L1 and L2 |
| iv ➥ L2 and L3 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Context free language | Help-Line |
| Q20➡ | Database management system Consider the following log sequence of two transactions on a bank account, with initial balance 12000, that transfer 2000 to a mortgage payment and then apply a 5% interest. T1 start T1 B old=12000 new=10000 T1 M old=0 new=2000 T1 commit T2 start T2 B old=10000 new=10500 T2 commit Suppose the database system crashes just before log record 7 is written. When the system is restarted, which one statement is true of the recovery procedure? |
| i ➥ We must redo log record 6 to set B to 10500. |
| ii ➥ We must undo log record 6 to set B to 10000 and then redo log records 2 and 3. |
| iii ➥ We need not redo log records 2 and 3 because transaction T1 has committed. |
| iv ➥ We can apply redo and undo operations in arbitrary order because they are idempotent. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Transactions | Help-Line |
| Q21➡ | Database management system For each element in a set of size 2n, an unbiased coin is tossed. The 2n coin tosses are independent. An element is chosen if the corresponding coin toss were head. The probability that exactly n elements are chosen is: |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Probability | Help-Line |
| Q22➡ Engineering mathematics Let E, F and G be finite sets. Let X = (E ∩ F) – (F ∩ G) and Y = (E – (E ∩ G)) – (E – F). Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ X ⊂ Y |
| ii ➥ X ⊃ Y |
| iii ➥ X = Y |
| iv ➥ X – Y ≠ ∅ and Y – X ≠ ∅ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sets and relations | Help-Line |
| Q23➡ | Engineering mathematics Fis an n×n real matrix. b is an n×1 real vector. Suppose there are two n×1 vectors, u and v such that, u≠v and Fu=b, Fv=b. Which one of the following statements is false? |
| i ➥ Determinant of F is zero |
| ii ➥ There are an infinite number of solutions to Fx=b |
| iii ➥ There is an x≠0 such that Fx=0 |
| iv ➥ F must have two identical rows |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear algebra | Help-Line |
| Q24➡ | Engineering mathematics Given a set of elements N = {1, 2, …, n} and two arbitrary subsets A⊆N and B⊆N, how many of the n! permutations π from N to N satisfy min(π(A)) = min(π(B)), where min(S) is the smallest integer in the set of integers S, and π(S) is the set of integers obtained by applying permutation π to each element of S? |
| i ➥ (n-|A ∪ B|) |A| |B| |
| ii ➥ (|A|2+|B|2)n2 |
| iii ➥ n!(|A∩B|/|A∪B|) |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Combinatorics | Help-Line |
| Q25➡ | Engineering mathematics Let S = {1, 2, 3, …., m}, m>3. Let x1, x2,….xn be the subsets of S each of size 3. Define a function f from S to the set of natural numbers as, f(i) is the number of sets of Xj that contain the element i. That is f(i) = |
| i ➥ 3m |
| ii ➥ 3n |
| iii ➥ 2m+1 |
| iv ➥ 2n+1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sets and functions | Help-Line |
| Q26➡ | Engineering mathematics Which one of the first order predicate calculus statements given below correctly express the following English statement? Tigers and lions attack if they are hungry or threatened. |
| i ➥ ∀x [(tiger(x) ∧ lion(x)) → {(hungry(x) ∨ threatened(x)) → attacks(x)}] |
| ii ➥ ∀x [(tiger(x) ∨ lion(x)) → {(hungry(x) ∨ threatened(x)) ∧ attacks(x)}] |
| iii ➥ ∀x [(tiger(x) ∨ lion(x)) → {(attacks(x) → (hungry (x)) ∨ threatened (x))}] |
| iv ➥ ∀x [(tiger(x) ∨ lion(x)) → {(hungry(x) ∨ threatened(x)) → attacks(x)}] |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Propositional logic | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | Engineering mathematics Consider the following propositional statements: P1 : ((A ∧ B) → C)) ≡ ((A → C) ∧ (B → C)) P2 : ((A ∨ B) → C)) ≡ ((A → C) ∨ (B → C)) Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ P1 is a tautology, but not P2 |
| ii ➥ P2 is a tautology, but not P1 |
| iii ➥ P1 and P2 are both tautologies |
| iv ➥ Both P1 and P2 are not tautologies |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Propositional logic | Help-Line |
| Q28➡ | Engineering mathematics A logical binary relation □ ,is defined as follows: 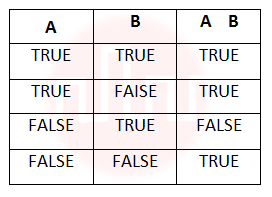 Let ~ be the unary negation (NOT) operator, with higher precedence than □. Which one of the following is equivalent to A∧B ? |
| i ➥ (~A B) |
| ii ➥ ~(A ~B) |
| iii ➥ ~(~A ~B) |
| iv ➥ ~(~ A B) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sets and relations | Help-Line |
| Q29➡ | Theory of computation If s is a string over (0 + 1)* then let n0(s) denote the number of 0’s in s and n1(s) the number of 1’s in s. Which one of the following languages is not regular? |
| i ➥ L = {s ∈ (0+1)* | n0(s) is a 3-digit prime} |
| ii ➥ L = {s ∈ (0+1)* | for every prefix s’ of s,|n0(s’) – n1(s’)| ≤ 2} |
| iii ➥ L = {s ∈ (0+1)* |n0(s) – n1(s)| ≤ 4} |
| iv ➥ L = {s ∈ (0+1)* | n0(s) mod 7 = n1(s) mod 5 = 0} |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Regular language | Help-Line |
| Q30➡ | Theory of computation For S ∈ (0 + 1) * let d(s) denote the decimal value of s (e.g. d(101) = 5). Let L = {s ∈ (0 + 1)* d(s)mod5 = 2 and d(s)mod7 != 4}. Which one of the following statements is true? |
| i ➥ L is recursively enumerable, but not recursive |
| ii ➥ L is recursive, but not context-free |
| iii ➥ L is context-free, but not regular |
| iv ➥ L is regular |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Identity class language | Help-Line |
| Q31➡ | Algorithms Let SHAM3 be the problem of finding a Hamiltonian cycle in a graph G = (V,E) with |V| divisible by 3 and DHAM3 be the problem of determining if a Hamiltonian cycle exists in such graphs. Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ Both DHAM3 and SHAM3 are NP-hard |
| ii ➥ SHAM3 is NP-hard, but DHAM3 is not |
| iii ➥ DHAM3 is NP-hard, but SHAM3 is not |
| iv ➥ Neither DHAM3 nor SHAM3 is NP-hard |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | P-NP | Help-Line |
| Q32➡ | Theory of computation Consider the following statements about the context free grammar G = {S → SS, S → ab, S → ba, S → Ε} I. G is ambiguous II. G produces all strings with equal number of a’s and b’s III. G can be accepted by a deterministic PDA. Which combination below expresses all the true statements about G? |
| i ➥ I only |
| ii ➥ I and III only |
| iii ➥ II and III only |
| iv ➥ I,II and III |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Context free language | Help-Line |
| Q33➡ | Theory of computation Let L1 be a regular language, L2 be a deterministic context-free language and L3 a recursively enumerable, but not recursive, language. Which one of the following statements is false? |
| i ➥ L1 ∩ L2 is a deterministic CFL |
| ii ➥ L3 ∩ L1 is recursive |
| iii ➥ L1 ∪ L2 is context free |
| iv ➥ L1 ∩ L2 ∩ L3 is recursively enumerable |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Identify class language | Help-Line |
| Q34➡ | Theory of computation Consider the regular language L = (111 + 11111)*. The minimum number of states in any DFA accepting this language is: |
| i ➥ 3 |
| ii ➥ 5 |
| iii ➥ 8 |
| iv ➥ 9 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Finite automata | Help-Line |
Q35➡ | Digital logic design 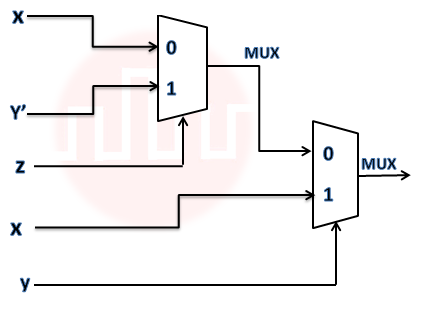 Consider the circuit above. Which one of the following options correctly represents f(x,y,z)? |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Multiplexer | Help-Line |
| Q36➡ | Digital logic design Given two three bit numbers a2a1a0 and b2b1b0 and c, the carry in, the function that represents the carry generate function when these two numbers are added is: |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Carry generator | Help-Line |
| Q37➡ | Digital logic design Consider the circuit in the diagram. The ⊕ operator represents Ex-OR. The D flipflops are initialized to zeroes (cleared). 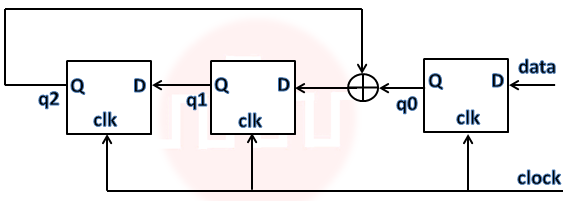 The following data: 100110000 is supplied to the “data” terminal in nine clock cycles. After that the values of q2q1q0 are: |
| i ➥ 000 |
| ii ➥ 001 |
| iii ➥ 010 |
| iv ➥ 101 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sequential circuits | Help-Line |
| Q38➡ | Digital logic design Consider a Boolean function f (w, x, y, z). Suppose that exactly one of its inputs is allowed to change at a time. If the function happens to be true for two input vectors i1 = 〈w1, x1, y1, z1〉 and i2 = 〈w2, x2, y2, z2〉, we would like the function to remain true as the input changes from vectors i1 to i2 (i1 and i2 differ in exactly one bit position), without becoming false momentarily. Let f(w, x, y, z) = ∑(5, 7, 11, 12, 13, 15). Which of the following cube covers of f will ensure that the required property is satisfied? |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | K-map | Help-Line |
| Q39➡ | Digital logic design We consider the addition of two 2’s complement numbers bn-1bn-2…b0 and an-1an-2…a0. A binary adder for adding unsigned binary numbers is used to add the two numbers. The sum is denoted by cn-1cn-2c0 and the carry-out by cout. Which one of the following options correctly identifies the overflow condition? |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Carry generator | Help-Line |
| Q40➡ | Digital logic design Consider numbers represented in 4-bit gray code. Let h3h2h1h0 be the gray code representation of a number n and let g3g2g1g0 be the gray code of (n+1) (modulo 16) value of the number. Which one of the following functions is correct? |
| i ➥ g0(h3h2h1h0) = Σ(1,2,3,6,10,13,14,15) |
| ii ➥ g1(h3h2h1h0) = Σ(4,9,10,11,12,13,14,15) |
| iii ➥ g2(h3h2h1h0) = Σ(2,4,5,6,7,12,13,15) |
| iv ➥ g3(h3h2h1h0) = Σ(0,1,6,7,10,11,12,13) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Number systems | Help-Line |
| Q41➡ | Computer organization A CPU has a five-stage pipeline and runs at 1 GHz frequency. Instruction fetch happens in the first stage of the pipeline. A conditional branch instruction computes the target address and evaluates the condition in the third stage of the pipeline. The processor stops fetching new instructions following a conditional branch until the branch outcome is known. A program executes 109 instructions out of which 20% are conditional branches. If each instruction takes one cycle to complete on average, the total execution time of the program is: |
| i ➥ 92 ns |
| ii ➥ 104 ns |
| iii ➥ 172 ns |
| iv ➥ 184 ns |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | cache | Help-Line |
| Q42➡ | Computer organization A CPU has a five-stage pipeline and runs at 1 GHz frequency. Instruction fetch happens in the first stage of the pipeline. A conditional branch instruction computes the target address and evaluates the condition in the third stage of the pipeline. The processor stops fetching new instructions following a conditional branch until the branch outcome is known. A program executes 109 instructions out of which 20% are conditional branches. If each instruction takes one cycle to complete on average, the total execution time of the program is: |
| i ➥ 1.0 second |
| ii ➥ 1.2 second |
| iii ➥ 1.4 second |
| iv ➥ 1.6 second |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Pipelining | Help-Line |
| Q43➡ | Computer organization Consider a new instruction named branch-on-bit-set (mnemonic bbs). The instruction “bbs reg, pos, label” jumps to label if bit in position pos of register operand reg is one. A register is 32 bits wide and the bits are numbered 0 to 31, bit in position 0 being the least significant. Consider the following emulation of this instruction on a processor that does not have bbs implemented. temp¬reg & mask Branch to label if temp is non-zero. The variable temp is a temporary register. For correct emulation, the variable mask must be generated by: |
| i ➥ mask ← 0×1 □ pos |
| ii ➥ mask ← 0×ffffffff □ pos |
| iii ➥ mask ← pos |
| iv ➥ mask ← 0×f |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Machine instructions | Help-Line |
| Q44➡ | Computer networks Station A uses 32 byte packets to transmit messages to Station B using a sliding window protocol. The round trip delay between A and B is 80 milliseconds and the bottleneck bandwidth on the path between A and B is 128 kbps. What is the optimal window size that A should use? |
| i ➥ 20 |
| ii ➥ 40 |
| iii ➥ 160 |
| iv ➥ 320 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sliding window protocol | Help-Line |
| Q45➡ | Computer networks Two computers C1 and C2 are configured as follows. C1 has IP address 203.197.2.53 and netmask 255.255.128.0. C2 has IP address 203.197.75.201 and netmask 255.255.192.0. Which one of the following statements is true? |
| i ➥ C1 and C2 both assume they are on the same network |
| ii ➥ C2 assumes C1 is on same network, but C1 assumes C2 is on a different network |
| iii ➥ C1 assumes C2 is on same network, but C2 assumes C1 is on a different network |
| iv ➥ C1 and C2 both assume they are on different networks |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | IP address | Help-Line |
| Q46➡ | Computer networks Station A needs to send a message consisting of 9 packets to Station B using a sliding window (window size 3) and go-back-n error control strategy. All packets are ready and immediately available for transmission. If every 5th packet that A transmits gets lost (but no acks from B ever get lost), then what is the number of packets that A will transmit for sending the message to B? |
| i ➥ 12 |
| ii ➥ 14 |
| iii ➥ 16 |
| iv ➥ 18 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sliding protocol | Help-Line |
| Q47➡ | Algorithms Consider the following graph: 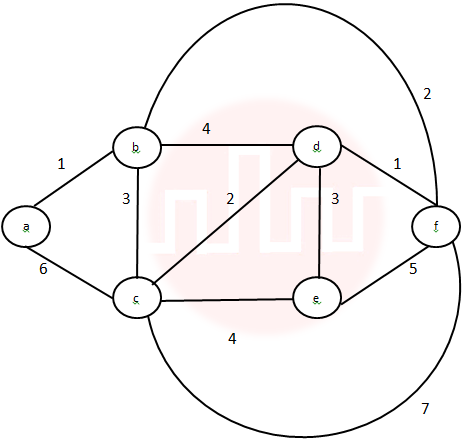 Which one of the following cannot be the sequence of edges added, in that order, to a minimum spanning tree using Kruskal’s algorithm? |
| i ➥ (a—b),(d—f),(b—f),(d—c),(d—e) |
| ii ➥ (a—b),(d—f),(d—c),(b—f),(d—e) |
| iii ➥ (d—f),(a—b),(d—c),(b—f),(d—e) |
| iv ➥ (d—f),(a—b),(b—f),(d—e),(d—c) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Minimum spanning tree | Help-Line |
| Q48➡ | Data structures Let T be a depth first search tree in an undirected graph G. Vertices u and n are leaves of this tree T. The degrees of both u and v in G are at least 2. Which one of the following statements is true? |
| i ➥ There must exist a vertex w adjacent to both u and v in G |
| ii ➥ There must exist a vertex w whose removal disconnects u and v in G |
| iii ➥ There must exist a cycle in G containing u and v |
| iv ➥ There must exist a cycle in G containing u and all its neighbours in G |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graphs | Help-Line |
| Q49➡ | Data structures An implementation of a queue Q, using two stacks S1 and S2, is given below: void insert(Q, x) { push (S1, x); } void delete(Q){ if(stack-empty(S2)) then if(stack-empty(S1)) then { print(“Q is empty”); return; } else while (!(stack-empty(S1))){ x=pop(S1); push(S2,x); } x=pop(S2); } Let n insert and m (<=n) delete operations be performed in an arbitrary order on an empty queue Q. Let x and y be the number of push and pop operations performed respectively in the process. Which one of the following is true for all m and n? |
| i ➥ n+m ≤ x < 2n and 2m ≤ y ≤ n+m |
| ii ➥ n+m ≤ x< 2n and 2m ≤y ≤ 2n |
| iii ➥ 2m ≤ x< 2n and 2m ≤ y ≤ n+m |
| iv ➥ 2m ≤ x < 2n and 2m ≤ y ≤ 2n |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Stack and Queue | Help-Line |
| Q50➡ | Algorithms A set X can be represented by an array x[n] as follows:  Consider the following algorithm in which x,y and z are Boolean arrays of size n: Consider the following algorithm in which x,y and z are Boolean arrays of size n:algorithm zzz(x[] , y[], z []) { int i; for (i=O; i<n; ++i) z[i] = (x[i] ^ ~y[i]) V (~x[i] ^ y[i]) } The set Z computed by the algorithm is: |
| i ➥ (X ∪ Y) |
| ii ➥ (X ∩ Y) |
| iii ➥ (X-Y) ∩ (Y-X) |
| iv ➥ (X-Y) ∪ (Y-X) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Identify Function | Help-Line |
| Q51➡ | Algorithms Consider the following recurrence: Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ T(n) = θ(loglogn) |
| ii ➥ T(n) = θ(logn) |
| iii ➥ T(n) = θ(√n) |
| iv ➥ T(n) = θ(n) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Time Complexity | Help-Line |
| Q52➡ | Algorithms The median of n elements can be found in O(n) time. Which one of the following is correct about the complexity of quick sort, in which median is selected as pivot? |
| i ➥ θ(n) |
| ii ➥ θ(nlog n) |
| iii ➥ θ(n2) |
| iv ➥ θ(n3) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Time Complexity | Help-Line |
| Q53➡ | Algorithms Consider the following C-function in which a[n] and b[m] are two sorted integer arrays and c[n + m] be another integer array. void xyz(int a[], int b [], int c[]) { int i, j, k; i = j = k = O; while ((i<n) && (j<m)) if (a[i] < b[j]) c[k++] = a[i++]; else c[k++] = b[j++]; } Which of the following condition(s) hold(s) after the termination of the while loop? (GATE CS 2006) (i) j < m, k = n+j-1, and a[n-1] < b[j] if i = n (ii) i < n, k = m+i-1, and b[m-1] <= a[i] if j = m |
| i ➥ only (i) |
| ii ➥ only (ii) |
| iii ➥ either (i) or (ii) but not both |
| iv ➥ neither (i) nor (ii) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Identify Function | Help-Line |
| Q54➡ | Algorithms Given two arrays of numbers a1, a2, a3,…an and b1, b2, .. bn where each number is 0 or 1, the fastest algorithm to find the largest span(i, j) such that ai + ai+1, ….aj = bi + bi+1, .. bj. or report that there is not such span, |
| i ➥ Takes O(3n) and Ω(2n) time if hashing is permitted |
| ii ➥ Takes O(n3) and Ω(n2.5) time in the key comparison model |
| iii ➥ Takes θ(n) time and space |
| iv ➥ Takes O(√n) time only if the sum of the 2n elements is an even number |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Time Complexity | Help-Line |
| Q55➡ | Compiler design Consider the following code written in a pass-by-reference language like FORTRAN and these statements about the code. subroutine swap(ix,iy) it = ix L1 : ix = iy L2 : iy = it end ia = 3 ib = 8 call swap (ia, 1b+5) print *, ia, ib end S1: The compiler will generate code to allocate a temporary nameless cell, initialize it to 13, and pass the address of the cell swap S2: On execution the code will generate a runtime error on line L1 S3: On execution the code will generate a runtime error on line L2 S4: The program will print 13 and 8 S5: The program will print 13 and -2 Exactly the following set of statement(s) is correct: |
| i ➥ S1 is false and S2 is false |
| ii ➥ S1 is false and S2 is true |
| iii ➥ S1 is true and S2 is false |
| iv ➥ S1 is true and S2 is false |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Code optimization | Help-Line |
| Q56➡ | Programming Consider the following code written in a pass-by-reference language like FORTRAN and these statements about the code. subroutine swap(ix,iy) it = ix L1 : ix = iy L2 : iy = it end ia = 3 ib = 8 call swap (ia, 1b+5) print *, ia, ib end S1: The compiler will generate code to allocate a temporary nameless cell, initialize it to 13, and pass the address of the cell swap S2: On execution the code will generate a runtime error on line L1 S3: On execution the code will generate a runtime error on line L2 S4: The program will print 13 and 8 S5: The program will print 13 and -2 Exactly the following set of statement(s) is correct: |
| i ➥ S1 and S2 |
| ii ➥ S1 and S4 |
| iii ➥ S3 |
| iv ➥ S1 and S5 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | C Programming | Help-Line |
| Q57➡ | Programming Consider this C code to swap two integers and these five statements after it: void swap(int *px, int *py) { *px = *px – *py; *py = *px + *py; *px = *py – *px; } S1: will generate a compilation error S2: may generate a segmentation fault at runtime depending on the arguments passed S3: correctly implements the swap procedure for all input pointers referring to integers stored in memory locations accessible to the process S4: implements the swap procedure correctly for some but not all valid input pointers S5: may add or subtract integers and pointers. |
| i ➥ S1 |
| ii ➥ S1 and S3 |
| iii ➥ S2 and S4 |
| iv ➥ S2 and S5 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | C programming | Help-Line |
| Q58➡ | Compiler design Consider the following grammar: S → FR R → S | ε F → id In the predictive parser table, M, of the grammar the entries M[S, id] and M[R, $] respectively. |
| i ➥ {S → FR} and {R → ε} |
| ii ➥ {S → FR} and { } |
| iii ➥ {S → FR} and {R → *S} |
| iv ➥ {F → id} and {R → ε} |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Parsers | Help-Line |
| Q59➡ | Compiler design Consider the following translation scheme. S → ER R → *E{print(“*”);}R | ε E → F + E {print(“+”);} | F F → (S) | id {print(id.value);} Here id is a token that represents an integer and id.value represents the corresponding integer value. For an input ‘2 * 3 + 4’, this translation scheme prints |
| i ➥ 2 * 3 + 4 |
| ii ➥ 2 * +3 4 |
| iii ➥ 2 3 * 4 + |
| iv ➥ 2 3 4+* |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Syntax Directed Translation | Help-Line |
| Q60➡ | Compiler design Consider the following C code segment. for (i = 0, i<n; i++) { for (j=0; j<n; j++) { if (i%2) { x += (4*j + 5*i); y += (7 + 4*j); } } } Which one of the following is false? |
| i ➥ The code contains loop invariant computation |
| ii ➥ There is scope of common sub-expression elimination in this code |
| iii ➥ There is scope of strength reduction in this code |
| iv ➥ There is scope of dead code elimination in this code |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Code Optimization | Help-Line |
| Q61➡ | The atomic fetch-and-set x, y instruction unconditionally sets the memory location x to 1 and fetches the old value of x n y without allowing any intervening access to the memory location x. consider the following implementation of P and V functions on a binary semaphore S. void P (binary_semaphore *s) { unsigned y; unsigned *x = &(s->value); do { fetch-and-set x, y; } while (y); } void V (binary_semaphore *s) { S->value = 0; } Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ The implementation may not work if context switching is disabled in P |
| ii ➥ Instead of using fetch-and-set, a pair of normal load/store can be used |
| iii ➥ The implementation of V is wrong |
| iv ➥ The code does not implement a binary semaphore |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q62➡ | A CPU generates 32-bit virtual addresses. The page size is 4 KB. The processor has a translation look-aside buffer (TLB) which can hold a total of 128 page table entries and is 4-way set associative. The minimum size of the TLB tag is: |
| i ➥ 11 bits |
| ii ➥ 13 bits |
| iii ➥ 15 bits |
| iv ➥ 20 bits |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Virtual Memory | Help-Line |
| Q63➡ | A computer system supports 32-bit virtual addresses as well as 32-bit physical addresses. Since the virtual address space is of the same size as the physical address space, the operating system designers decide to get rid of the virtual memory entirely. Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ Efficient implementation of multi-user support is no longer possible |
| ii ➥ The processor cache organization can be made more efficient now |
| iii ➥ Hardware support for memory management is no longer needed |
| iv ➥ CPU scheduling can be made more efficient now |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Virtual Memory | Help-Line |
| Q64➡ | Consider three processes (process id 0, 1, 2 respectively) with compute time bursts 2, 4 and 8 time units. All processes arrive at time zero. Consider the longest remaining time first (LRTF) scheduling algorithm. In LRTF ties are broken by giving priority to the process with the lowest process id. The average turnaround time is: |
| i ➥ 13 units |
| ii ➥ 14 units |
| iii ➥ 15 units |
| iv ➥ 16 units |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process Scheduling | Help-Line |
| Q65➡ | Consider three processes, all arriving at time zero, with total execution time of 10, 20 and 30 units, respectively. Each process spends the first 20% of execution time doing I/O, the next 70% of time doing computation, and the last 10% of time doing I/O again. The operating system uses a shortest remaining compute time first scheduling algorithm and schedules a new process either when the running process gets blocked on I/O or when the running process finishes its compute burst. Assume that all I/O operations can be overlapped as much as possible. For what percentage of time does the CPU remain idle? |
| i ➥ 0% |
| ii ➥ 10.6% |
| iii ➥ 30.0% |
| iv ➥ 89.4% |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process Scheduling | Help-Line |
| Q66➡ | Consider the following snapshot of a system running n processes. Process i is holding xi instances of a resource R, 1 ≤ i ≤ n. Currently, all instances of R are occupied. Further, for all i, process i has placed a request for an additional yi instances while holding the xi instances it already has. There are exactly two processes p and q such that yp = yq = 0. Which one of the following can serve as a necessary condition to guarantee that the system is not approaching a deadlock? |
| i ➥ min (xp, xq) < maxk≠p,qyk |
| ii ➥ xp + xq ≥ mink≠p,qyk |
| iii ➥ max (xp, xq) > 1 |
| iv ➥ min (xp, xq) > 1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Deadlock | Help-Line |
| Q67➡ | Consider the relation account (customer, balance) where customer is a primary key and there are no null values. We would like to rank customers according to decreasing balance. The customer with the largest balance gets rank 1. ties are not broke but ranks are skipped: if exactly two customers have the largest balance they each get rank 1 and rank 2 is not assigned Query1: select A.customer, count(B.customer) from account A, account B where A.balance <=B.balance group by A.customer Query2: select A.customer, 1+count(B.customer) from account A, account B where A.balance < B.balance group by A.customer Consider these statements about Query1 and Query2. 1. Query1 will produce the same row set as Query2 for some but not all databases. 2. Both Query1 and Query2 are correct implementation of the specification 3. Query1 is a correct implementation of the specification but Query2 is not 4. Neither Query1 nor Query2 is a correct implementation of the specification 5. Assigning rank with a pure relational query takes less time than scanning in decreasing balance order assigning ranks using ODBC. Which two of the above statements are correct? |
| i ➥ 2 and 5 |
| ii ➥ 1 and 3 |
| iii ➥ 1 and 4 |
| iv ➥ 3 and 5 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | SQL | Help-Line |
| Q68➡ | Consider the relation “enrolled(student, course)” in which (student, course) is the primary key, and the relation “paid(student, amount)” where student is the primary key. Assume no null values and no foreign keys or integrity constraints. Given the following four queries: Query1: select student from enrolled where student in (select student from paid) Query2: select student from paid where student in (select student from enrolled) Query3: select E.student from enrolled E, paid P where E.student = P.student Query4: select student from paid where exists (select * from enrolled where enrolled.student = paid.student) Which one of the following statements is correct? |
| i ➥ All queries return identical row sets for any database. |
| ii ➥ Query2 and Query4 return identical row sets for all databases but there exist databases for which Query1 and Query2 return different row sets. |
| iii ➥ There exist databases for which Query3 returns strictly fewer rows than Query2. |
| iv ➥ There exist databases for which Query4 will encounter an integrity violation at runtime. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | SQL | Help-Line |
| Q69➡ | Consider the relation enrolled(student, course) in which (student, course) is the primary key, and the relation paid(student, amount), where student is the primary key. Assume no null values and no foreign keys or integrity constraints. Assume that amounts 6000, 7000, 8000, 9000 and 10000 were each paid by 20% of the students. Consider these query plans (Plan 1 on left, Plan 2 on right) to “list all courses taken by students who have paid more than x”. 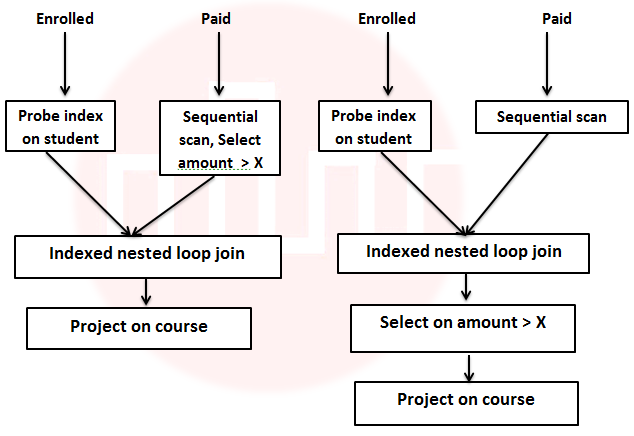 A disk seek takes 4ms, disk data transfer bandwidth is 300 MB/s and checking a tuple to see if amount is greater than x takes 10 micro-seconds. Which of the following statements is correct? |
| i ➥ Plan 1 and Plan 2 will not output identical row sets for all databases. |
| ii ➥ A course may be listed more than once in the output of Plan 1 for some databases. |
| iii ➥ For x = 5000, Plan 1 executes faster than Plan 2 for all databases. |
| iv ➥ For x = 9000, Plan I executes slower than Plan 2 for all databases. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | SQL | Help-Line |
| Q70➡ | The following functional dependencies are given: AB CD, AF D, DE F, C G , F E, G A Which one of the following options is false? |
| i ➥ {CF}+ = {ACDEFG} |
| ii ➥ {BG}+ = {ABCDG} |
| iii ➥ {AF}+ = {ACDEFG} |
| iv ➥ {AB}+ = {ABCDFG} |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Functional Dependency | Help-Line |
| Q71➡ | The 2n vertices of a graph G corresponds to all subsets of a set of size n, for n >= 6 . Two vertices of G are adjacent if and only if the corresponding sets intersect in exactly two elements. The number of vertices of degree zero in G is: |
| i ➥ 1 |
| ii ➥ n |
| iii ➥ n+1 |
| iv ➥ 2n |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graph Theory | Help-Line |
| Q72➡ | The 2n vertices of a graph G corresponds to all subsets of a set of size n, for n >= 6. Two vertices of G are adjacent if and only if the corresponding sets intersect in exactly two elements. The maximum degree of a vertex in G is: |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ 2n-2 |
| iii ➥ 2n-3 × 3 |
| iv ➥ 2n-1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graph Theory | Help-Line |
| Q73➡ | The 2n vertices of a graph G corresponds to all subsets of a set of size n, for n >= 6. Two vertices of G are adjacent if and only if the corresponding sets intersect in exactly two elements. The number of connected components in G is: |
| i ➥ n |
| ii ➥ n+2 |
| iii ➥ 2n/2 |
| iv ➥ 2n / n |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graph Theory | Help-Line |
| Q74➡ | Consider two cache organizations: The first one is 32 KB 2-way set associative with 32-byte block size. The second one is of the same size but direct mapped. The size of an address is 32 bits in both cases. A 2-to-1 multiplexer has a latency of 0.6 ns while a kbit comparator has a latency of k/10 ns. The hit latency of the set associative organization is h1 while that of the direct mapped one is h2. The value of h1 is: |
| i ➥ 2.4 ns |
| ii ➥ 2.3 ns |
| iii ➥ 1.8 ns |
| iv ➥ 1.8 ns |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache | Help-Line |
| Q75➡ | Consider two cache organizations: The first one is 32 KB 2-way set associative with 32-byte block size. The second one is of the same size but direct mapped. The size of an address is 32 bits in both cases. A 2-to-1 multiplexer has a latency of 0.6 ns while a kbit comparator has a latency of k/10 ns. The hit latency of the set associative organization is h1 while that of the direct mapped one is h2. The value of h2 is: |
| i ➥ 2.4 ns |
| ii ➥ 2.3 ns |
| iii ➥ 1.8 ns |
| iv ➥ 1.7 ns |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache | Help-Line |
| Q76➡ | A 3-ary max heap is like a binary max heap, but instead of 2 children, nodes have 3 children. A 3-ary heap can be represented by an array as follows: The root is stored in the first location, a[0], nodes in the next level, from left to right, is stored from a[1] to a[3]. The nodes from the second level of the tree from left to right are stored from a[4] location onward. An item x can be inserted into a 3-ary heap containing n items by placing x in the location a[n] and pushing it up the tree to satisfy the heap property. Which one of the following is a valid sequence of elements in an array representing 3-ary max heap? |
| i ➥ 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9 |
| ii ➥ 9, 6, 3, 1, 8, 5 |
| iii ➥ 9, 3, 6, 8, 5, 1 |
| iv ➥ 9, 5, 6, 8, 3, 1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Heap Tree | Help-Line |
| Q77➡ | A 3-ary max heap is like a binary max heap, but instead of 2 children, nodes have 3 children. A 3-ary heap can be represented by an array as follows: The root is stored in the first location, a[0], nodes in the next level, from left to right, is stored from a[1] to a[3]. The nodes from the second level of the tree from left to right are stored from a[4] location onward. An item x can be inserted into a 3-ary heap containing n items by placing x in the location a[n] and pushing it up the tree to satisfy the heap property. Suppose the elements 7, 2, 10 and 4 are inserted, in that order, into the valid 3- ary max heap found in the above question, Which one of the following is the sequence of items in the array representing the resultant heap? |
| i ➥ 10, 7, 9, 8, 3, 1, 5, 2, 6, 4 |
| ii ➥ 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 |
| iii ➥ 10, 9, 4, 5, 7, 6, 8, 2, 1, 3 |
| iv ➥ 10, 8, 6, 9, 7, 2, 3, 4, 1, 5 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Heap Tree | Help-Line |
| Q78➡ | Barrier is a synchronization construct where a set of processes synchronizes globally i.e. each process in the set arrives at the barrier and waits for all others to arrive and then all processes leave the barrier. Let the number of processes in the set be three and S be a binary semaphore with the usual P and V functions. Consider the following C implementation of a barrier with line numbers shown on left. void barrier (void) { 1: P(S); 2: process_arrived++; 3. V(S); 4: while (process_arrived !=3); 5: P(S); 6: process_left++; 7: if (process_left==3) { 8: process_arrived = 0; 9: process_left = 0; 10: } 11: V(S); } The variables process_arrived and process_left are shared among all processes and are initialized to zero. In a concurrent program all the three processes call the barrier function when they need to synchronize globally. The above implementation of barrier is incorrect. Which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ The barrier implementation is wrong due to the use of binary semaphore S |
| ii ➥ The barrier implementation may lead to a deadlock if two barriers in invocations are used in immediate succession |
| iii ➥ Lines 6 to 10 need not be inside a critical section |
| iv ➥ The barrier implementation is correct if there are only two processes instead of three |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process Synchronization | Help-Line |
| Q79➡ | Barrier is a synchronization construct where a set of processes synchronizes globally i.e. each process in the set arrives at the barrier and waits for all others to arrive and then all processes leave the barrier. Let the number of processes in the set be three and S be a binary semaphore with the usual P and V functions. Consider the following C implementation of a barrier with line numbers shown on left. void barrier (void) { 1: P(S); 2: process_arrived++; 3. V(S); 4: while (process_arrived !=3); 5: P(S); 6: process_left++; 7: if (process_left==3) { 8: process_arrived = 0; 9: process_left = 0; 10: } 11: V(S); } The variables process_arrived and process_left are shared among all processes and are initialized to zero. In a concurrent program all the three processes call the barrier function when they need to synchronize globally. Which one of the following rectifies the problem in the implementation? |
| i ➥ Lines 6 to 10 are simply replaced by process_arrived– |
| ii ➥ At the beginning of the barrier the first process to enter the barrier waits until process_arrived becomes zero before proceeding to execute P(S). |
| iii ➥ Context switch is disabled at the beginning of the barrier and re-enabled at the end. |
| iv ➥ The variable process_left is made private instead of shared. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Procss Synchronization | Help-Line |
| Q80➡ | A CPU has a 32 KB direct mapped cache with 128-byte block size. Suppose A is a twodimensional array of size 512×512 with elements that occupy 8-bytes each. Consider the following two C code segments, P1 and P2. P1: for (i=0; i<512; i++) { for (j=0; j<512; j++) { x += A[i][j]; } } P2: for (i=0; i<512; i++) { for (j=0; j<512; j++) { x += A[j][i]; } } P1 and P2 are executed independently with the same initial state, namely, the array A is not in the cache and i, j, x are in registers. Let the number of cache misses experienced by P1 be M1 and that for P2 be M2 . The value of M1 is: |
| i ➥ 0 |
| ii ➥ 2048 |
| iii ➥ 16384 |
| iv ➥ 262144 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache | Help-Line |
| Q81➡ | A CPU has a 32 KB direct mapped cache with 128-byte block size. Suppose A is a twodimensional array of size 512×512 with elements that occupy 8-bytes each. Consider the following two C code segments, P1 and P2. P1: for (i=0; i<512; i++) { for (j=0; j<512; j++) { x += A[i][j]; } } P2: for (i=0; i<512; i++) { for (j=0; j<512; j++) { x += A[j][i]; } } P1 and P2 are executed independently with the same initial state, namely, the array A is not in the cache and i, j, x are in registers. Let the number of cache misses experienced by P1 be M1 and that for P2 be M2 . The value of the ratio M1/M2 is: |
| i ➥ 0 |
| ii ➥ 1/16 |
| iii ➥ 1/8 |
| iv ➥ 16 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache | Help-Line |
| Q82➡ | Consider the diagram shown below where a number of LANs are connected by (transparent) bridges. In order to avoid packets looping through circuits in the graph, the bridges organize themselves in a spanning tree. First, the root bridge is identified as the bridge with the least serial number. Next, the root sends out (one or more) data units to enable the setting up of the spanning tree of shortest paths from the root bridge to each bridge. Each bridge identifies a port (the root port) through which it will forward frames to the root bridge. Port conflicts are always resolved in favour of the port with the lower index value. When there is a possibility of multiple bridges forwarding to the same LAN (but not through the root port), ties are broken as follows: bridges closest to the root get preference and between such bridges, the one with the lowest serial number is preferred. 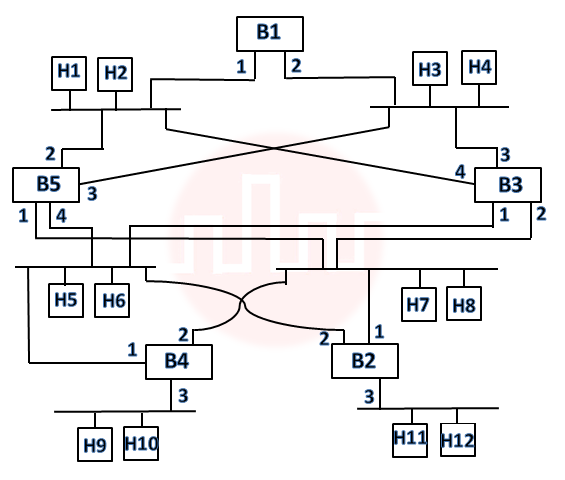 For the given connection of LANs by bridges, which one of the following choices represents the depth first traversal of the spanning tree of bridges? |
| i ➥ B1, B5, B3, B4, B2 |
| ii ➥ B1, B3, B5, B2, B4 |
| iii ➥ B1, B3, B5, B2, B4 |
| iv ➥ B1, B3, B4, B5, B2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Bridges | Help-Line |
| Q83➡ | Consider the diagram shown below where a number of LANs are connected by (transparent) bridges. In order to avoid packets looping through circuits in the graph, the bridges organize themselves in a spanning tree. First, the root bridge is identified as the bridge with the least serial number. Next, the root sends out (one or more) data units to enable the setting up of the spanning tree of shortest paths from the root bridge to each bridge. Each bridge identifies a port (the root port) through which it will forward frames to the root bridge. Port conflicts are always resolved in favour of the port with the lower index value. When there is a possibility of multiple bridges forwarding to the same LAN (but not through the root port), ties are broken as follows: bridges closest to the root get preference and between such bridges, the one with the lowest serial number is preferred. 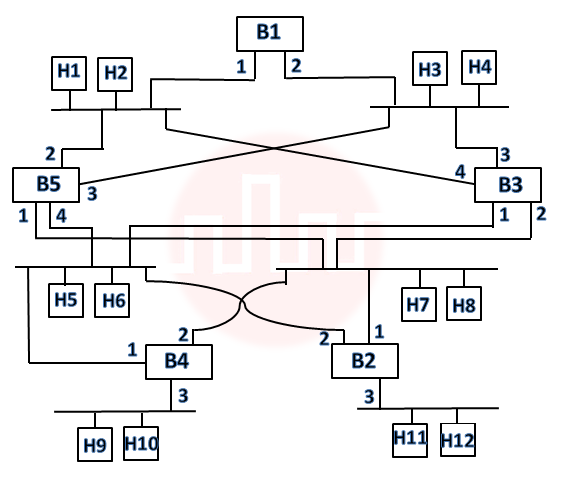 For the given connection of LANs by bridges, which one of the following choices represents the depth first traversal of the spanning tree of bridges? |
i ➥  |
ii ➥ 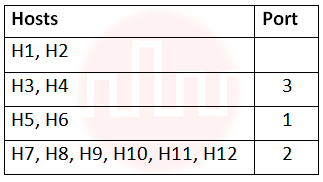 |
iii ➥ 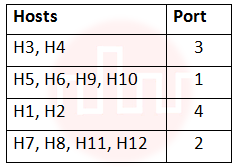 |
iv ➥ 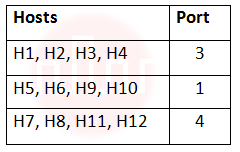 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Bridges | Help-Line |
| Q84➡ | Which one of the following grammars generates the language L = {aibj | i≠j}? |
| i ➥ S→AC|CB C→aCb|a|b A→aA|ϵ B→Bb|ϵ |
| ii ➥ S→aS|Sb|a|b |
| iii ➥ S→AC|CB C→aCb|ϵ A→aA|ϵ B→Bb|ϵ |
| iv ➥ S→AC|CB C→aCb|ϵ A→aA|a B→Bb|b |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Grammar | Help-Line |
| Q85➡ | In the correct grammar of above question, what is the length of the derivation (number of steps starting from S) to generate the string albm with l≠m? |
| i ➥ max(l,m)+2 |
| ii ➥ l+m+2 |
| iii ➥ l+m+3 |
| iv ➥ max(l, m)+3 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Grammar | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
