Methods of Teaching- Teaching Aptitude Questions and Answers
| Q1➡ |Methods of Teaching Maximum participation of students during teaching is possible through |
| i ➥ Inductive method |
| ii ➥ Textbook method |
| iii ➥ Lecture method |
| iv ➥ Demonstration method |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q2➡ |Methods of Teaching Which one of the following is the best method of teaching ? |
| i ➥ Question-Answer method |
| ii ➥ Demonstration method |
| iii ➥ Discussion method |
| iv ➥ Lecture method |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q3➡ |Methods of Teaching Which one of the following is the best method of teaching? |
| i ➥ Narration |
| ii ➥ Demonstration |
| iii ➥ Discussion |
| iv ➥ Lecture |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q4➡ |Methods of Teaching Which combination of methods of teaching is likely to optimize learning? |
| i ➥ Lecturing, demonstrations and PowerPoint based presentations |
| ii ➥ Interactive lecture sessions followed by buzz sessions, brainstorming and projects |
| iii ➥ Interactive discussions, planned lectures and PowerPoint based presentations |
| iv ➥ Lecturing, discussions and seminar method |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q5➡ |Methods of Teaching The best way for providing value education is through |
| i ➥ Mentoring/reflective sessions on values |
| ii ➥ Seminars/symposium on values |
| iii ➥ Lecture/discourses on values |
| iv ➥ Discussions on scriptural texts |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q6➡ |Methods of Teaching In a classroom, a communicator’s trust level is determined by: |
| i ➥ Eye contact |
| ii ➥ The use of abstract concepts |
| iii ➥ The change of voice level |
| iv ➥ The use of hyperbole |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q7➡ |Methods of Teaching In which teaching method learner’s participation is made optimal and proactive? |
| i ➥ Project method |
| ii ➥ Brainstorming session method |
| iii ➥ Buzz session method |
| iv ➥ Discussion method |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q8➡ |Methods of Teaching Which of the following statement is not correct? |
| i ➥ During Lecture Method students are passive |
| ii ➥ Lecture Method is one way process |
| iii ➥ Lecture Method can develop knowledge |
| iv ➥ Lecture Method can develop reasoning |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q9➡ |Methods of Teaching The first Indian chronicler of Indian history was: |
| i ➥ Kalhan |
| ii ➥ Huan Tsang |
| iii ➥ Fahiyan |
| iv ➥ Megasthanese |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q10➡ |Methods of Teaching Maximum participation of students is possible in teaching through: |
| i ➥ text book method |
| ii ➥ audio-visual aids |
| iii ➥ lecture method |
| iv ➥ discussion method |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q11➡ |Methods of Teaching Which among the following gives more freedom to the learner to interact? |
| i ➥ Viewing country-wide classroom programme on TV |
| ii ➥ Lectures by experts |
| iii ➥ Small group discussion |
| iv ➥ Use of film |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q12➡ |Methods of Teaching Moral values can be effectively inculcated among the students when the teacher |
| i ➥ talks of Gods and Goddesses |
| ii ➥ tells stories of great persons |
| iii ➥ himself practices them |
| iv ➥ frequently talks about values |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q13➡ |Methods of Teaching The best method of teaching is to |
| i ➥ initiate a discussion and participate in it |
| ii ➥ suggest good reference material |
| iii ➥ ask students to read books |
| iv ➥ impart information |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q14➡ |Methods of Teaching Discussion Method can be used when : |
| i ➥ The topic is difficult |
| ii ➥ The topic is very difficult |
| iii ➥ The topic is easy |
| iv ➥ All |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q15➡ |Methods of Teaching To organize discussion method in teaching effectively, which of the following conditions should be met? (a) Topic be easy (b) Topic be declared in advance (c) Topic of common interest (d) Availability of more than one teacher (e) language facility of participants Select appropriate answer from the options given below |
| i ➥ (c), (d) and (e) |
| ii ➥ (a), (b) and (e) |
| iii ➥ (a), (b) and (c) |
| iv ➥ (b), (c) and (e) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q16➡ |Methods of Teaching In the two lists given below, List I provides the list of teaching methods, while List II indicates the factors helpful in rendering them effective. Match the two lists and choose the correct answer from the code given below.  |
| i ➥ (iv) (iii) (ii) (i) |
| ii ➥ (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) |
| iii ➥ (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) |
| iv ➥ (iii) (i) (ii) (iv) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q17➡ |Methods of Teaching In the two sets given below Set – I indicates methods of teaching while Set – II provides the basic requirements for success/effectiveness. Match the two sets and indicate your answer by choosing from the code : 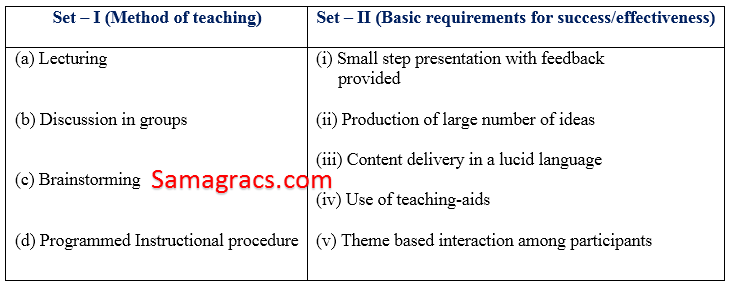 |
| i ➥ (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv) |
| ii ➥ (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(v) |
| iii ➥ (a)-(iii), (b)-(v), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i) |
| iv ➥ (a)-(iv), (b)-(ii), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q18➡ |Methods of Teaching |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q19➡ |Methods of Teaching |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q20➡ |Methods of Teaching |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| Q1➡ |Methods of Teaching |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
UGC NET Paper 1 Subjects And Topic Wise Previous Question papers
| Unit -I Teaching Aptitude Questions and Answers ⇝ Methods of Teaching ⇝Teaching Aids ⇝Teaching Theory ⇝Evaluation System ⇝Factors Affecting teaching ⇝learner’s Characteristics ⇝Teaching Nature ⇝Modes of Learning ⇝Levels of Teaching ⇝Teaching Objective ⇝Teaching Characteristics Teaching Basic Requirements |
| Unit -II Research Aptitude Questions and Answers Research Type Methods of Research Steps of Research Thesis writing Research Ethics Paper Artical workshop seminar conference symposium |
| Unit-III Comprehension A Passage to be set with questions to be answered. |
| Unit-IV Communication Questions and Answers Communication. Nature. Characteristics. Types of Communications. Barriers. Effective Classroom Communications. |
| Unit-V Reasoning Number Series Latter Serise Codes Relationships Classifacations |
| Unit-VI Logical Reasoning Understanding the structure of arguments: argument forms, structure of categorical propositions, Mood and Figure, Formal and Informal fallacies, Uses of language, Connotations and denotations of terms, Classical square of opposition. Evaluating and distinguishing deductive and inductive reasoning. Analogies. Venn diagram: Simple and multiple use for establishing validity of arguments. Indian Logic: Means of knowledge. Pramanas: Pratyaksha (Perception), Anumana (Inference), Upamana (Comparison), Shabda (Verbal testimony), Arthapatti (Implication) and Anupalabddhi (Non-apprehension). Structure and kinds of Anumana (inference), Vyapti (invariable relation), Hetvabhasas (fallacies of inference). |
| Unit-VII Data Interpretation Sources, acquisition and classification of Data. Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Graphical representation (Bar-chart, Histograms, Pie-chart, Table-chart and Line-chart) and mapping of Data. Data Interpretation. Data and Governance. |
| Unit- VIII Information and Communication Technology (ICT) ICT: General abbreviations and terminology. Basics of Internet, Intranet, E-mail, Audio and Video-conferencing. Digital initiatives in higher education. ICT and Governance |
| Unit-IX People, Development and Environment Development and environment: Millennium development and Sustainable development goals. – Human and environment interaction: Anthropogenic activities and their impacts on environment. -Environmental issues: Local, Regional and Global; Air pollution, Water pollution, Soil pollution, Noise pollution, Waste (solid, liquid, biomedical, hazardous, electronic), Climate change and its Socio-Economic and Political dimensions. – Impacts of pollutants on human health. – Natural and energy resources: Solar, Wind, Soil, Hydro, Geothermal, Biomass, Nuclear and Forests. -Natural hazards and disasters: Mitigation strategies. -Environmental Protection Act (1986), National Action Plan on Climate Change, International agreements/efforts -Montreal Protocol, Rio Summit, Convention on Biodiversity, Kyoto Protocol, Paris Agreement, International Solar Alliance. |
| Unit-X Higher Education System Institutions of higher learning and education in ancient India. Evolution of higher learning and research in Post Independence India. Oriental, Conventional and Non-conventional learning programmes in India. Professional, Technical and Skill Based education. Value education and environmental education. Policies, Governance, and Administration. |
