Types of Communication UGC NET
Types of Communication
In this tutorial, we will discuss the Types of Communication.
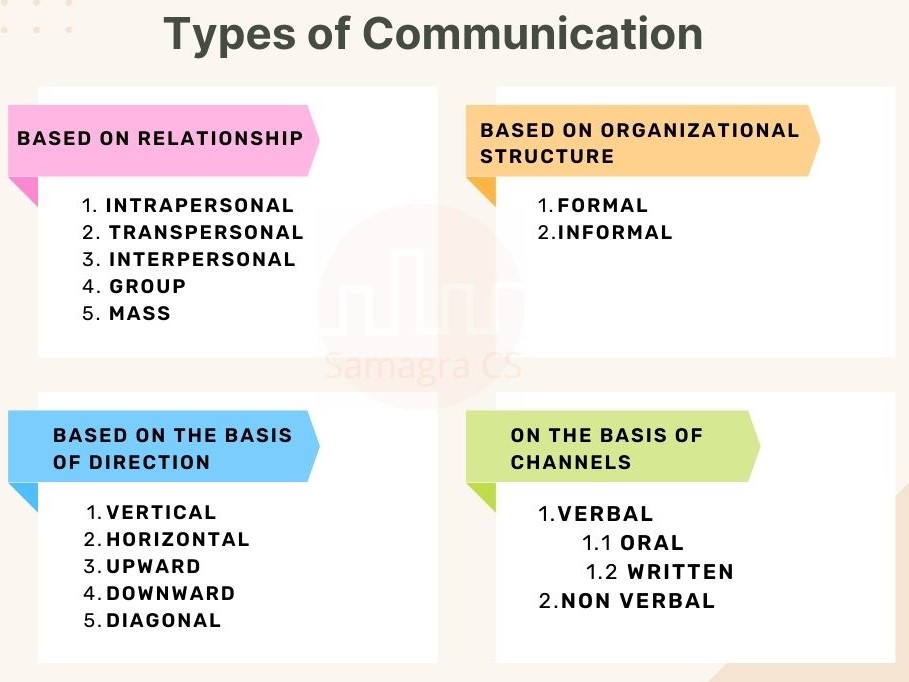
Based on relationship
1. Intrapersonal Communication.
2. Transpersonal Communication.
3. Interpersonal Communication.
4. Group Communication.
5. Mass Communication.
1. Intrapersonal Communication:
| ✰ It may take place within an individual, it is talking to oneself in one’s own mind. ✰ Intrapersonal communication incorporates acts of imagination, self-talk, visualization, recall, and other sorts of internal vocalization. |
2. Transpersonal Communication:
| ✰ It takes place within a person’s spiritual domain. ✰ The purpose of it is to realize self-hood, enhance spirituality and answer the questions that are spiritual in nature. |
3. Interpersonal Communication:
| ✰ It is an exchange of information, ideas, and feelings between two people through verbal or non-verbal methods. ✰ Immediate feedback is possible in it. ✰ Both sender and receiver are present in it. |
4. Group Communication:
| ✰ Group communication is the act of sending and receiving messages to a number of people called group members. ✰ It can be among small or large groups, like an organization, club, or classroom, in which all individuals retain their individual identity. |
Social loafing:
Social loafing is the phenomenon of a person exerting less effort to achieve a goal when they work in a group than when working alone.
5. Mass Communication:
| ✰ Mass communication is the process of imparting and exchanging information through mass media to large segments of the population. ✰ Mass communication is practiced in multiple mediums, such as radio, television, social networking, billboards, newspapers, magazines, books, film, and the Internet. ✰ The study of mass communication is mainly concerned with how the content of mass communication persuades or otherwise affects the behavior, attitude, opinion, or emotion of the people receiving the information. |
Based on organizational structure
1. Formal Communication.
2. Informal Communication.
1. Formal Communication:
| ✰ In formal communication, certain rules, regulations, conventions, and protocols are followed while formulating and communicating messages. ✰ In these use of the right language and correct pronunciation are required. ✰ It may be upward, downward and horizontal. ✰ For example, in case an Assistant Professor has to communicate with College Principal, it is usually through the Head of Department (HoD). |
2. Informal Communication:
| ✰ In informal communication, there are no formal rules and regulations for communication. ✰ It is unstructured, unofficial, and unplanned. ✰ Informal communication is a result of social interaction and satisfies the natural desire of people to communicate with each other. ✰ It is also referred to as grapevine communication. ✰ It runs in all directions-horizontal, vertical, diagonal. ✰ Informal communication occurs when people come together and talk about their working conditions, family, co-workers, etc. ✰ Rumors and gossip are examples of informal communication. |
Based on the basis of the direction
1. Vertical Communication.
2. Horizontal Communication.
3. Upward Communication.
4. Downward Communication.
5. Diagonal Communication.
1. Vertical Communication:
| ✰ This is basically formal communication. ✰ This can be upwards (bottom-up) and downwards (top-bottom). |
2. Horizontal Communication:
| ✰ When communication takes place between two or more persons who are working at the same levels it is known as horizontal or lateral communication. ✰ This may combine both formal and informal communications. |
3. Upward Communication:
| ✰ The Communication that flows from bottom to top, which is from lower hierarchical level to a higher level, is called Upward Communication. ✰ The main function of upward communication is to supply information to the upper levels about what is happening at the lower levels. It is just the reverse of downward communication. ✰ The upward communication process is non-directive in nature, unlike the downward process, which is directive. Effective upward communication is possible only when organizations empower their employees and allow them to participate freely in decision-making. |
4. Downward Communication:
| ✰ The Communication that flows from Top to Bottom is known as downward communication. ✰ Downward communication is one of the important processes of organizational communication. ✰ Communication that takes place from superiors to subordinates in a chain of command is known as downward communication. ✰ Downward communication has five purposes: 1. To give instruction to employees regarding their jobs and specific tasks. 2. To provide information about organizational procedures and practices to new employees. 3. To explain the rationale of a job to a new employee. 4. To provide subordinates feedback about their job performance. 5. To give information required by different teams and departments for the achievement of goals. |
5.Diagonal Communication:
| ✰ Diagonal communication is an exchange of information between persons at a different levels across departmental lines. ✰ It facilitates building relationships and bonding between the superior and the subordinate. ✰ As an example, the Communication between the Training Supervisor and Marketing Manager, regarding the Training of a few employees of the Marketing Department, is Diagonal Communication. |
.
On the basis of channels:
1. Verbal Communication.
1.1 Oral Communication.
1.2. Written Communication.
2. Non verbal Communication.
.
1. Verbal Communication.
| ✰ It means communicating with words, written or spoken. Verbal communication consists of speaking, listening, writing, reading, and thinking. It may further be classified as Oral or Written Communication. ✰ In verbal communication, remember the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple). ✰ In order to deliver the right message, the communicator must be empathetic. |
| Examples of Verbal communication skills are: ✰ Listen carefully ✰ Be confidence ✰ Be clear while speaking ✰ Avoid distraction ✰ Maintain eye contact ✰ Be open-minded ✰ Focus on the non-verbal communication cues ✰ Don’t interrupt the speaker ✰ Be soft-spoken person ✰ Be brief and concise |
Verbal communication is further classified into two types.
1. Verbal Communication.
1.1 Oral Communication.
1.2. Written Communication.
1.1 Oral Communication.
You Should Learn for Better Performance
You should learn previous year solution on this topic. GO Below ☟
| Communication Content : |
