Normalization DBMS UGC NET CSA
| Q1➡ | NTA UGC NET June 2021 Given a relation scheme R(x,y,z,w) with functional dependencies set F={x→y, z→w}. All attributes take single and atomic values only. A. Relation R is in First Normal FORM B. Relation R is in Second Normal FORM C. Primary key of R is xz Choose the correct answer from the options given below: |
| i ➥ A and C only |
| ii ➥ B and C only |
| iii ➥ B only |
| iv ➥ C only |
| Answer – I Explanation: Given, Functional dependencies set F={x→y, z→w} (xz)+ = xyzw Therefore, xz is a Candidate key. Concept, First Normal Form: A relation is in first normal form if every field contains only atomic values. Second Normal Form: In 2NF, part of the candidate key should not determined another Attributes( No partial dependency allow). Statement A: Relation R is in First Normal FORM (True) It is given All attributes take single and atomic values only. Therefore, Relation R is in 1NF. Statement B: Relation R is in Second Normal FORM (False) x→y, z→w Here, part of the candidate key (x) determined another attribute y. The Relation have partial Dependency. Therefore, The Relation is not in 2 NF. Statement C: Primary key of R is xz (True) we already seen above, xz is a primary key. So, Option(I) is correct. |
| Q2➡ | NTA UGC NET November 2020 Consider a relational schema S=(U,V,W,X,Y,Z) on which the following functional dependence hold: { U → V, VW → X, Y → W, X → U} Which are the candidate keys among following options? |
| i ➥ UY, VY |
| ii ➥ UY, VY, XY |
| iii ➥ UYZ, VYZ, VWZ |
| iv ➥ UYZ, VYZ, XYZ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q3➡ | UGC NET December 2019 Comprehension: Answer question (3-7) based on the problem statement given below: An organization needs to maintain database having five attributes A, B, C, D, E. These attributes are functionally dependent on each other for which functionally dependency set F is given as : F: {A→ BC, D → E, BC → D, A →D}. Consider a universal relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with functional dependency set F. Also all attributes are simple and take atomic values only. :→ Minimal cover F’ of functional dependency set F is |
| i ➥ F’ = {A → B, A → C, BC → D, D →E} |
| ii ➥ F’ = {A → BC, B → D, D → E} |
| iii ➥ F’ = {A → B, A → C, A → D, D → E} |
| iv ➥ F’ = {A → B, A → C, B → D, C → D,D → E} |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q4➡ | UGC NET December 2019 Comprehension: Answer question (3-7) based on the problem statement given below: An organization needs to maintain database having five attributes A, B, C, D, E. These attributes are functionally dependent on each other for which functionally dependency set F is given as : F: {A→ BC, D → E, BC → D, A →D}. Consider a universal relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with functional dependency set F. Also all attributes are simple and take atomic values only. → Assume that given table R is decomposed in two tables Which of the following option is true w.r.t. given decomposition? |
| i ➥ Dependency preservation property is followed |
| ii ➥ R1 and R2 are both in 2 NF |
| iii ➥ R2 is in 2 NF and R3 is in 3 NF |
| iv ➥ R1 is in 3 NF and R2 is in 2 NF |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q5➡ | UGC NET December 2019 Comprehension: Answer question (3-7) based on the problem statement given below: An organization needs to maintain database having five attributes A, B, C, D, E. These attributes are functionally dependent on each other for which functionally dependency set F is given as : F: {A→ BC, D → E, BC → D, A →D}. Consider a universal relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with functional dependency set F. Also all attributes are simple and take atomic values only. → Identify the redundant functional dependency in F |
| i ➥ BC→D |
| ii ➥ D→E |
| iii ➥ A→D |
| iv ➥ A→BC |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q6➡ | UGC NET December 2019 Comprehension: Answer question (4-7) based on the problem statement given below: An organization needs to maintain database having five attributes A, B, C, D, E. These attributes are functionally dependent on each other for which functionally dependency set F is given as : F: {A→ BC, D → E, BC → D, A →D}. Consider a universal relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with functional dependency set F. Also all attributes are simple and take atomic values only. → Identify primary key of table R with functional dependency set F |
| i ➥ BC |
| ii ➥ AD |
| iii ➥ A |
| iv ➥ AB |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q7➡ | UGC NET December 2019 Comprehension: Answer question (3-7) based on the problem statement given below: An organization needs to maintain database having five attributes A, B, C, D, E. These attributes are functionally dependent on each other for which functionally dependency set F is given as : F: {A→ BC, D → E, BC → D, A →D}. Consider a universal relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with functional dependency set F. Also all attributes are simple and take atomic values only. → Identify the normal form in which relation R belong to |
| i ➥ 1 NF |
| ii ➥ 2 NF |
| iii ➥ 3 NF |
| iv ➥ BCNF |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q8➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2019 In relational database, if a relation R is in BCNF, then which of the following is true about relation R? |
| i ➥ R is in 4NF |
| ii ➥ R is not in 1NF |
| iii ➥ R is in 2Nf and not in 3NF |
| iv ➥ R is in 2NF and 3NF |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q9➡ | UGC NET December 2018 Consider the schema R=(A, B, C, D, E, F) on which the following functional dependencies hold : A➝B B,C➝D E➝C D➝A What are the candidate keys of R ? |
| i ➥ AEF, BEF and DEF |
| ii ➥ AEF, BEF and BCF |
| iii ➥ AE and BE |
| iv ➥ AE, BE and DE |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q10➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2018 Relations produced from E-R Model will always be in . |
| i ➥ 1 NF |
| ii ➥ 2 NF |
| iii ➥ 3 NF |
| iv ➥ 4 NF |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q11➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2018 For a database relation R(a, b, c, d) where the domains of a, b, c and d include only atomic values, and only the following functional dependencies and those that can be inferred from them hold : a → c b → d The relation is in . |
| i ➥ First normal form but not in second normal form |
| ii ➥ Second normal form but not in third normal form |
| iii ➥ Third normal form |
| iv ➥ BCNF |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q12➡ | UGC NET JUNE 2018 A many-to-one relationship exists between entity sets r1 and r2. How will it be represented using functional dependencies if Pk(r) denotes the primary key attribute of relation r? |
| i ➥ Pk(r1 ) → Pk(r2 ) |
| ii ➥ Pk(r2 ) → Pk(r1 ) |
| iii ➥ Pk(r2 ) → Pk(r1 ) and Pk(r1 ) → Pk(r2 ) |
| iv ➥ Pk(r2 ) → Pk(r1 ) or Pk(r1 ) → Pk(r2 ) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q13➡ | UGC NET November 2017 Paper-II In RDBMS, different classes of relations are created using ________ technique to prevent modification anomalies. |
| i ➥ Functional Dependencies |
| ii ➥ Data integrity |
| iii ➥ Referential integrity |
| iv ➥ Normal forms |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q14➡ | UGC NET November 2017 Paper-III If every non-key attribute is functionally dependent on the primary key, then the relation is in ________ . |
| i ➥ First normal form |
| ii ➥ Second normal form |
| iii ➥ Third normal form |
| iv ➥ Fourth normal form |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q15➡ | UGC NET November 2017 Paper-III Consider a relation R (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H), where each attribute is atomic, and following functional dependencies exist. CH → G A → BC B → CFH E → A F → EG The relation R is __ . |
| i ➥ in 1NF but not in 2NF |
| ii ➥ in 2NF but not in 3NF |
| iii ➥ in 3NF but not in BCNF |
| iv ➥ in BCNF |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q16➡ | UGC NET November 2017 Paper-III Consider a schema R(A, B, C, D) and following functional dependencies. A → B B → C C → D D → B Then decomposition of R into R1(A, B), R2(B, C) and R3(B, D) is __ . |
| i ➥ Dependency preserving and lossless join. |
| ii ➥ Lossless join but not dependency preserving. |
| iii ➥ Dependency preserving but not lossless join. |
| iv ➥ Not dependency preserving and not lossless join. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q17➡ | UGC NET January 2017 Paper-II Consider a schema R(MNPQ) and functional dependencies M → N, P → Q. Then the decomposition of R into R1 (MN) and R2 (PQ) is________. |
| i ➥ Dependency preserving but not lossless join |
| ii ➥ Dependency preserving and lossless join |
| iii ➥ Lossless join but not dependency preserving |
| iv ➥ Neither dependency preserving nor lossless join. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q18➡ | UGC NET January 2017 Paper-III Let pk(R) denotes primary key of relation R. A many-to-one relationship that exists between two relations R1 and R2 can be expressed as follows : |
| i ➥ pk(R2) → pk(R1) |
| ii ➥ pk(R1) → pk(R2) |
| iii ➥ pk(R2) → R1 ∩ R2 |
| iv ➥ pk(R1) → R1 ∩ R2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q19➡ | UGC NET January 2017 Paper-III For a database relation R(A, B, C, D) where the domains of A, B, C and D include only atomic values, only the following functional dependencies and those that can be inferred from them are : A → C B → D The relation R is in________. |
| i ➥ First normal form but not in second normal form. |
| ii ➥ Both in first normal form as well as in second normal form. |
| iii ➥ Second normal form but not in third normal form. |
| iv ➥ Both in second normal form as well as in third normal form. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q20➡ | UGC NET July 2016 Paper-II Consider the following database table having A, B, C and D as its four attributes and four possible candidate keys (I, II,III and IV) for this table : 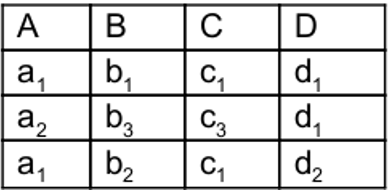 I : {B} II : {B, C} III : {A, D} IV : {C, D} If different symbols stand for different values in the table (e.g., d1 is definitely not equal to d2 ), then which of the above could not be the candidate key for the database table ? |
| i ➥ I and III only |
| ii ➥ III and IV only |
| iii ➥ II only |
| iv ➥ I only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q21➡ | UGC NET July 2016 Paper-III Consider the table R with attributes A, B and C. The functional dependencies that hold on R are : A → B, C → AB. Which of the following statements is/are True ? I. The decomposition of R into R1(C, A) and R2(A, B) is lossless. II. The decomposition of R into R1(A, B) and R2(B, C) is lossy. |
| i ➥ Only I |
| ii ➥ Only II |
| iii ➥ Both I and II |
| iv ➥ Neither I nor II |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q22➡ | UGC NET August 2016 Paper-II Relational database schema normalization is NOT for: |
| i ➥ reducing the number of joins required to satisfy a query. |
| ii ➥ eliminating uncontrolled redundancy of data stored in the database. |
| iii ➥ eliminating number of anomalies that could otherwise occur with inserts and deletes. |
| iv ➥ ensuring that functional dependencies are enforced. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q23➡ | UGC NET August 2016 Paper-II Consider the following statements regarding relational database model: (a) NULL values can be used to opt a tuple out of enforcement of a foreign key. (b) Suppose that table T has only one candidate key. If Q is in 3NF, then it is also in BCNF. (c) The difference between the project operator (Π) in relational algebra and the SELECT keyword in SQL is that if the resulting table/set has more than one occurrences of the same tuple, then Π will return only one of them, while SQL SELECT will return all. One can determine that: |
| i ➥ (a) and (b) are true. |
| ii ➥ (a) and (b) are true |
| iii ➥ (b) and (c) are true |
| iv ➥ (a), (b) and (c) are true |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q24➡ | UGC NET August 2016 Paper-II Consider the following Entity-Relationship (E-R) diagram and three possible relationship sets (I, II and III) for this E-R diagram: 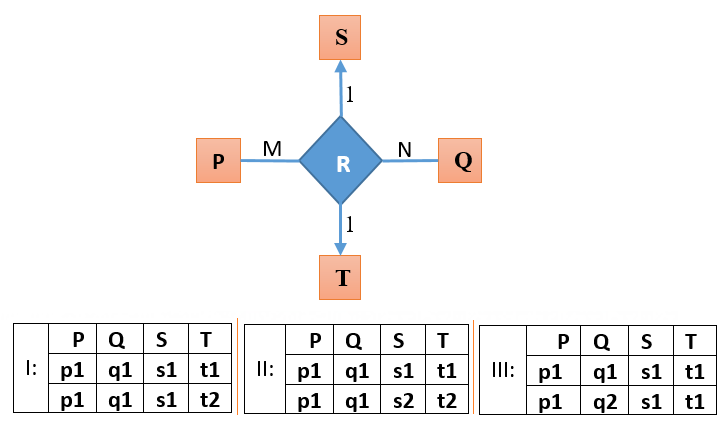 If different symbols stand for different values (e.g., t1 is definitely not equal to t2 ) , then which of the above could not be the relationship set for the E-R diagram ? |
| i ➥ I only |
| ii ➥ I and II only |
| iii ➥ II only |
| iv ➥ I, II and III |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
| Q25➡ | UGC NET August 2016 Paper-III Which of the following statements is TRUE? D1 : The decomposition of the schema R(A, B, C) into R1(A, B) and R2 (A, C) is always lossless. D2 : The decomposition of the schema R(A, B, C, D, E) having AD → B, C → DE, B → AE and AE → C, into R1 (A, B, D) and R2 (A, C, D, E) is lossless. |
| i ➥ Both D1 and D2 |
| ii ➥ Neither D1 nor D2 |
| iii ➥ Only D1 |
| iv ➥ Only D2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Learn Topic Wise | Help-Line |
