GATE 2017 SET-1 CS Computer Science and information technology
[Q1 – Q18 Multiple choice Question(MCQ),carry ONE mark each (for each wrong answer: – 1/3) ]
| Q1➡ | Data Structure Let T be a binary search tree with 15 nodes. The minimum and maximum possible heights of T are: Note: The height of a tree with a single node is 0. |
| i ➥ 4 and 14 respectively |
| ii ➥ 3 and 15 respectively |
| iii ➥ 3 and 14 respectively |
| iv ➥ 4 and 15 respectively |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Binary Tree | Help-Line |
| Q2➡ | Algorithm Consider the following table: 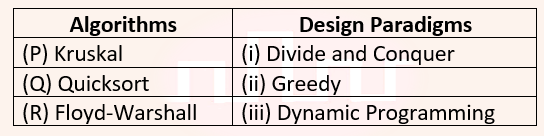 Match the algorithm to design paradigms they are based on: |
| i ➥ (P)↔(ii), Q↔(i), (R)↔(iii) |
| ii ➥ (P)↔(ii), Q↔(iii), (R)↔(i) |
| iii ➥ (P)↔(i), Q↔(ii), (R)↔(iii) |
| iv ➥ (P)↔(iii), Q↔(i), (R)↔(ii) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Design paradigms | Help-Line |
| Q3➡ | Algorithm Consider the following functions from positives integers to real numbers 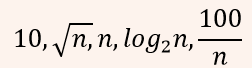 The CORRECT arrangement of the above functions in increasing order of asymptotic complexity is: |
i ➥ 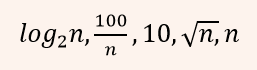 |
ii ➥ 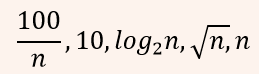 |
iii ➥ 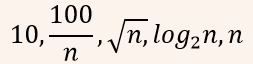 |
iv ➥ 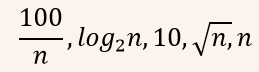 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Asymptotic Complexity | Help-Line |
| Q4➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let c1, cn be scalars not all zero. Such that 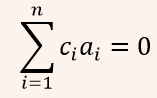 where ai are column vectors in Rn. Consider the set of linear equations. where ai are column vectors in Rn. Consider the set of linear equations.Ax = B. where A = [a1…….an] and 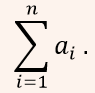 Set of equations has Set of equations has |
| i ➥ no solution |
| ii ➥ a unique solution at x = Jn where Jn denotes a n-dimensional vector of all 1 |
| iii ➥ finitely many solutions |
| iv ➥ infinitely many solutions |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q5➡ | Engineering Mathematics Consider the first-order logic sentence F: ∀x(∃yR(x,y)). Assuming non-empty logical domains, which of the sentences below are implied by F? I. ∃y(∃xR(x,y)) II. ∃y(∀xR(x,y)) III. ∀y(∃xR(x,y)) IV. ¬∃x(∀y¬R(x,y)) |
| i ➥ IV only |
| ii ➥ II and III only |
| iii ➥ I and IV only |
| iv ➥ II only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Propositional Logic | Help-Line |
| Q6➡ | Engineering Mathematics The statement (¬p) ⇒ (¬q) is logically equivalent to which of the statements below? I. p ⇒ q II. q ⇒ p III. (¬q) ∨ p IV. (¬p) ∨ q |
| i ➥ I and IV only |
| ii ➥ I only |
| iii ➥ II and III only |
| iv ➥ II only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Propositional Logic | Help-Line |
| Q7➡ | Compiler Design Consider the following intermediate program in three address code p = a – b q = p * c p = u * v q = p + q Which of the following corresponds to a static single assignment form of the above code? |
| i ➥ p1 = a – b q1 = p * c p2 = u * v q2 = p + q |
| ii ➥ p1 = a – b q1 = p1 * c p1 = u * v q1 = p1 + q1 |
| iii ➥ p3 = a – b q4 = p3 * c p4 = u * v q5 = p4 + q4 |
| iv ➥ p1 = a – b q1 = p2 * c p3 = u * v q2 = p4 + q3 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Static Single Assignment Form | Help-Line |
| Q8➡ | Computer Organization Consider the C struct defined below: 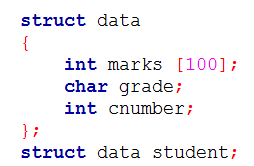 The base address of student is available in register R1. The field student.grade can be accessed efficiently using |
| i ➥ Index addressing mode, X(R1), where X is an offset represented in 2’s complement 16-bit representation |
| ii ➥ Register direct addressing mode, R1 |
| iii ➥ Post-increment addressing mode, (R1)+ |
| iv ➥ Pre-decrement addressing mode, -(R1) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Addressing Modes | Help-Line |
| Q9➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the following context-free grammar over the alphabet Σ = {a, b, c} with S as the start symbol: S → abScT | abcT T → bT | b Which one of the following represents the language generated by the above grammar? |
| i ➥ {(ab)n (cbn)m│m,n ≥ 1} |
| ii ➥ {(ab)n (cb)n│n ≥ 1} |
| iii ➥ {(ab)n (cbm)n│m,n ≥ 1} |
| iv ➥ {(ab)n cbm1 cbm2 …cbmn │n,m1,m2,…,mn ≥ 1} |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Context Free Grammer | Help-Line |
| Q10➡ | Digital Logic Design When two 8-bit numbers A7…A0 and B7…B0 in 2’s complement representation (with A0 and B0 as the least significant bits) are added using a ripple-carry adder, the sum bits obtained are S7…S0 and the carry bits are C7…C0. An overflow is said to have occurred if |
| i ➥ (A7 . B7 . S7‘ + A7‘. B7‘. S7) is 1 |
| ii ➥ the carry bit C7 is 1 |
| iii ➥ (A0 . B0 . S0‘ + A0‘. B0‘. S0) is 1 |
| iv ➥ all the carry bits (C7,…,C0) are 1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Number System | Help-Line |
| Q11➡ | Data Structure Consider the C code fragment given below.  Assuming that m and n point to valid NULL-terminated linked lists, invocation of join will |
| i ➥ either cause a null pointer dereference or append list m to the end of list n. |
| ii ➥ cause a null pointer dereference for all inputs. |
| iii ➥ append list n to the end of list m for all inputs. |
| iv ➥ append list m to the end of list n for all inputs. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linked List | Help-Line |
| Q12➡ | Digital Logic Design The n-bit fixed-point representation of an unsigned real number X uses f bits for the fraction part. Let i = n-f. The range of decimal values for X in this representation is |
| i ➥ 0 to 2i |
| ii ➥ 0 to (2i – 2-f ) |
| iii ➥ 2-f to 2i |
| iv ➥ 2-f to (2i – 2-f) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Number System | Help-Line |
| Q13➡ | Operating Systems Threads of a process share |
| i ➥ both heap and global variables. |
| ii ➥ neither global variables nor heap. |
| iii ➥ heap but not global variables. |
| iv ➥ global variables but not heap. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Threads | Help-Line |
| Q14➡ | Compiler Design Consider the following grammar: 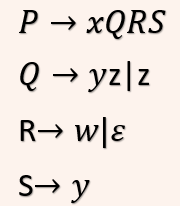 What is FOLLOW(Q)? |
| i ➥ {w, y} |
| ii ➥ {w, $} |
| iii ➥ {R} |
| iv ➥ {w} |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Parsers | Help-Line |
| Q15➡ | Database Management System The following functional dependencies hold true for the relational schema {V, W, X, Y, Z} : • V → W • VW → X • Y → VX • Y → Z Which of the following is irreducible equivalent for this set of functional dependencies? |
| i ➥ V→W W→X Y→V Y→Z |
| ii ➥ V→W W→X Y→V Y→X Y→Z |
| iii ➥ V→W V→X Y→V Y→Z |
| iv ➥ V→W V→X Y→V Y→X Y→Z |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Functional Dependency | Help-Line |
| Q16➡ | Computer Network A sender S sends a message m to receiver R, which is digitally signed by S with its private key. In this scenario, one or more of the following security violations can take place. (I) S can launch a birthday attack to replace m with a fraudulent message. (II) A third party attacker can launch a birthday attack to replace m with a fraudulent message. (III) R can launch a birthday attack to replace m with a fraudulent message. Which of the following are possible security violations? |
| i ➥ I only |
| ii ➥ I and II only |
| iii ➥ II and III only |
| iv ➥ II only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Network Security | Help-Line |
| Q17➡ | Computer Network Consider a TCP client and a TCP server running on two different machines. After completing data transfer, the TCP client calls close to terminate the connection and a FIN segment is sent to the TCP server. Server-side TCP responds by sending an ACK, which is received by the client-side TCP. As per the TCP connection state diagram (RFC 793), in which state does the client-side TCP connection wait for the FIN from the server-side TCP? |
| i ➥ FIN-WAIT-2 |
| ii ➥ LAST-ACK |
| iii ➥ TIME-WAIT |
| iv ➥ FIN-WAIT-1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | TCP | Help-Line |
| Q18➡ | Programming Consider the following C code:  The code suffers from which one of the following problems: |
| i ➥ compiles successfully but execution may result in memory leak |
| ii ➥ compiles successfully but execution may result in dangling pointer |
| iii ➥ compiler error as the return of malloc is not typecast approximately |
| iv ➥ compiler error because the comparison should be made as x==NULL and not as shown |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | malloc Function | Help-Line |
[Q19 – Q25 Multiple choice Question(MCQ),carry ONE mark each (no negative marks) ]
| Q19➡ | Computer Organization Consider a two-level cache hierarchy with L1 and L2 caches. An application incurs 1.4 memory accesses per instruction on average. For this application, the miss rate of L1 cache is 0.1; the L2 cache experiences, on average, 7 misses per 1000 instructions. The miss rate of L2 expressed correct to two decimal places is _______. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache | Help-Line |
| Q20➡ | Operating System Consider the following CPU processes with arrival times (in milliseconds) and length of CPU bursts (in milliseconds) as given below: 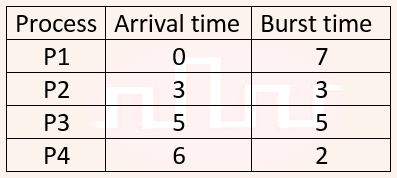 If the pre-emptive shortest remaining time first scheduling algorithm is used to schedule the processes, then the average waiting time across all processes is _________ milliseconds. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process Scheduling | Help-Line |
| Q21➡ | Database Management System Consider a database that has the relation schema EMP (EmpId, EmpName, and DeptName). An instance of the schema EMP and a SQL query on it are given below: 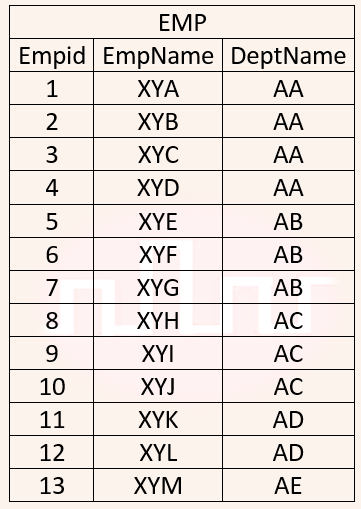 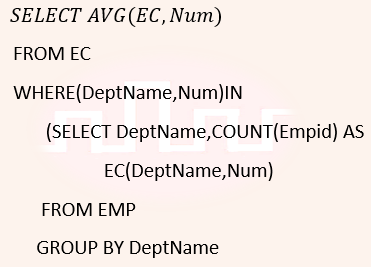 The output of executing the SQL query is __________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | SQL | Help-Line |
| Q22➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the language L given by the regular expression (a+b)*b(a+b) over the alphabet {a,b}. The smallest number of states needed in deterministic finite-state automation (DFA) accepting L is ________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Finite Automata | Help-Line |
| Q23➡ | Digital Logic Design Consider the Karnaugh map given below, where X represents “don’t care” and blank represents 0. Assume for all inputs (a, b, c, d) , the respective complements (a’, b’, c’, d’) are also available. The above logic is implemented using 2-input NOR gates only. The minimum number of gates required is ___________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Boolean Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q24➡ | Data Structure Let T be a tree with 10 vertices. The sum of the degrees of all the vertices in T is _______. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Tree | Help-Line |
| Q25➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let X be a Gaussian random variable with mean 0 and variance σ2. Let Y = max(X, 0) where max(a,b) is the maximum of a and b. The median of Y is ___________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Probability | Help-Line |
[Q26 – Q42 Multiple choice Question(MCQ),carry TWO mark each (for each wrong answer: – 2/3) ]
| Q26➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let A be m×n real valued square symmetric matrix of rank 2 with expression given below. 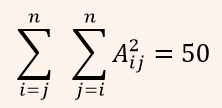 Consider the following statements (i) One eigenvalue must be in [-5, 5]. (ii) The eigenvalue with the largest magnitude must be strictly greater than 5. Which of the above statements about engenvalues of A is/are necessarily CORRECT? |
| i ➥ (I) only |
| ii ➥ Neither (I) nor (II) |
| iii ➥ (II) only |
| iv ➥ Both (I) and (II) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let u and v be two vectors in R2 whose Euclidean norms satisfy ||u||=2||v||. What is the value of α such that w = u + αv bisects the angle between u and v? |
| i ➥ -1/2 |
| ii ➥ 2 |
| iii ➥ 1/2 |
| iv ➥ 1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q28➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let p, q and r be prepositions and the expression (p → q) → r be a contradiction. Then, the expression (r → p) → q is |
| i ➥ a contradiction |
| ii ➥ always TRUE when q is TRUE |
| iii ➥ a tautology |
| iv ➥ always TRUE when p is FALSE |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Propositional Logic | Help-Line |
| Q29➡ | Engineering Mathematics The value of 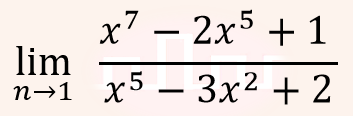 |
| i ➥ is 1 |
| ii ➥ does not exist |
| iii ➥ is 0 |
| iv ➥ is -1 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Calculus | Help-Line |
| Q30➡ | Operating Systems A multithreaded program P executes with x number of threads and used y number of locks for ensuring mutual exclusion while operating on shared memory locations. All locks in the program are non-reentrant, i.e., if a thread holds a lock l, then it cannot re-acquire lock l without releasing it. If a thread is unable to acquire a lock, it blocks until the lock becomes available. The minimum value of x and the minimum value of y together for which execution of P can result in a deadlock are: |
| i ➥ x = 2, y = 1 |
| ii ➥ x = 1, y = 1 |
| iii ➥ x = 1, y = 2 |
| iv ➥ x = 2, y = 2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process Synchronization | Help-Line |
| Q31➡ | Algorithms Let G = (V, E) be any connected undirected edge-weighted graph. The weights of the edges in E are positive and distinct. Consider the following statements: (I) Minimum Spanning Tree of G is always unique. (II) Shortest path between any two vertices of G is always unique. Which of the above statements is/are necessarily true? |
| i ➥ (II) only |
| ii ➥ (I) only |
| iii ➥ neither (I) nor (II) |
| iv ➥ both (I) and (II) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Minimum Spanning Tree | Help-Line |
| Q32➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the context-free grammars over the alphabet {a, b, c} given below. S and T are non-terminals. G1: S → aSb|T, T → cT|ϵ G2: S → bSa|T, T → cT|ϵ The language L(G1) ∩ L(G2) is |
| i ➥ Context-Free but not regular |
| ii ➥ Recursive but not context-free |
| iii ➥ Finite |
| iv ➥ Not finite but regular |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Context Free Grammer | Help-Line |
| Q33➡ | Programming Consider the C functions foo and bar given below:  Invocations of foo(3) and bar(3) will result in: |
| i ➥ Abnormal termination and infinite loop respectively. |
| ii ➥ Both terminating abnormally. |
| iii ➥ Return of 6 and 6 respectively. |
| iv ➥ Infinite loop and abnormal termination respectively. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Function | Help-Line |
| Q34➡ | Programming Consider the following two functions:  The output printed when fun1(5) is called is |
| i ➥ 53423122132435 |
| ii ➥ 53423122233445 |
| iii ➥ 53423120112233 |
| iv ➥ 53423120213243 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Function | Help-Line |
| Q35➡ | Theory of Computation If G is a grammar with productions S → SaS | aSb | bSa | SS | ϵ where S is the start variable, then which one of the following strings is not generated by G? |
| i ➥ babba |
| ii ➥ abbaa |
| iii ➥ abab |
| iv ➥ aaab |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Grammer | Help-Line |
| Q36➡ | Digital Logic Design Consider a combination of T and D flip-flops connected as shown below. The output of the D flip-flop is connected to the input of the T flip-flop and the output of the T flip-flop is connected to the input of the D flip-flop: 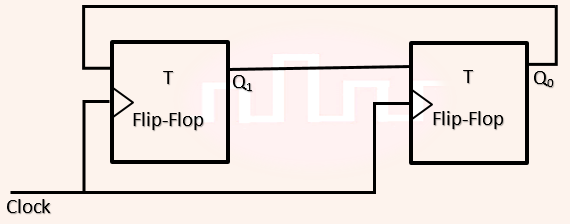 Initially, both Q0 and Q1 are set to 1 (before the 1st clock cycle). The outputs |
| i ➥ Q1Q0 after the 3rd cycle are 00 and after the 4th cycle are 11 respectively |
| ii ➥ Q1Q0 after the 3rd cycle are 11 and after the 4th cycle are 00 respectively |
| iii ➥ Q1Q0 after the 3rd cycle are 01 and after the 4th cycle are 01 respectively |
| iv ➥ Q1Q0 after the 3rd cycle are 11 and after the 4th cycle are 01 respectively |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sequential Circuits | Help-Line |
| Q37➡ | Computer Network A computer network uses polynomials over GF(2) for error checking with 8 bits as information bits and uses x3 + x + 1 as the generator polynomial to generate the check bits. In this network, the message 01011011 is transmitted as |
| i ➥ 01011011100 |
| ii ➥ 01011011010 |
| iii ➥ 01011011101 |
| iv ➥ 01011011011 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Error Control | Help-Line |
| Q38➡ | Database Management System In a database system, unique timestamps are assigned to each transaction using Lamport’s logical clock. Let TS(T1) and TS(T2) be the timestamps of transactions T1 and T2 respectively. Besides, T1 holds a lock on the resource R and T2 has requested a conflicting lock on the same resource R. The following algorithm is used to prevent deadlocks in the database system assuming that a killed transaction is restarted with the same timestamp. if TS(T2)<TS(T1) then T1 is killed else T2 waits. Assume any transaction that is not killed terminates eventually. Which of the following is TRUE about the database system that uses the above algorithm to prevent deadlocks? |
| i ➥ The database system is deadlock-free, but not starvation-free. |
| ii ➥ The database system is starvation-free, but not deadlock-free. |
| iii ➥ The database system is neither deadlock-free nor starvation-free. |
| iv ➥ The database system is both deadlock-free and starvation-free. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Transaction Management | Help-Line |
| Q39➡ | Database Management System Consider a database that has the relation schemas EMP(EmpId, EmpName, DeptId), and DEPT(DeptName, DeptId). Note that the DeptId can be permitted to a NULL in the relation EMP. Consider the following queries on the database expressed in tuple relational calculus. (I) {t│∃u ∈ EMP(t[EmpName] = u[EmpName] ∧ ∀v ∈ DEPT(t[DeptId] ≠ v[DeptId]))} (II) {t│∃u ∈ EMP(t[EmpName] = u[EmpName] ∧ ∃v ∈ DEPT(t[DeptId] ≠ v[DeptId]))} (III) {t│∃u ∈ EMP(t[EmpName] = u[EmpName] ∧ ∃v ∈ DEPT(t[DeptId] = v[DeptId]))} Which of the above queries are safe? |
| i ➥ (I), (II) and (III) |
| ii ➥ (I) and (III) only |
| iii ➥ (I) and (II) only |
| iv ➥ (II) and (III) only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Relational Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q40➡ | Operating System Recall that Belady’s anomaly is that the page-fault rate may increase as the number of allocated frames increases. Now, consider the following statements: S1: Random page replacement algorithm (where a page chosen at random is replaced) suffers from Belady’s anomaly S2: LRU page replacement algorithm suffers from Belady’s anomaly Which of the following is CORRECT? |
| i ➥ S1 is false, S2 is false |
| ii ➥ S1 is true, S2 is false |
| iii ➥ S1 is true, S2 is true |
| iv ➥ S1 is false, S2 is true |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Page Replacement Algorithm | Help-Line |
| Q41➡ | Theory of Computation Let A and B be finite alphabets and let # be a symbol outside both A and B. Let f be a total function from A* to B*. We say f is computable if there exists a Turing machine M which given an input x in A, always halts with f(x) on its tape. Let Lf denote the language {x # f(x)│x ∈ A*}. Which of the following statements is true: |
| i ➥ If f is computable then Lf is recursively enumerable, but not conversely. |
| ii ➥ If f is computable then Lf is recursive, but not conversely. |
| iii ➥ f is computable if and only if Lf is recursive. |
| iv ➥ f is computable if and only if Lf is recursively enumerable. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Computability | Help-Line |
| Q42➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the following languages over the alphabet Σ = {a, b, c}. Let L1 = {an bn cm│m,n ≥ 0} and L2 = {am bn cn│m,n ≥ 0} Which of the following are context-free languages? I. L1∪ L2 II. L1∩ L2 |
| i ➥ II only |
| ii ➥ I only |
| iii ➥ Neither I nor II |
| iv ➥ I and II |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Context Free Language | Help-Line |
[Q43 – Q55 Multiple choice Question(MCQ),carry TWO mark each (no negative marks) ]
| Q43➡ | Algorithms Let A be an array of 31 numbers consisting of a sequence of 0’s followed by a sequence of 1’s. The problem is to find the smallest index i such that A[i] is 1 by probing the minimum number of locations in A. The worst case number of probes performed by an optimal algorithm is ___________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Searching | Help-Line |
| Q44➡ | Engineering Mathematics The number of integers between 1 and 500 (both inclusive) that are divisible by 3 or 5 or 7 is __________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Combinatorics | Help-Line |
| Q45➡ | Database Management System Consider a database that has the relation schema CR(StudentName, CourseName). An instance of the schema CR is as given below: 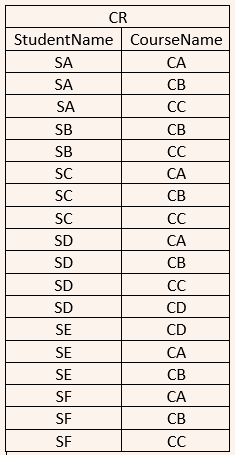 The following query is made on the database. T1 ← πCourseName(σStudentName=’SA’(CR)) T2 ← CR ÷ T1 The number of rows in T2 is _________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Relational Algebra | Help-Line |
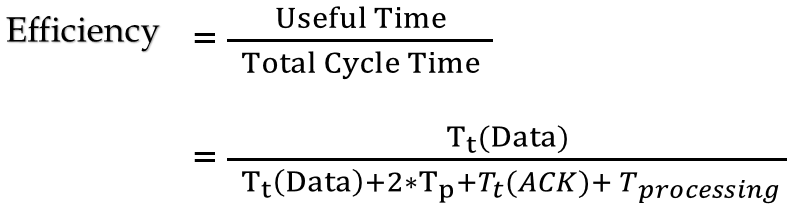
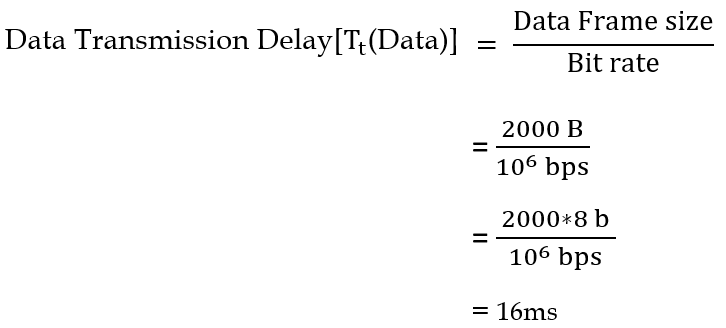
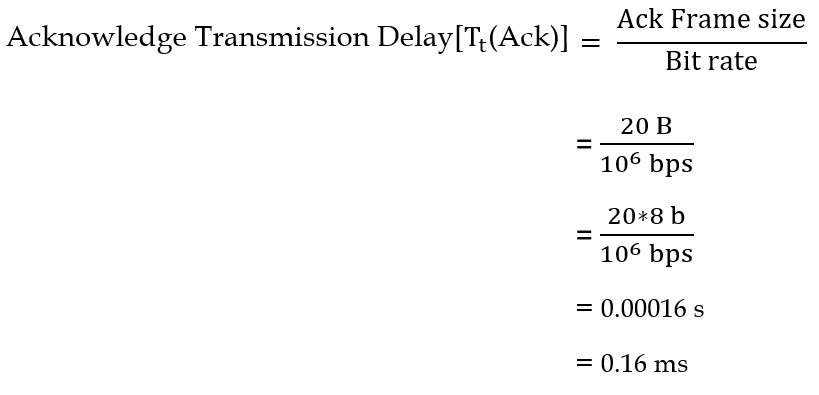
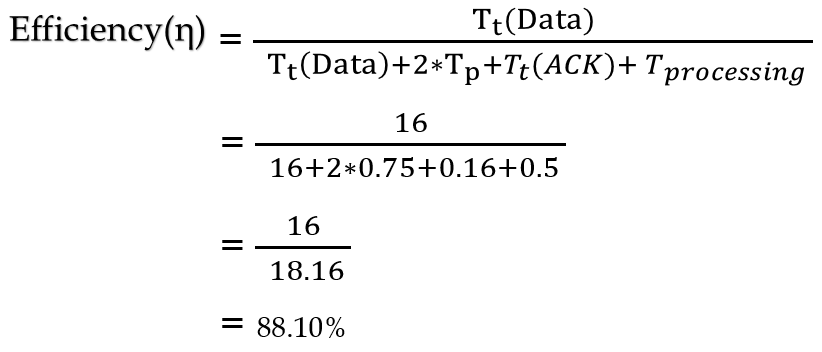
| Q46➡ | Computer Network The value of parameters for the Stop-and-Wait ARQ protocol are as given below: Bit rate of the transmission channel = 1 Mbps. Propagation delay from sender to receiver = 0.75 ms. Time to process a frame = 0.25 ms. Number of bytes in the information frame = 1980. Number of bytes in the acknowledge frame = 20. Number of overhead bytes in the information frame = 20. Assume that there are no transmission errors. Then, the transmission efficiency (expressed in percentage) of the Stop-and-Wait ARQ protocol for the above parameters is _ (correct to 2 decimal places). |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Flow Control | Help-Line |
| Q47➡ | Computer Network In a RSA cryptosystem, a participant A uses two prime numbers p = 13 and q = 17 to generate her public and private keys. If the public key of A is 35, then the private key of A is ____________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Network Security | Help-Line |
| Q48➡ | Compiler Design Consider the following grammar: stmt → if expr then expr else expr; stmt | ȯ expr → term relop term | term term → id | number id → a | b | c number → [0-9] where relop is a relational operator (e.g., <, >, …), ȯ refers to the empty statement, and if, then, else are terminals. Consider a program P following the above grammar containing ten if terminals. The number of control flow paths in P is ________. For example, the program if e1 then e2 else e3 has 2 control flow paths, e1 → e2 and e1 → e3. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Parsers | Help-Line |
| Q49➡ | Computer Organization A cache memory unit with capacity of N words and block size of B words is to be designed. If it is designed as a direct mapped cache, the length of the TAG field is 10 bits. If the cache unit is now designed as a 16-way set-associative cache, the length of the TAG field is ________ bits. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache Memory | Help-Line |
| Q50➡ | Programming Consider the following C program:  Recall that strlen is defined in string.h as returning a value of type size_t, which is an unsigned int. The output of the program is _________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Function | Help-Line |
| Q51➡ | Compiler Design Consider the expression (a-1)*( ( (b+c) /3) +d). Let X be the minimum number of registers required by an optimal code generation (without any register spill) algorithm for a load/store architecture, in which (i) only load and store instructions can have memory operands and (ii) arithmetic instructions can have only register or immediate operands. The value of X is ________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Register Allocation | Help-Line |
| Q52➡ | Computer Organization Consider a 2-way set associative cache with 256 blocks and uses LRU replacement. Initially the cache is empty. Conflict misses are those misses which occur due to contention of multiple blocks for the same cache set. Compulsory misses occur due to first time access to the block. The following sequence of accesses to memory blocks (0, 128, 256, 128, 0, 128, 256, 128, 1, 129, 257, 129, 1, 129, 257, 129) is repeated 10 times. The number of conflict misses experienced by the cache is _________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache Memory | Help-Line |
| Q53➡ | Computer Organization Instruction execution in a processor is divided into 5 stages, Instruction Fetch (IF), Instruction Decode (ID), Operand Fetch (OF), Execute (EX), and Write Back (WB). These stages take 5, 4, 20, 10 and 3 nanoseconds (ns) respectively. A pipelined implementation of the processor requires buffering between each pair of consecutive stages with a delay of 2 ns. Two pipelined implementations of the processor are contemplated: (i) a naive pipeline implementation (NP) with 5 stages and (ii) an efficient pipeline (EP) where the OF stage is divided into stages OF1 and OF2 with execution times of 12 ns and 8 ns respectively. The speedup (correct to two decimal places) achieved by EP over NP in executing 20 independent instructions with no hazards is _______. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Pipelining | Help-Line |
| Q54➡ | Computer Organization Consider a RISC machine where each instruction is exactly 4 bytes long. Conditional and unconditional branch instructions use PC-relative addressing mode with Offset specified in bytes to the target location of the branch instruction. Further the Offset is always with respect to the address of the next instruction in the program sequence. Consider the following instruction sequence If the target of the branch instruction is i, then the decimal value of the Offset is ________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Instruction Cycle | Help-Line |
| Q55➡ | Programming The output of executing the following C program is _________.  |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Function | Help-Line |