GATE 2018 CS Computer Science and information technology
[Q1 – Q25 ,Carry ONE mark each]
| Q1➡ | Theory of Computation Let N be an NFA with n states. Let k be the number of states of a minimal DFA which is equivalent to N. Which one of the following is necessarily true? |
| i ➥ k ≤ n2 |
| ii ➥ k ≤ 2n |
| iii ➥ k ≥ 2n |
| iv ➥ k ≥ n |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | NFA/DFA | Help-Line |
| Q2➡ | Computer Organization Consider the following processor design characteristics. I. Register-to-register arithmetic operations only II. Fixed-length instruction format III. Hardwired control unit Which of the characteristics above are used in the design of a RISC processor? |
| i ➥ I and III only |
| ii ➥ I, II and III |
| iii ➥ I and II only |
| iv ➥ II and III only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | RISC | Help-Line |
| Q3➡ | Digital Logic Design Let ⊕ and ⊙ denote the Exclusive OR and Exclusive NOR operations, respectively. Which one of the following is NOT CORRECT? |
| i ➥ |
| ii ➥ |
| iii ➥ |
| iv ➥ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Boolean Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q4➡ | Data Structure A queue is implemented using a non-circular singly linked list. The queue has a head pointer and a tail pointer, as shown in the figure. Let n denote the number of nodes in the queue. Let ‘enqueue’ be implemented by inserting a new node at the head, and ‘dequeue’ be implemented by deletion of a node from the tail. 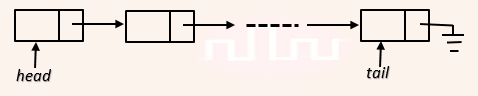 Which one of the following is the time complexity of the most time-efficient implementation of ‘enqueue’ and ‘dequeue, respectively, for this data structure? |
| i ➥ θ(n), θ(1) |
| ii ➥ θ(n), θ(n) |
| iii ➥ θ(1), θ(1) |
| iv ➥ θ(1), θ(n) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Queue | Help-Line |
Q5➡ | Programming in C  |
| i ➥ ‘0’, ‘a+2’ |
| ii ➥ ‘0’, ‘c’ |
| iii ➥ 0, c |
| iv ➥ 0, a+2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Programming in C | Help-Line |
| Q6➡ | Engineering-Mathematics Which one of the following is a closed form expression for the generating function of the sequence {an}, where an = 2n + 3 for all n = 0, 1, 2,… ? |
| i ➥ 2-x/(1-x)2 |
| ii ➥ 3-x/(1-x)2 |
| iii ➥ 3/(1-x)2 |
| iv ➥ 3x/(1-x)2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Engineering Mathematics | Help-Line |
| Q7➡ | Database Management System Consider the following two tables and four queries in SQL. Book (isbn, bname), Stock (isbn, copies) Query 1: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies FROM Book B INNER JOIN Stock S ON B.isbn = S.isbn; Query 2: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies FROM Book B LEFT OUTER JOIN Stock S ON B.isbn = S.isbn; Query 3: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies FROM Book B RIGHT OUTER JOIN Stock S ON B.isbn = S.isbn; Query 4: SELECT B.isbn, S.copies FROM Book B FULL OUTER JOIN Stock S ON B.isbn = S.isbn; Which one of the queries above is certain to have an output that is a superset of the outputs of the other three queries? |
| i ➥ Query 4 |
| ii ➥ Query 3 |
| iii ➥ Query 1 |
| iv ➥ Query 2 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | SQL | Help-Line |
| Q8➡ | Computer Organization The following are some events that occur after a device controller issues an interrupt while process L is under execution. (P) The processor pushes the process status of L onto the control stack. (Q)The processor finishes the execution of the current instruction. (R) The processor executes the interrupt service routine. (S) The processor pops the process status of L from the control stack. (T) The processor loads the new PC value based on the interrupt. Which one of the following is the correct order in which the events above occur? |
| i ➥ QTPRS |
| ii ➥ TRPQS |
| iii ➥ PTRSQ |
| iv ➥ QPTRS |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | interrupt | Help-Line |
| Q9➡ | Computer Organization Consider a process executing on an operating system that uses demand paging. The average time for a memory access in the system is M units if the corresponding memory page is available in memory, and D units if the memory access causes a page fault. It has been experimentally measured that the average time taken for a memory access in the process is X units. Which one of the following is the correct expression for the page fault rate experienced by the process? |
| i ➥ (D – M) / (X – M) |
| ii ➥ (X – M) / (D – M) |
| iii ➥ (D – X) / (D – M) |
| iv ➥ (X – M) / (D – X) |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | paging | Help-Line |
| Q10➡ | Database Management System In an Entity-Relationship (ER) model, suppose R is a many-to-one relationship from entity set E1 to entity set E2. Assume that E1 and E2 participate totally in R and that the cardinality of E1 is greater than the cardinality of E2. Which one of the following is true about R? |
| i ➥ Every entity in E1 is associated with exactly one entity in E2. |
| ii ➥ Some entity in E1 is associated with more than one entity in E2. |
| iii ➥ Every entity in E2 is associated with exactly one entity in E1. |
| iv ➥ Every entity in E2 is associated with at most one entity in E1. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | ER model | Help-Line |
| Q11➡ | Compiler Design Which one of the following statements is FALSE? |
| i ➥ Context-free grammar can be used to specify both lexical and syntax rules. |
| ii ➥ Type checking is done before parsing. |
| iii ➥ High-level language programs can be translated to different Intermediate Representations. |
| iv ➥ Arguments to a function can be passed using the program stack. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Compiler | Help-Line |
| Q12➡ | Theory of Computation The set of all recursively enumerable languages is |
| i ➥ closed under complementation. |
| ii ➥ closed under intersection. |
| iii ➥ a subset of the set of all recursive languages. |
| iv ➥ an uncountable set. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Closure-Property | Help-Line |
| Q13➡ | Engineering Mathematics Two people, P and Q, decide to independently roll two identical dice, each with 6 faces, numbered 1 to 6. The person with the lower number wins. In case of a tie, they roll the dice repeatedly until there is no tie. Define a trial as a throw of the dice by P and Q. Assume that all 6 numbers on each dice are equi-probable and that all trials are independent. The probability (rounded to 3 decimal places) that one of them wins on the third trial is_____. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | probability | Help-Line |
Q14➡ | Engineering Mathematics  |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Engineering Mathematics | Help-Line |
Q15➡ | Computer Network 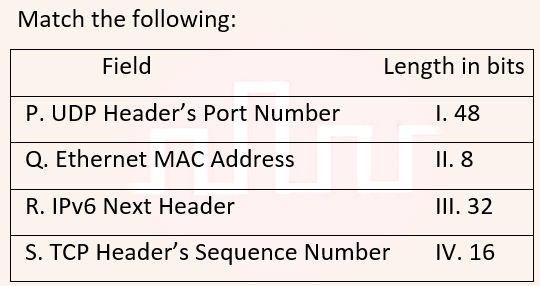 |
| i ➥ P-III, Q-IV, R-II, S-I |
| ii ➥ P-II, Q-I, R-IV, S-III |
| iii ➥ P-IV, Q-I, R-II, S-III |
| iv ➥ P-IV, Q-I, R-III, S-II |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Matching | Help-Line |
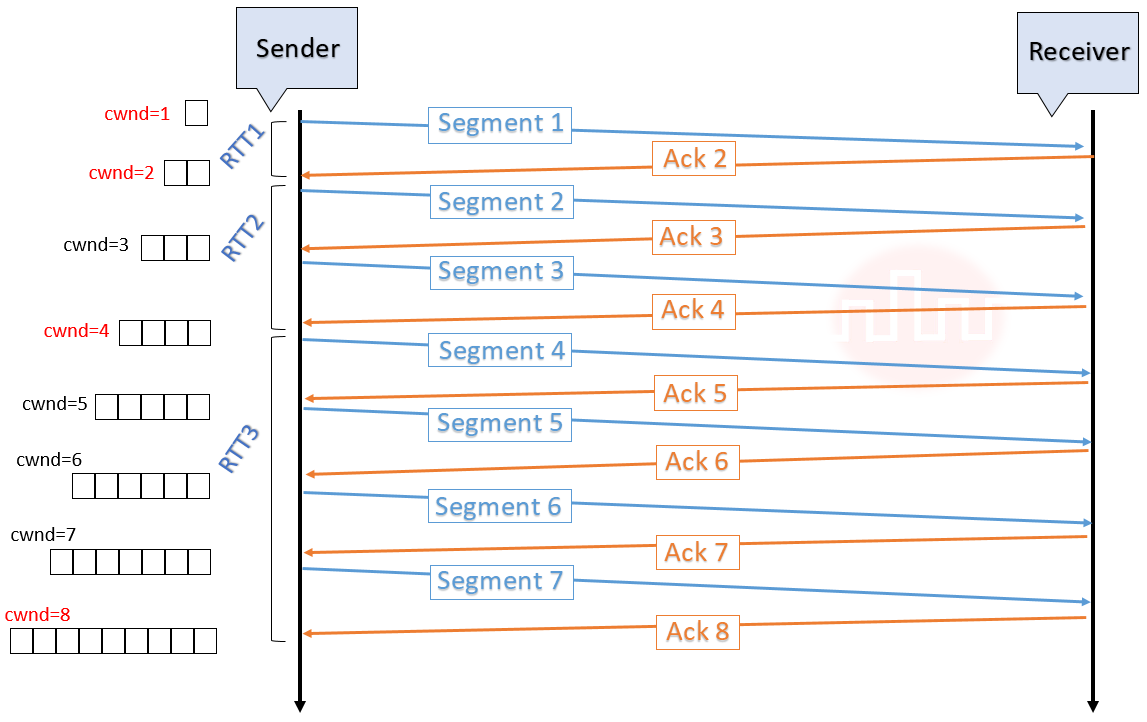
| Q16➡ | Computer Network Consider the following statements regarding the slow start phase of the TCP congestion control algorithm. Note that cwnd stands for the TCP congestion window and MSS denotes the Maximum Segment Size. (i) The cwnd increase by 2 MSS on every successful acknowledgement. (ii) The cwnd approximately doubles on every successful acknowledgement. (iii) The cwnd increase by 1 MSS every round trip time. (iv) The cwnd approximately doubles every round trip time. Which one of the following is correct? |
| i ➥ Only (ii) and (iii) are true |
| ii ➥ Only (i) and (iii) are true |
| iii ➥ Only (iv) is true |
| iv ➥ Only (i) and (iv) are true |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Routers | Help-Line |
Q17➡ | Engineering-Mathematics  |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q18➡ | Engineering-Mathematics The chromatic number of the following graph is _. 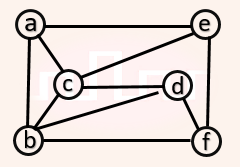 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graph-Theory | Help-Line |
| Q19➡ | Data Structure The postorder traversal of a binary tree is 8, 9, 6, 7, 4, 5, 2, 3, 1. The inorder traversal of the same tree is 8, 6, 9, 4, 7, 2, 5, 1, 3. The height of a tree is the length of the longest path from the root to any leaf. The height of the binary tree above is_____. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Trees Traversal | Help-Line |
| Q20➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let G be a finite group on 84 elements. The size of a largest possible proper subgroup of G is_________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Set Theory | Help-Line |
| Q21➡ | Computer Network Consider a long-lived TCP session with an end-to-end bandwidth of 1 Gbps (= 109 bits/second). The session starts with a sequence number of 1234. The minimum time (in seconds, rounded to the closest integer) before this sequence number can be used again is _______. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | TCP | Help-Line |
| Q22➡ | Operating Systems Consider a system with 3 processes that share 4 instances of the same resource type. Each process can request a maximum of K instances. Resource instances can be requested and released only one at a time. The largest value of K that will always avoid deadlock is _. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Deadlock | Help-Line |
| Q23➡ | Computer Organization A 32-bit wide main memory unit with a capacity of 1 GB is built using 256M × 4-bit DRAM chips. The number of rows of memory cells in the DRAM chip is 214. The time taken to perform one refresh operation is 50 nanoseconds. The refresh period is 2 milliseconds. The percentage (rounded to the closest integer) of the time available for performing the memory read/write operations in the main memory unit is _. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Memory Interfacing | Help-Line |
| Q24➡ | Digital Logic Design Consider the sequential circuit shown in the figure, where both flip-flops used are positive edge-triggered D flip-flops. 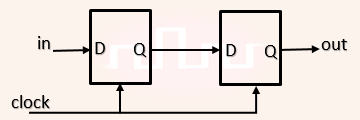 The number of states in the state transition diagram of this circuit that have a transition back to the same state on some value of “in” is __ |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Sequential Circuits | Help-Line |
| Q25➡ | Programming Consider the following C program:  The output of this program is __. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | C program | Help-Line |
[Q26 – Q55, Carry TWO marks each ]
| Q26➡ | Programming Consider the following C code. Assume that unsigned long int type length is 64 bits.  The value returned when we call fun with the input 240 is |
| i ➥ 4 |
| ii ➥ 5 |
| iii ➥ 6 |
| iv ➥ 40 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | For Loop | Help-Line |
| Q27➡ | Engineering Mathematics Assume that multiplying a matrix G1 of dimension p×q with another matrix G2 of dimension q×r requires pqr scalar multiplications. Computing the product of n matrices G1G2G3…Gn can be done by parenthesizing in different ways. Define GiGi+1 as an explicitly computed pair for a given parenthesization if they are directly multiplied. For example, in the matrix multiplication chain G1G2G3G4G5G6 using parenthesization(G1(G2G3))(G4(G5G6)), G2G3 and G5G6 are the only explicitly computed pairs. Consider a matrix multiplication chain F1F2F3F4F5, where matrices F1, F2, F3, F4 and F5 are of dimensions 2×25, 25×3, 3×16, 16×1 and 1×1000, respectively. In the parenthesization of F1F2F3F4F5 that minimizes the total number of scalar multiplications, the explicitly computed pairs is/ are |
| i ➥ F1F2 and F3F4 only |
| ii ➥ F2F3 only |
| iii ➥ F3F4 only |
| iv ➥ F1F2 and F4F5 only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q28➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let G be a simple un-directed graph. Let TD be a depth first search tree of G. Let TB be a breadth first search tree of G. Consider the following statements. (I) No edge of G is a cross edge with respect to TD (A cross edge in G is between two nodes neither of which is an ancestor of the other in TD (II) For every edge (u,v) of G, if u is at depth i and v is at depth j in TB , then ∣i−j∣ = 1. Which of the statements above must necessarily be true? |
| i ➥ I only |
| ii ➥ II only |
| iii ➥ Both I and II |
| iv ➥ Neither I nor II |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graphs | Help-Line |
| Q29➡ | Programming Consider the following C program: 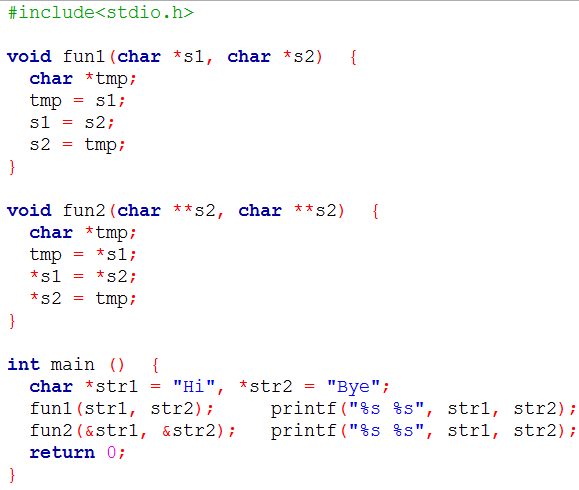 The output of the program above is. |
| i ➥ Hi Bye Bye Hi |
| ii ➥ Hi Bye Hi Bye |
| iii ➥ Bye Hi Hi Bye |
| iv ➥ Bye Hi Bye Hi |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Function | Help-Line |
| Q30➡ | Engineering Mathematics Consider the first-order logic sentence φ ≡ ∃s∃t∃u∀v∀w∀x∀y ψ(s,t,u,v,w,x,y) where ψ(s,t,u,v,w,x,y) is a quantifier-free first-order logic formula using only predicate symbols, and possibly equality, but no function symbols. Suppose φ has a model with a universe containing 7 elements. Which one of the following statements is necessarily true? |
| i ➥ There exists at least one model of φ with universe of size less than or equal to 3. |
| ii ➥ There exists no model of φ with universe of size less than or equal to 3 |
| iii ➥ There exists no model of φ with universe of size greater than 7. |
| iv ➥ Every model of φ has a universe of size equal to 7. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Propositional Logic | Help-Line |
| Q31➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let N be the set of natural numbers. Consider the following sets, P: Set of Rational numbers (positive and negative) Q: Set of functions from {0, 1} to N R: Set of functions from N to {0, 1} S: Set of finite subsets of N Which of the above sets are countable? |
| i ➥ Q and S only |
| ii ➥ P and S only |
| iii ➥ P and R only |
| iv ➥ P, Q and S only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q32➡ | Engineering Mathematics Consider a matrix P whose only eigenvectors are the multiples of Consider the following statements. (I) P does not have an inverse (II) P has a repeated eigenvalue (III) P cannot be diagonalized Which one of the following options is correct? |
| i ➥ Only I and II are necessarily true |
| ii ➥ Only II and III are necessarily true |
| iii ➥ Only I and III are necessarily true |
| iv ➥ Only II is necessarily true |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q33➡ | Digital-Logic-Design Consider the unsigned 8-bit fixed point binary number representation below. b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 . b2 b1 b0 where the position of the binary point is between b3 and b2 . Assume b7 is the most significant bit. Some of the decimal numbers listed below cannot be represented exactly in the above representation: (i) 31.500 (ii) 0.875 (iii) 12.100 (iv) 3.001 Which one of the following statements is true? |
| i ➥ None of (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) can be exactly represented |
| ii ➥ Only (ii) cannot be exactly represented |
| iii ➥ Only (iii) and (iv) cannot be exactly represented |
| iv ➥ Only (i) and (ii) cannot be exactly represented |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Number System | Help-Line |
| Q34➡ | Computer Organization The size of the physical address space of a processor is 2P bytes. The word length is 2W bytes. The capacity of cache memory is 2N bytes. The size of each cache block is 2M words. For a K-way set-associative cache memory, the length (in number of bits) of the tag field is |
| i ➥ P – N – log2K |
| ii ➥ P – N + log2K |
| iii ➥ P – N – M – W – log2K |
| iv ➥ P – N – M – W + log2K |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Cache | Help-Line |
Q35➡ | Theory of Computation  |
| i ➥ I and IV only |
| ii ➥ I and II only |
| iii ➥ II and III only |
| iv ➥ II and IV only |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Context Free Language | Help-Line |
| Q36➡ | Database Management System Consider the following four relational schemas. For each schema, all non-trivial functional dependencies are listed. The underlined attributes are the respective primary keys. Schema I: Registration(rollno, courses) Field ‘courses’ is a set-valued attribute containing the set of courses a student has registered for. Non-trivial functional dependency rollno → courses Schema II: Registration (rollno, courseid, email) Non-trivial functional dependencies: rollno, courseid → email email → rollno Schema III: Registration (rollno, courseid, marks, grade) Non-trivial functional dependencies: rollno, courseid, → marks, grade marks → grade Schema IV: Registration (rollno, courseid, credit) Non-trivial functional dependencies: rollno, courseid → credit courseid → credit Which one of the relational schemas above is in 3NF but not in BCNF? |
| i ➥ Schema I |
| ii ➥ Schema II |
| iii ➥ Schema III |
| iv ➥ Schema IV |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Normalization | Help-Line |
| Q37➡ | Database Management System Consider the relations r(A, B) and s(B, C), where s.B is a primary key and r.B is a foreign key referencing s.B. Consider the query Q: r ⋈ (σB<5 (s)) Let LOJ denote the natural left outer-join operation. Assume that r and s contain no null values. Which one of the following is NOT equivalent to Q? |
| i ➥ σB<5 (r ⨝ s) |
| ii ➥ σB<5 (r LOJ s) |
| iii ➥ r LOJ (σB<5(s)) |
| iv ➥ σB<5(r) LOJ s |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Relational Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q38➡ | Operating Systems Consider the following solution to the producer-consumer synchronization problem. The shared buffer size is N. Three semaphores empty, full and mutex are defined with respective initial values of 0, N and 1. Semaphore empty denotes the number of available slots in the buffer, for the consumer to read from. Semaphore full denotes the number of available slots in the buffer, for the producer to write to. The placeholder variables, denoted by P, Q, R and S, in the code below can be assigned either empty or full. The valid semaphore operations are: wait() and signal().  Which one of the following assignments to P, Q, R and S will yield the correct solution? |
| i ➥ P: full, Q: full, R: empty, S: empty |
| ii ➥ P: empty, Q: empty, R: full, S: full |
| iii ➥ P: full, Q: empty, R: empty, S: full |
| iv ➥ P: empty, Q: full, R: full, S: empty |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Process Synchronization | Help-Line |
| Q39➡ | Operating Systems In a system, there are three types of resources: E, F and G. Four processes P0, P1, P2 and P3 execute concurrently. At the outset, the processes have declared their maximum resource requirements using a matrix named Max as given below. For example, Max[P2, F] is the maximum number of instances of F that P2 would require. The number of instances of the resources allocated to the various processes at any given state is given by a matrix named Allocation. Consider a state of the system with the Allocation matrix as shown below, and in which 3 instances of E and 3 instances of F are the only resources available. 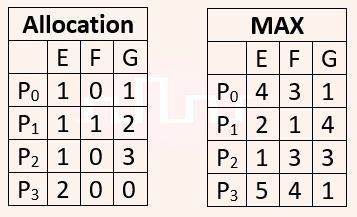 From the perspective of deadlock avoidance, which one of the following is true? |
| i ➥ The system is in safe state. |
| ii ➥ The system is not in safe state, but would be safe if one more instance of E were available. |
| iii ➥ The system is not in safe state, but would be safe if one more instance of F were available. |
| iv ➥ The system is not in safe state, but would be safe if one more instance of G were available. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Deadlock | Help-Line |
| Q40➡ | Compiler Design Consider the following parse tree for the expression a#b$c$d#e#f, involving two binary operators $ and #. 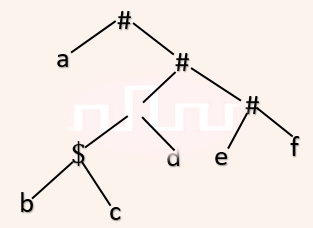 Which one of the following is correct for the given parse tree? |
| i ➥ $ has higher precedence and is left associative; # is right associative |
| ii ➥ # has higher precedence and is left associative; $ is right associative |
| iii ➥ $ has higher precedence and is left associative; # is left associative |
| iv ➥ # has higher precedence and is right associative; $ is left associative |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Associativity-and-Precedence | Help-Line |
| Q41➡ | Compiler Design A lexical analyzer uses the following patterns to recognize three tokens T1, T2, and T3 over the alphabet {a,b,c}. T1 : a?(a|c)*a T2 : b?(a∣c)*b T3 : c?(b∣a)*c Note that ‘x?’ means 0 or 1 occurrence of the symbol x. Note also that the analyzer outputs the token that matches the longest possible prefix. If the string bbaacabc is processes by the analyzer, which one of the following is the sequence of tokens it outputs? |
| i ➥ T1T2T3 |
| ii ➥ T1T1T3 |
| iii ➥ T2T1T3 |
| iv ➥ T3T3 |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Compilers | Help-Line |
| Q42➡ | Theory of Computation Consider the following problems. L(G) denotes the language generated by a grammar G. L(M) denotes the language accepted by a machine M. (I) For an unrestricted grammar G and a string w, whether w∈L(G) (II) Given a Turing machine M, whether L(M) is regular (III) Given two grammar G1 and G2 whether L(G1 )=L(G2) (IV) Given an NFA N, whether there is a deterministic PDA P such that N and P accept the same language Which one of the following statement is correct? |
| i ➥ Only I and II are undecidable |
| ii ➥ Only III is undecidable |
| iii ➥ Only II and IV are undecidable |
| iv ➥ Only I, II and III are undecidable |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Undecidability | Help-Line |
| Q43➡ | Engineering Mathematics Let G be a graph with 100! vertices, with each vertex labeled by a distinct permutation of the numbers 1, 2, …, 100. There is an edge between vertices u and v if and only if the label of u can be obtained by swapping two adjacent numbers in the label of v. Let y denote the degree of a vertex in G, and z denote the number of connected components in G. Then, y + 10z =______. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Graph Theory | Help-Line |
| Q44➡ | Engineering Mathematics Consider Guwahati (G) and Delhi (D) whose temperatures can be classified as high (H), medium (M) and low (L). Let P(HG) denote the probability that Guwahati has high temperature. Similarly, P(MG) and P(LG) denotes the probability of Guwahati having medium and low temperatures respectively. Similarly, we use P(HD), P(MD) and P(LD) for Delhi. The following table gives the conditional probabilities for Delhi’s temperature given Guwahati’s temperature. 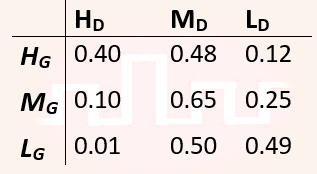 Consider the first row in the table above. The first entry denotes that if Guwahati has high temperature (HG) then the probability of Delhi also having a high temperature (HD) is 0.40; i.e., P(HD ∣ HG) = 0.40. Similarly, the next two entries are P(MD ∣ HG) = 0.48 and P(LD ∣ HG) = 0.12. Similarly for the other rows. If it is known that P(HG) = 0.2, P(MG) = 0.5, and P(LG) = 0.3, then the probability (correct to two decimal places) that Guwahati has high temperature given that Delhi has high temperature is_____. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Linear Algebra | Help-Line |
Q45➡ | Programming  |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Function | Help-Line |
| Q46➡ | Computer-Organization The instruction pipeline of a RISC processor has the following stages: Instruction Fetch (IF), Instruction Decode (ID), Operand Fetch (OF), Perform Operation (PO) and Writeback (WB). The IF, ID, OF and WB stages take 1 clock cycle each for every instruction. Consider a sequence of 100 instructions. In the PO stage, 40 instructions take 3 clock cycles each, 35 instructions take 2 clock cycles each, and the remaining 25 instructions take 1 clock cycle each. Assume that there are no data hazards and no control hazards. The number of clock cycles required for completion of execution of the sequence of instructions is_____. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Pipeling | Help-Line |
| Q47➡ | Digital-Logic-Design Consider the minterm list form of a Boolean function F given below.  Here, m denotes a minterm and d denotes a don’t care term. The number of essential prime implicants of the function F is _. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Boolean Algebra | Help-Line |
| Q48➡ | Algorithms Consider the weights and values of items listed below. Note that there is only one unit of each item. 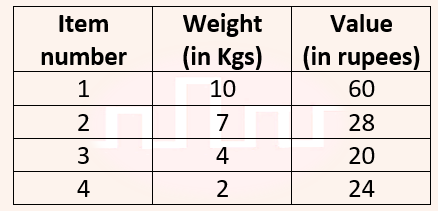 The task is to pick a subset of these items such that their total weight is no more than 11 Kgs and their total value is maximized. Moreover, no item may be split. The total value of items picked by an optimal algorithm is denoted by Vopt. A greedy algorithm sorts the items by their value-to-weight ratios in descending order and packs them greedily, starting from the first item in the ordered list. The total value of items picked by the greedy algorithm is denoted by Vgreedy. The value of Vopt − Vgreedy is __ . |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | 0/1-Knapsack | Help-Line |
| Q49➡ | Algorithms Consider the following undirected graph G: 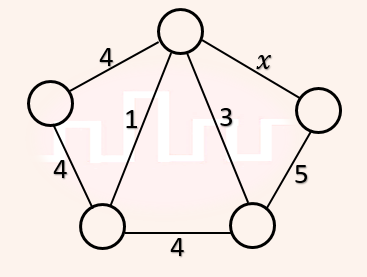 Choose a value for x that will maximize the number of minimum weight spanning trees (MWSTs) of G. The number of MWSTs of G for this value of x is _________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Minimum-Spanning-Tree | Help-Line |
| Q50➡ | Data-Structures The number of possible min-heaps containing each value from {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} exactly once is_______. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Heap-Tree | Help-Line |
| Q51➡ | Computer Network Consider a simple communication system where multiple nodes are connected by a shared broadcast medium (like Ethernet or wireless). The nodes in the system use the following carrier-sense based medium access protocol. A node that receives a packet to transmit will carrier-sense the medium for 5 units of time. If the node does not detect any other transmission in this duration, it starts transmitting its packet in the next time unit. If the node detects another transmission, it waits until this other transmission finishes, and then begins to carrier-sense for 5 time units again. Once they start to transmit, nodes do not perform any collision detection and continue transmission even if a collision occurs. All transmissions last for 20 units of time. Assume that the transmission signal travels at the speed of 10 meters per unit time in the medium. Assume that the system has two nodes P and Q, located at a distance d meters from each other. P starts transmitting a packet at time t=0 after successfully completing its carrier-sense phase. Node Q has a packet to transmit at time t=0 and begins to carrier-sense the medium. The maximum distance d (in meters, rounded to the closest integer) that allows Q to successfully avoid a collision between its proposed transmission and P’s ongoing transmission is _. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Ethernet | Help-Line |
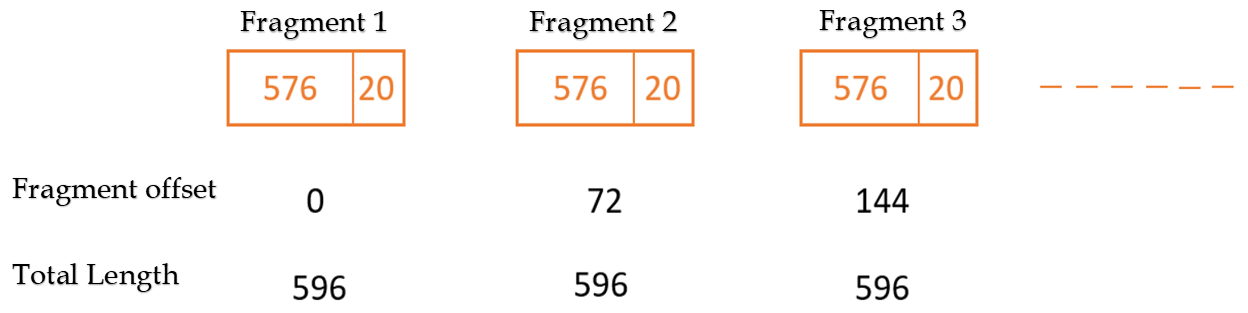
| Q52➡ | Computer Network Consider an IP packet with a length of 4,500 bytes that includes a 20-byte IPv4 header and a 40-byte TCP header. The packet is forwarded to an IPv4 router that supports a Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) of 600 bytes. Assume that the length of the IP header in all the outgoing fragments of this packet is 20 bytes. Assume that the fragmentation offset value stored in the first fragment is 0. The fragmentation offset value stored in the third fragment is __. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | IPv4 | Help-Line |
| Q53➡ | Operating System Consider a storage disk with 4 platters (numbered as 0, 1, 2 and 3), 200 cylinders (numbered as 0, 1, … , 199), and 256 sectors per track (numbered as 0, 1, … 255). The following 6 disk requests of the form [sector number, cylinder number, platter number] are received by the disk controller at the same time: [120, 72, 2], [180, 134, 1], [60, 20, 0], [212, 86, 3], [56, 116, 2], [118, 16, 1] Currently head is positioned at sector number 100 of cylinder 80, and is moving towards higher cylinder numbers. The average power dissipation in moving the head over 100 cylinders is 20 milliwatts and for reversing the direction of the head movement once is 15 milliwatts. Power dissipation associated with rotational latency and switching of head between different platters is negligible. The total power consumption in milliwatts to satisfy all of the above disk requests using the Shortest Seek Time First disk scheduling algorithm is __ . |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Disk-Scheduling | Help-Line |
| Q54➡ | Computer-Organization A processor has 16 integer registers (R0, R1, …, R15) and 64 floating point registers (F0, F1, …, F63). It uses a 2-byte instruction format. There are four categories of instructions: Type-1, Type-2, Type-3 and Type-4. Type-1 category consists of four instructions, each with 3 integer register operands (3Rs). Type-2 category consists of eight instructions, each with 2 floating point register operands (2Fs). Type-3 category consists of fourteen instructions, each with one integer register operand and one floating point register operand (1R+1F). Type-4 category consists of N instructions, each with a floating point register operand (1F). The maximum value of N is _________. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Machine-Instructions | Help-Line |
| Q55➡ | Theory of Computation Given a language L, define Li as follows: L0 = {ε} Li = Li-1 ∙ L for all i>0 The order of a language L is defined as the smallest k such that Lk = Lk+1. Consider the language L1 (over alphabet 0) accepted by the following automaton. 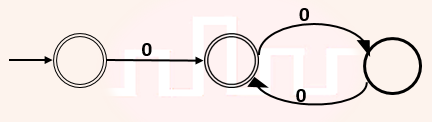 The order of L1 is __. |
Show Answer With Best Explanation
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Finite Automata | Help-Line |