Descriptive research UGC NET Paper 1
Descriptive research
| ✰ The term ‘Descriptive’ is self-explanatory and the research that describes a situation, an event and an institution is descriptive research. |
| ✰ The major purpose of descriptive research is description of the state of affairs as it exists at present. |
| ✰ This research clarifies ‘what is it’ and ‘what was it’. |
| ✰ Descriptive research is a quantitative research method. |
| ✰ In simple words, descriptive research is all about describing the phenomenon, observing and drawing conclusions from it. |
| ✰ The main characteristic of this method is that the researcher has no control over the variables; he can only report what has happened or what is happening. |
| ✰ Descriptive research includes surveys and fact-finding enquiries of different kinds. |
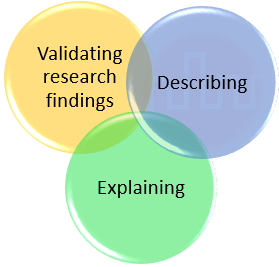
Three main purpose of descriptive studies:
1. Describing
2. Explaining
3. Validating research findingsThree main purpose of descriptive studies:
Example :
“School principal may be interested to know about the result of his own school in comparison to other schools in the district.”
Steps of Descriptive research
 |
Descriptive research can be of two types:
The types of descriptive research is completely depending upon the number of times the data is collected.
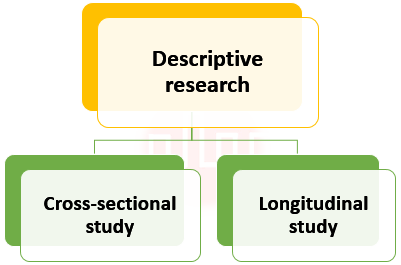 |
1. Cross-sectional study:
| ✰ Data are collected from multiple samples of the same population simultaneously. |
| ✰ Used to study or observe the phenomenon to gather data from multiple groups at the same time. |
| ✰ Researcher do not manipulate the study environment. |
2. Longitudinal study:
| ✰ Any social or development research involving collection of data from same sample across time. |
| ✰ Data are gathered at two or more different points in time. |
| ✰ Longitudinal study projects can extend over year or even decades. |
| ✰ Take more time, effort and cost more than cross sectional studies. |
| ✰ A “cohort study” is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort (a group of people who share a defining characteristic, typically those who experienced a common event in a selected period, such as birth or graduation), performing a cross-section at intervals through time. |
| ✰ It is used in the fields of medicine, pharmacy, nursing, psychology and social science. |
Cross sectional Study VS Longitudinal Study
| Cross sectional Study | Longitudinal Study |
|---|---|
| Multiple sample | Same sample |
| Collect data at a time | Collect data at a different time |
| Snapshot of a given situation | Long-term analysis of given situation |
| It takes less time than Longitudinal study | It takes more time than Cross sectional study |
| Participants are needed only once for the study purpose | Participants are engaged throughout study |
| Information about what is happening at a present | Information about what is happening in a certain period of time |
| Cannot establish cause and effect relationship | Can justify cause and effect relationship |
You Should Correlational research for Better Performance
You should learn previous year solution on this topic. GO Below ☟