Positivism or postpositivism of research NTA UGC NET
Positivism and Post-positivism Approaches of Research
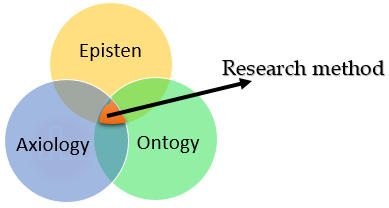
Metaphysics:
- Metaphysics considered one of the main branch of philosophy that deals with the nature, reality, most general and abstract concepts, such as being, knowing, identity, time and space.
- It is the thinking about the things that cannot be measured. It is logic and reason that is abstract.
- Metaphysics statement would be like “ I think therefore I am.”
- Metaphysics questions like: “what is the world around me really like”, “who am I” , “the existence of god”
Ontology:
- Ontology is derived from two greek words:
- Onto : “existence” or “being real”
- Logia: “knowledge” or “study”
- Ontology is a branch of metaphysics that studies concept such as existence, being and reality.
Epistemology:
- Epistemology is derived from 2 greek words:
- Episteme: knowledge or understanding
- Logia: science and study
- Epistemology is the study of knowledge. It deals with the origin, nature, scope and methods to acquire knowledge. There are basically two ways to acquire knowledge and they are rationalism and empiricism.
- Rationalism: Rationalism tends to believe that logic and reason as the means of acquiring knowledge. Mind is given the authority over senses. This is basically a prior use of logic and reason comes first to conclude something before experience. Rationalism is associated with deduction.
- Empiricism: Empiricists claim that sensing experience is the ultimate starting point for all our knowledge. The senses give us all our raw data about the world and without this raw material, there would be no knowledge at all. This is termed as a posteriori. It is related to induction.
Axiology:
- Axiology is the philosophical study of value. It is the branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of value and the types of value as morals, aesthetics, religion, and metaphysics. Axiology is engaged with assessment of the role of researcher’s own value on all stages of the research process. It is related to what is right or what is wrong.
Positivism Approach
- Positivism highlights that scientific inquiry should based on observable and measurable facts rather than on subjective experiences.
- The term positivism was coined by the French philosopher Auguste Comte in 19th century.
- Positivism is based on the study of facts and the gathering of physical evidence. It is related to the scientific view of the natural world as being one that operates via laws (such as gravity) that can be revealed by careful study and observation.
- Positivism depends on quantifiable observations that lead to statistical analyses. Here, the role of the researcher is limited to data collection and interpretation in an objective way.
- Positivists usually adopt deductive approach, the concentration is on facts.
- B.F. Skinner argued that psychology needed to concentrate only on the positive and negative reinforcers of behavior in order to predict how people will behave – everything else in between (like what the person is thinking) is irrelevant because it can’t be measured.
- The positivist believed in empiricism – the idea that observation and measurement was the core of the scientific endeavor.
- It is rejecting metaphysics and theism.
Specifically, positivism based on the following aspects of science.
- Science is deterministic as it explains the cause and effect relationships.
- Science is mechanistic as researchers develop hypotheses to be proved or disproved via application of specific research methods.
- Science uses methods such as selection of sample, measurements, analysis and reaching conclusions about hypotheses.
- Science deals with empiricism, where it is assessed as objective, as seen or measured. Science must be value free.
- In the positivist view, the universe is deterministic.
Downside of Positivism:
Positivism as an epistemology is associated with the following set of drawbacks.
- Positivism relies on experience as a valid source of knowledge.
- All types of processes can be perceived as a certain variation of actions of individuals or relationships between individuals.
- Adoption of positivism in business studies and other studies can be criticized for reliance on existing condition.
- Sometimes positivism is a rejection of metaphysics. It is a position that holds that the goal of knowledge which is simply to describe the phenomena that we experience.
Post- Positivism Approach
- As we discussed, positivism is associated with quantitative research strategies. There is one particular view of how research should be conducted, which suggests that we should carry out research in social sciences in ways that are similar to the methods within the natural sciences (Physics, Chemistry and Biology).
- Two people observe the same event and understand it differently, based upon their own experiences and beliefs. Objectivity can be achieved by using multiple measurements and observations and triangulating the data to gain a clearer understanding of what is happening in reality. It is important to note that the post-positivists share a lot in common with positivists, but most of the research approaches and practices in social science today fit better into the post-positivist category.
- Since the inception of 21st century, the focus of research shifted from ‘reality’ to ‘critical reality’.
- A critical realist believes that there is a reality independent of our thinking about it that science can study.
- The difference is that the post-positivist critical realist recognizes that all observation is fallible and has error and that all theory is revisable.
- Just because I have my world view based on my experiences and you have yours doesn’t mean that we can’t hope to translate from each other’s experiences or understand each other. That is the idea that we can never understand each other because we come from different experiences and cultures.
- Post-positivism also assumes that the scientists are never objective and are biased due to their cultural beliefs. In this sense, pure objectivity cannot be achieved.
- The emphasis was turned away from absolute certainty to probability.
- It describes a less strict form of positivism. It also called as Logical empiricism.
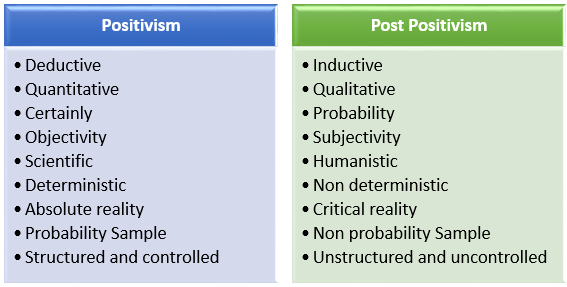
Some example of Positivism and Post Positivism Approaches of Research
You Should Learn Characteristics of research for Better Performance
You should learn previous year solution on this topic. GO Below ☟
| Q1➡ | NET Nov 2020 24 Sept Shift-I Which one of the following research procedures will figure under a post positivist approach? |
| i ➥ Normative survey |
| ii ➥ Experimental study |
| iii ➥ Ethnographic study |
| iv ➥ Ex post facto study |
| Answer – III |
| More Discussion | Explanation On YouTube | Positivism and Post-positivism | Help-Line |
