parametric and non parametric test
parametric and non parametric test
In this tutorial, we will discuss parametric and non parametric test in research.
Key Points:
1. Parametric Test ?
2. Non Parametric Test ?
3. Difference between parametric and non parametric test ?
1.Parametric
1.Parametric Test
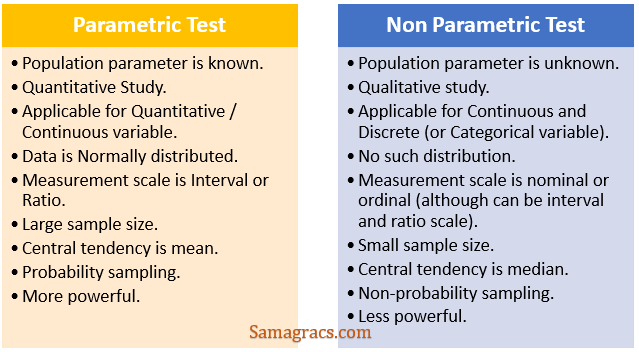
| ✰ Parametric tests usually assume certain properties of the parent population from which we draw samples. ✰ The value assumed about population(eg mean, standard deviation, mode, etc) is called ‘population parameter’. ✰ Data are normally distributed in the case of parametric tests. |
Parametric test are used when:
Parametric test are used when:
Parametric test are used when:
| ✔ Population parameter is known. ✔ Measurement scale is interval or ratio. ✔ Population data is normally distributed. |
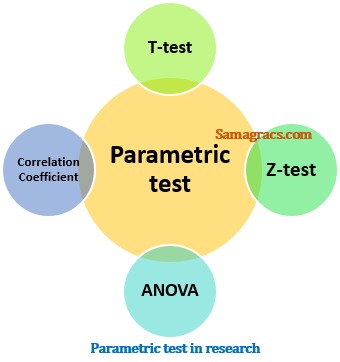
the main example of parametric tests are following:
the main example of parametric tests are following:
the main example of parametric tests are following:
| ✔ T-test. ✔ Z-test. ✔ ANOVA. ✔ Correlation Coefficient. |
Parametric test in research
Z-Test
Z-Test
| ✰ Z-Test is based on the normal probability distribution. Z- value is calculated with population parameters such as the population mean and population variance. ✰ Z- test is used when: ⟹The sample size is greater than 30 ⟹Large population ⟹Population Standard deviation is known 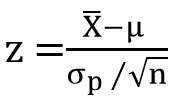 Where, μ = Population mean σp = Standard deviation of population n = Number of observations |
T-Test
T-Test
F-test (ANOVA)
| ✰ Like Z-test, the T-test is also based on the normal probability distribution. ✰ A T-test is a form of the statistical test to find out the p-value (Probability value) which can be used to accept or reject the Null hypothesis. ✰ It is also called student’s T-distribution test. ✰ It is used to compare the difference between the means of two samples in the case of small sample(s) when population variance is not known. ✰ T- test is used when: ⟹The sample size is less than 30. ⟹Small population. ⟹ Population Standard deviation is unknown. 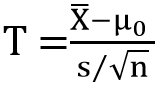 Where, μ = Population mean. s = standard deviation of sample. n = number of observations. |
F-test (ANOVA)
| ✰ F- test is used to compare two population variance. ✰ The variance ratio = S12/S22 ✰ F- test is used when: ⟹The sample can be any size. ⟹Sample must be independent. 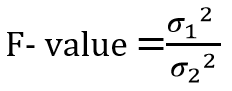 Where, σ1 = variance of first sample σ2 = variance of second sample |
2.Non Parametric Test
2.Non Parametric Test
| ✰ Non-parametric tests do not depend on any assumption about the parameters of the parent population. ✰ Non- parametric tests are ‘distribution-free’ tests. ✰ In a non-parametric test, skewness, and kurtosis may deviate a lot from the normal distribution. |
Non parametric test are used when:
Non parametric test are used when:
| ✔ Population parameter is unknown. ✔ Measurement scale is nominal or ordinal. |
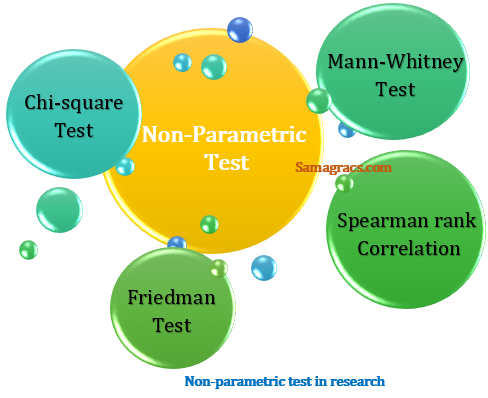
the main example of parametric tests are following:
the main example of parametric tests are following:
| ✔ Chi-square test. ✔ Friedman test. ✔ Mann-Whitney test. ✔ Spearman rank Correlation. |
Non-parametric test in research
Chi-Square test
Chi-Square test
| ✰ It is non parametric test. ✰ Making inferences about 2 or more 2 populations. ✰ Making inferences about population variance. ✰ Chi-square is one-tailed test(right). ✰ Conducting goodness to fit the test, the extent to which observed data matches with expected data. Example: suppose the expected marks of a student in an exam is 90+. Then chi-square test is used to see the extent to which observed data matches with expected data. 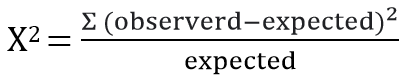 |
3. difference between parametric and non parametric test
3. Difference between parametric and non parametric test:
3. Difference between parametric and non parametric test:
You Should Learn Writing Research Report for Better Performance
You should learn previous year solution on this topic. GO Below ☟
| Research Content : |
- Introduction of Research
- Objective of Research
- Desirable Motivation
- Characteristics of research
- Positivism or postpositivism
- Classification of research
- Fundamental research
- Applied research
- Difference between fundamental and applied research
- Quantitative research
- Qualitative research
- Descriptive research
- Correlational research
- Exploratory research
- Explanatory research
- Experimental Research
- True experimental VS Quasi-experimental
- Inductive Research
- Deductive Research
- Inductive Research VS Deductive Research
- Conceptual Research
- Empirical Research
- Conceptual Research VS Empirical Research
- Structured Research
- Unstructured Research
- Ex-post facto Research
- Historical Research
- Analytical research
- Steps of research
- Formulating the research problem
- Research variables
- measuring scales
- Attitudinal scale
- Hypothesis formulating
- S2-> Preparing the research design
- S3->Tools of data collection
- S4->Sampling methods
- S5->Research proposal
- S6->collecting data
- S7->Processing and Analysis Data
- S8->Writing Research Report